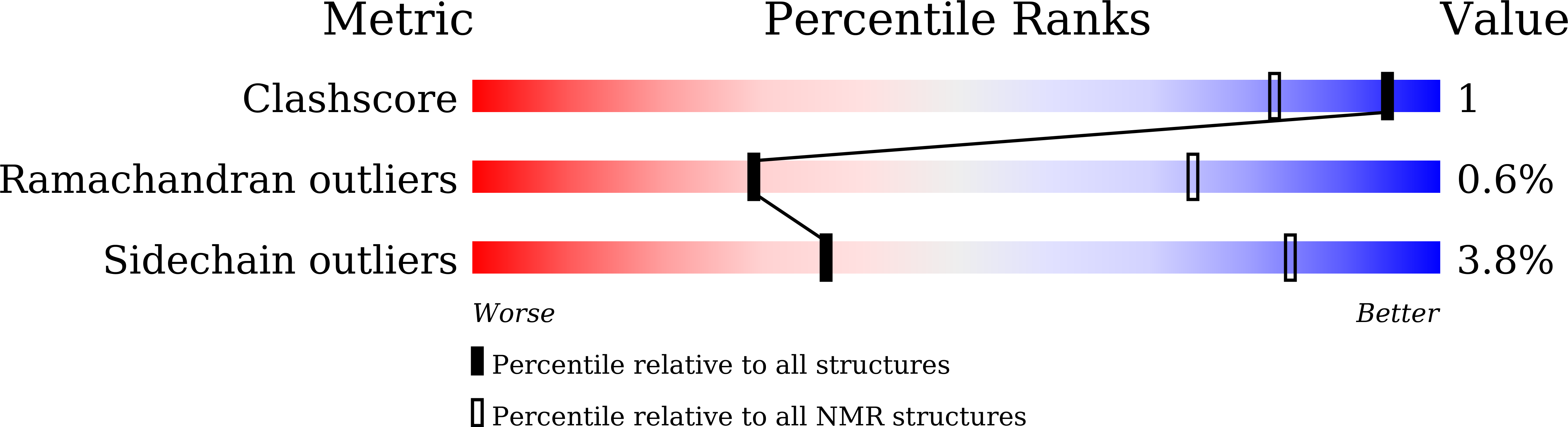Deposition Date
2023-07-28
Release Date
2024-07-31
Last Version Date
2025-03-19
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
8K81
Keywords:
Title:
Solution NMR Structure of ZF3 (fragment 346-396) from human Insulinoma-associated protein 1(INSM1)
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Homo sapiens (Taxon ID: 9606)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Conformers Calculated:
100
Conformers Submitted:
20
Selection Criteria:
all calculated structures submitted