Deposition Date
2023-07-25
Release Date
2023-11-15
Last Version Date
2024-03-20
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
8K6Y
Keywords:
Title:
Serial femtosecond crystallography structure of photo dissociated CO from ba3- type cytochrome c oxidase determined by extrapolation method
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Thermus thermophilus HB8 (Taxon ID: 300852)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
2.00 Å
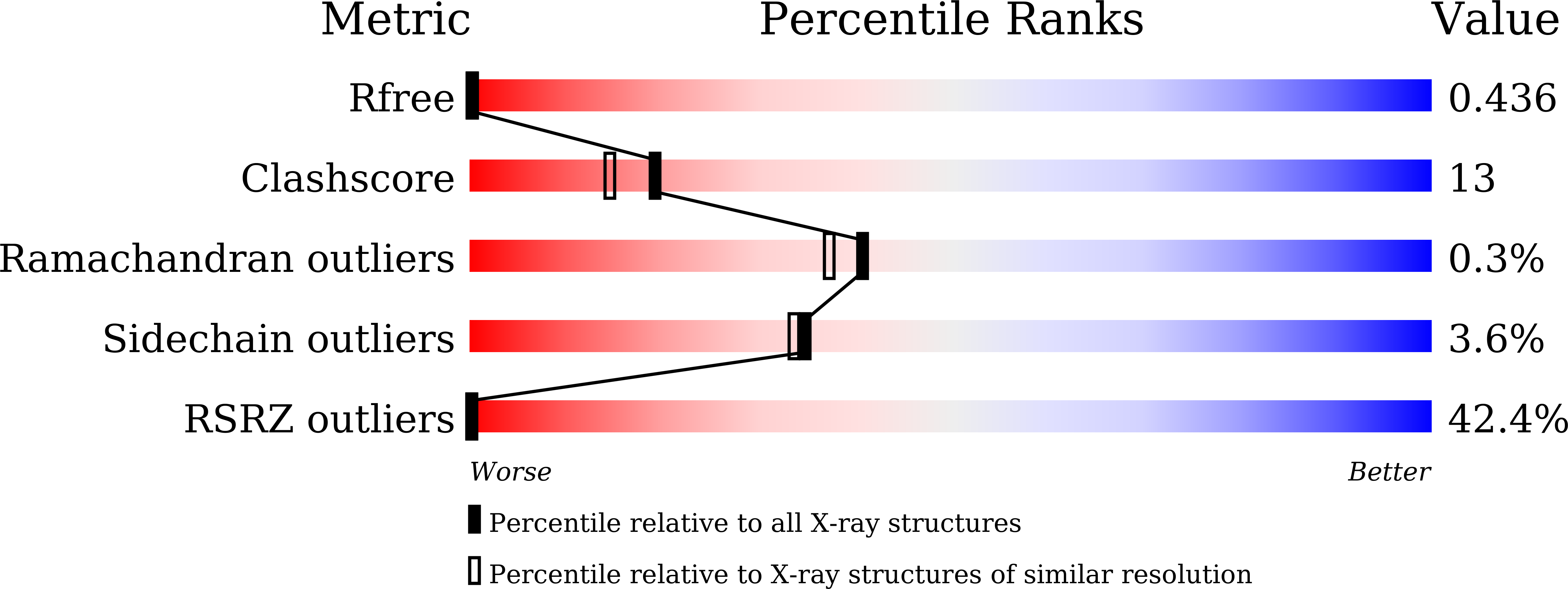
R-Value Free:
0.43
R-Value Work:
0.39
Space Group:
C 1 2 1