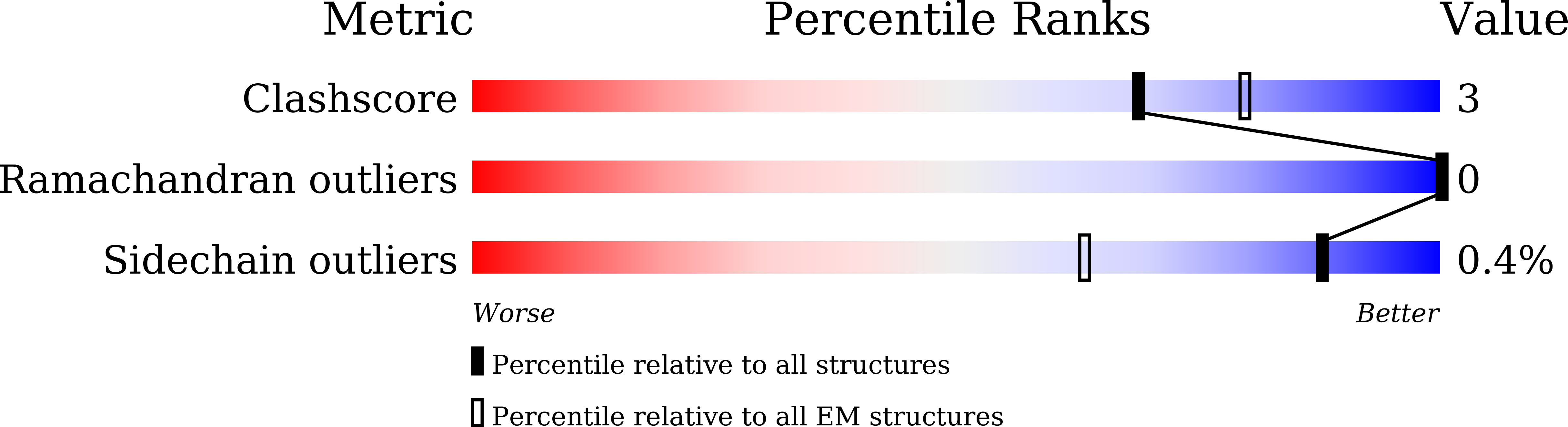
Deposition Date
2023-07-01
Release Date
2024-09-04
Last Version Date
2024-10-30
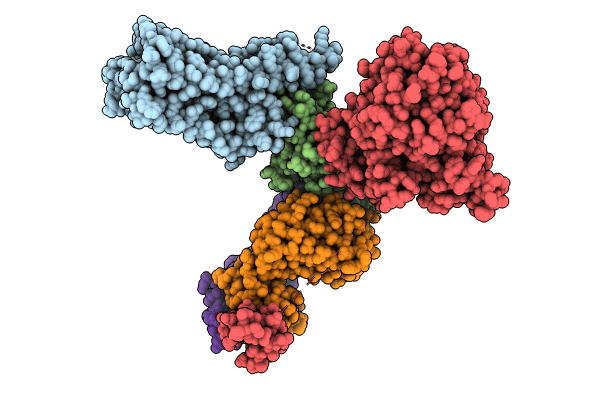
Entry Detail
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Homo sapiens (Taxon ID: 9606)
Escherichia coli O157:H7 (Taxon ID: 83334)
Staphylococcus aureus (Taxon ID: 1280)
Staphylococcus aureus subsp. aureus Mu50 (Taxon ID: 158878)
Streptococcus sp. 'group G' (Taxon ID: 1320)
Mus musculus (Taxon ID: 10090)
Escherichia coli O157:H7 (Taxon ID: 83334)
Staphylococcus aureus (Taxon ID: 1280)
Staphylococcus aureus subsp. aureus Mu50 (Taxon ID: 158878)
Streptococcus sp. 'group G' (Taxon ID: 1320)
Mus musculus (Taxon ID: 10090)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
3.57 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE