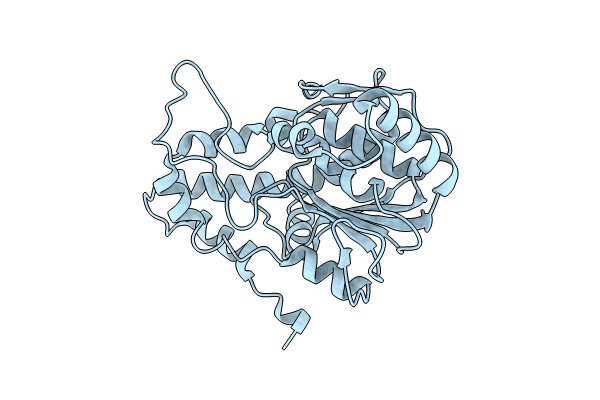
Deposition Date
2023-05-15
Release Date
2023-12-06
Last Version Date
2023-12-06
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
8JED
Keywords:
Title:
Crystal structure of mRNA cap (guanine-N7) methyltransferase E12 subunit from monkeypox virus and discovery of its inhibitors
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Monkeypox virus (Taxon ID: 10244)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
2.16 Å
R-Value Free:
0.25
R-Value Work:
0.19
R-Value Observed:
0.20
Space Group:
P 1 21 1


