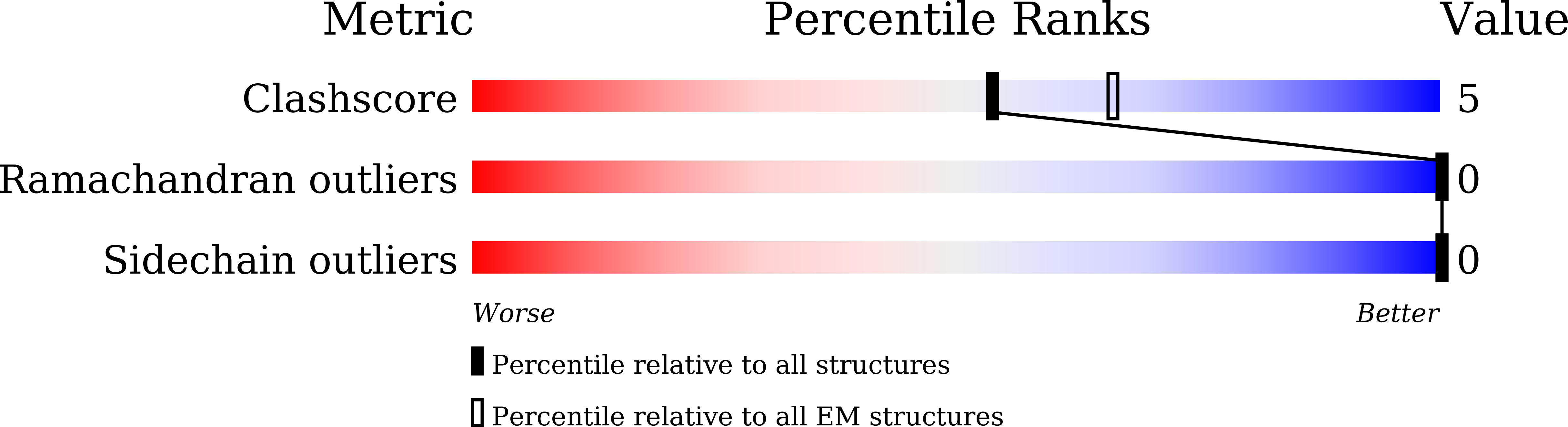
Deposition Date
2023-05-10
Release Date
2024-11-13
Last Version Date
2024-11-13
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
8JC9
Keywords:
Title:
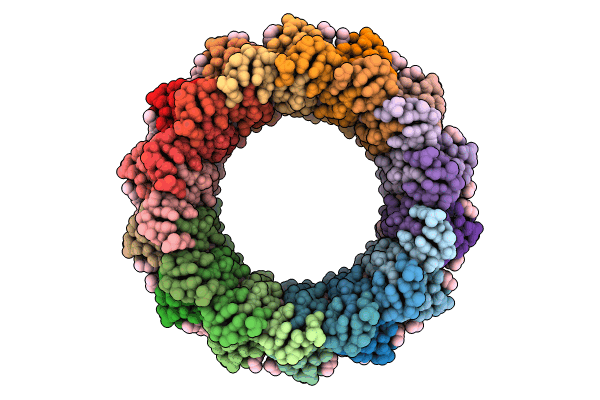
Cryo-EM structure of the LH1 complex from thermochromatium tepidum
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Thermochromatium tepidum (Taxon ID: 1050)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
3.32 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE