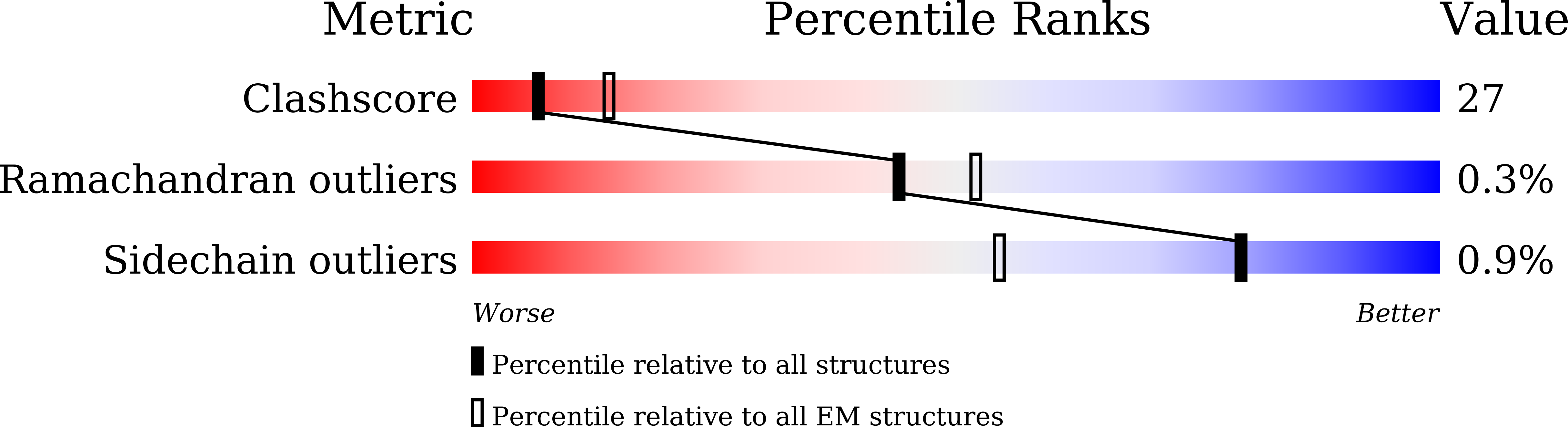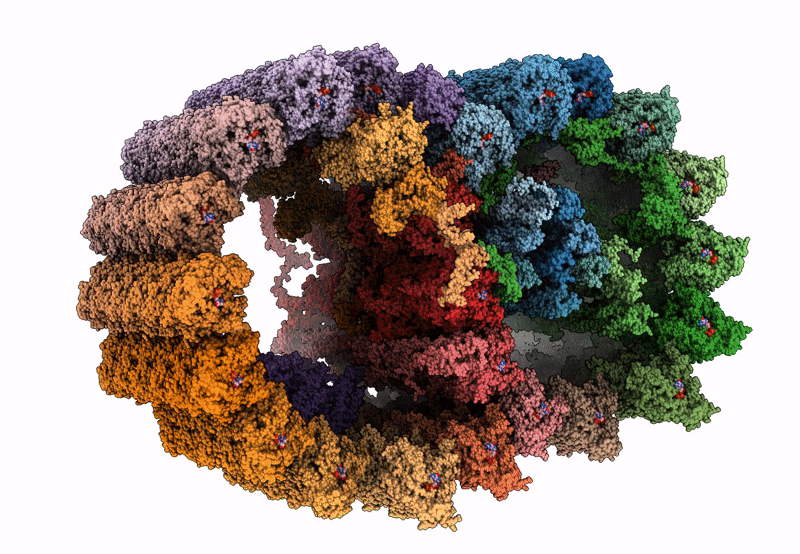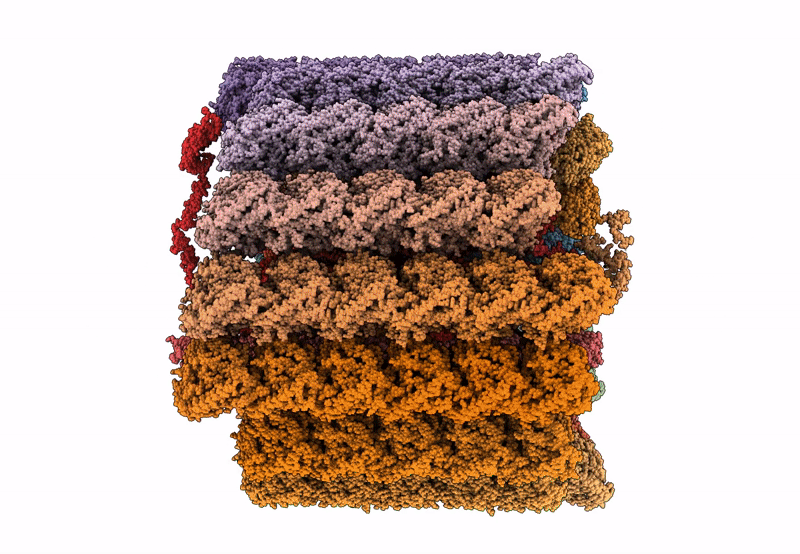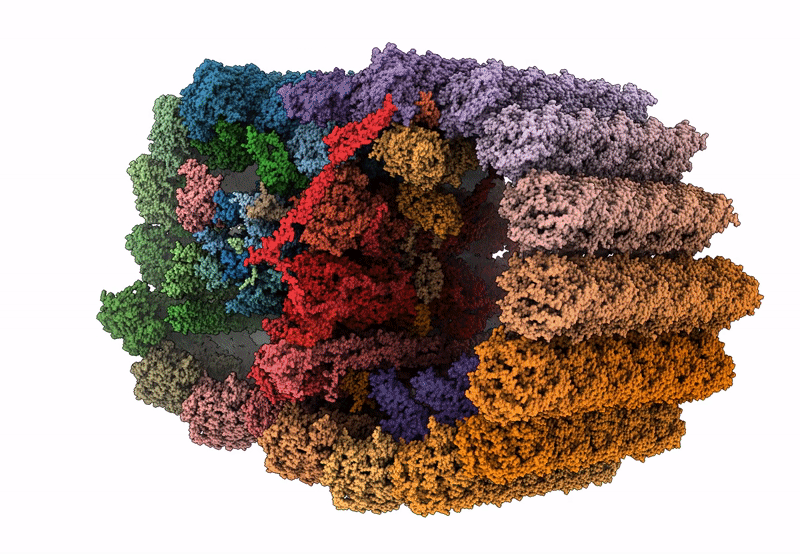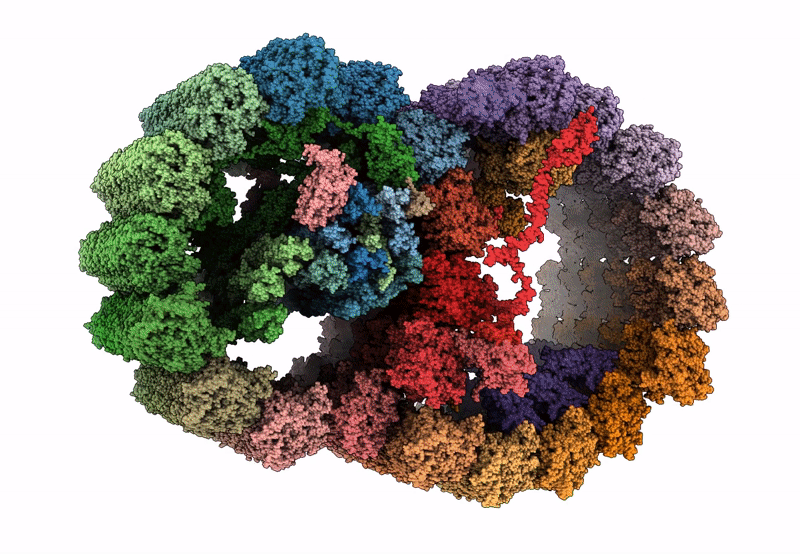
Deposition Date
2023-02-01
Release Date
2023-10-11
Last Version Date
2025-09-17
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
8I7O
Keywords:
Title:
In situ structure of axonemal doublet microtubules in mouse sperm with 16-nm repeat
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
Mus musculus (Taxon ID: 10090)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
4.50 Å
Aggregation State:
CELL
Reconstruction Method:
SUBTOMOGRAM AVERAGING