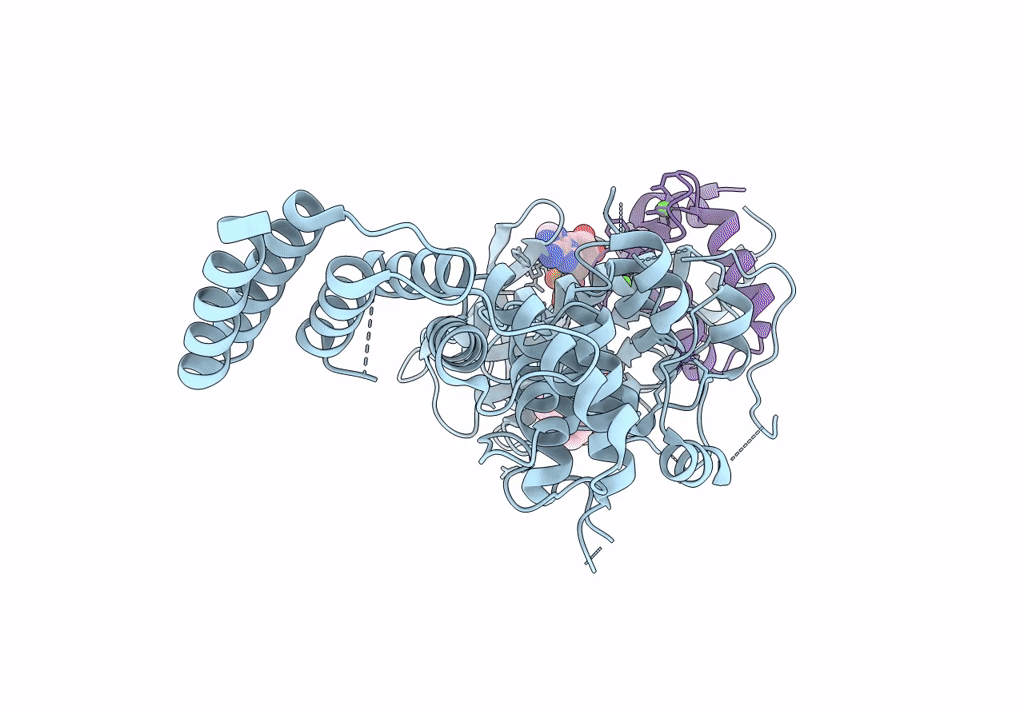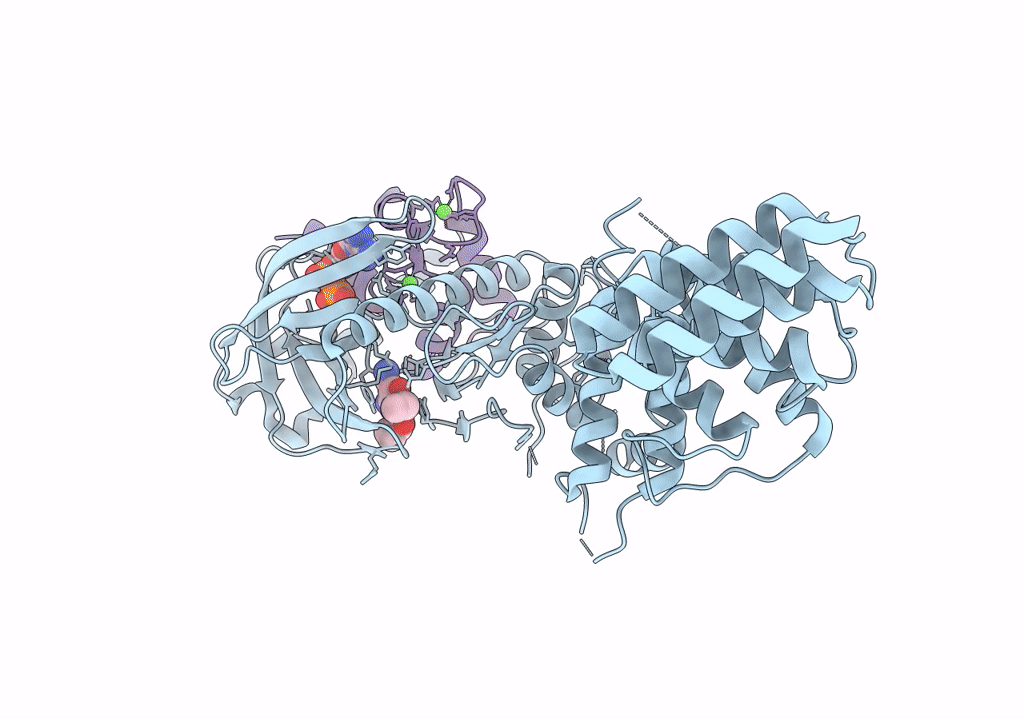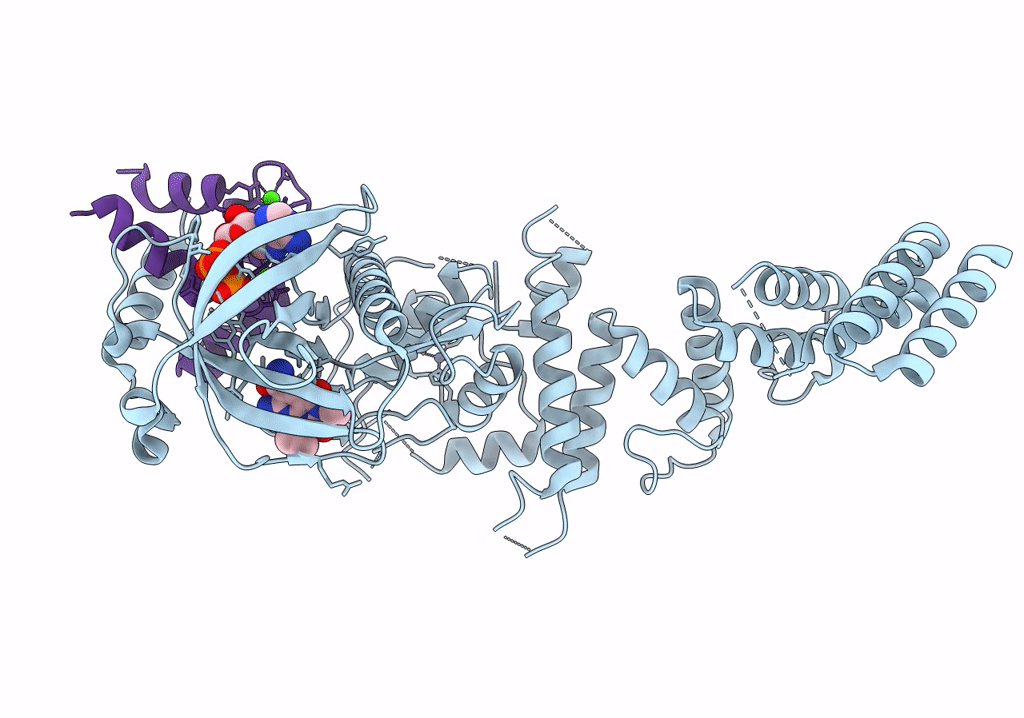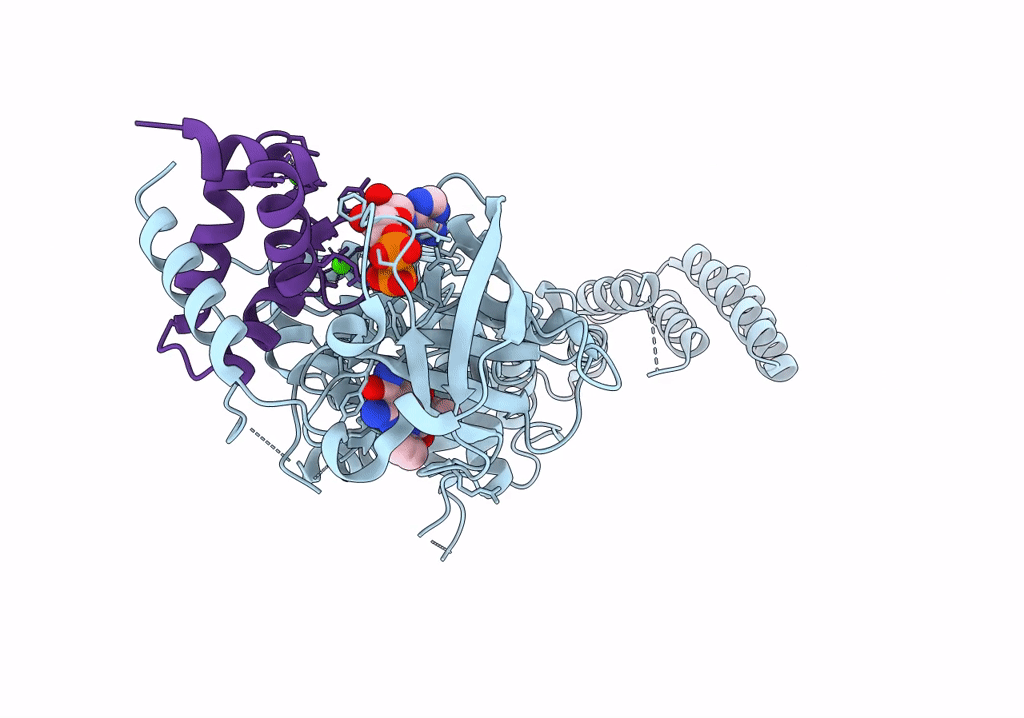
Deposition Date
2023-03-24
Release Date
2023-05-31
Last Version Date
2024-11-20
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
8GM5
Keywords:
Title:
Functional construct of the Eukaryotic elongation factor 2 kinase bound to Calmodulin, ADP and to the A-484954 inhibitor and showing two conformations for the 498-520 loop
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
Homo sapiens (Taxon ID: 9606)
Host Organism:
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
2.12 Å
R-Value Free:
0.22
R-Value Work:
0.18
R-Value Observed:
0.18
Space Group:
P 1 21 1


