Deposition Date
2023-01-17
Release Date
2023-06-07
Last Version Date
2024-06-19
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
8FUG
Keywords:
Title:
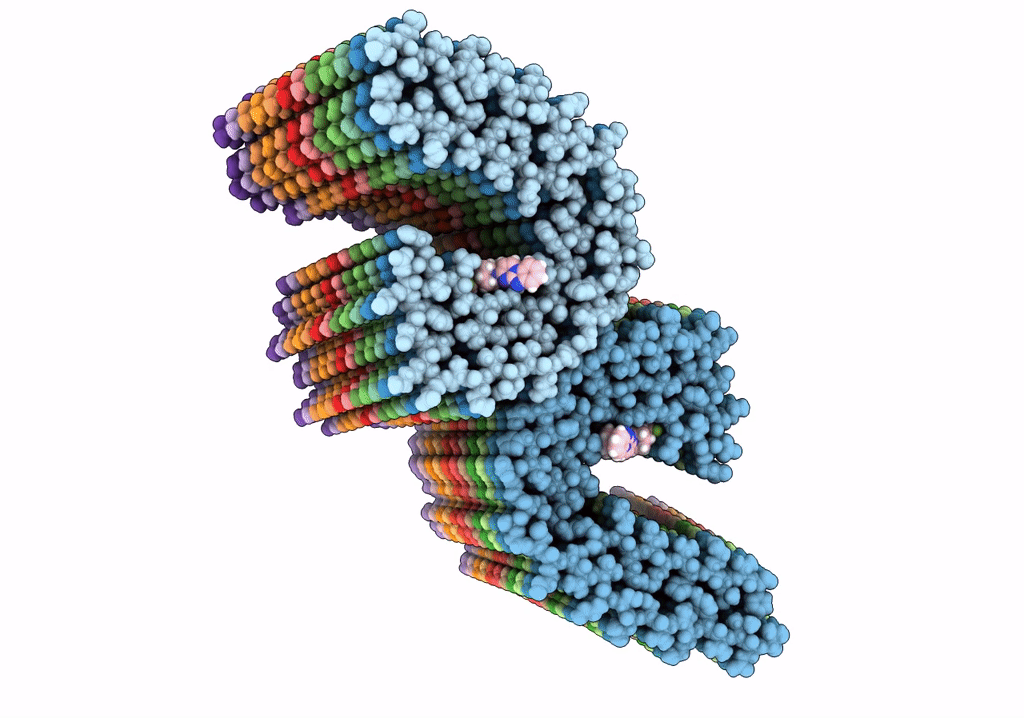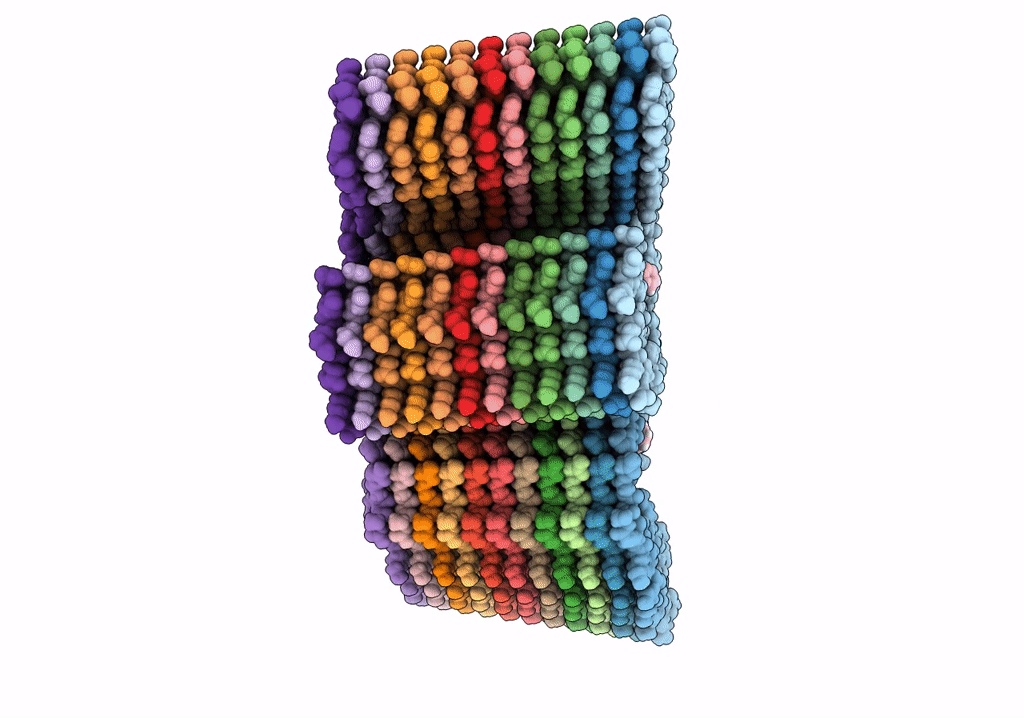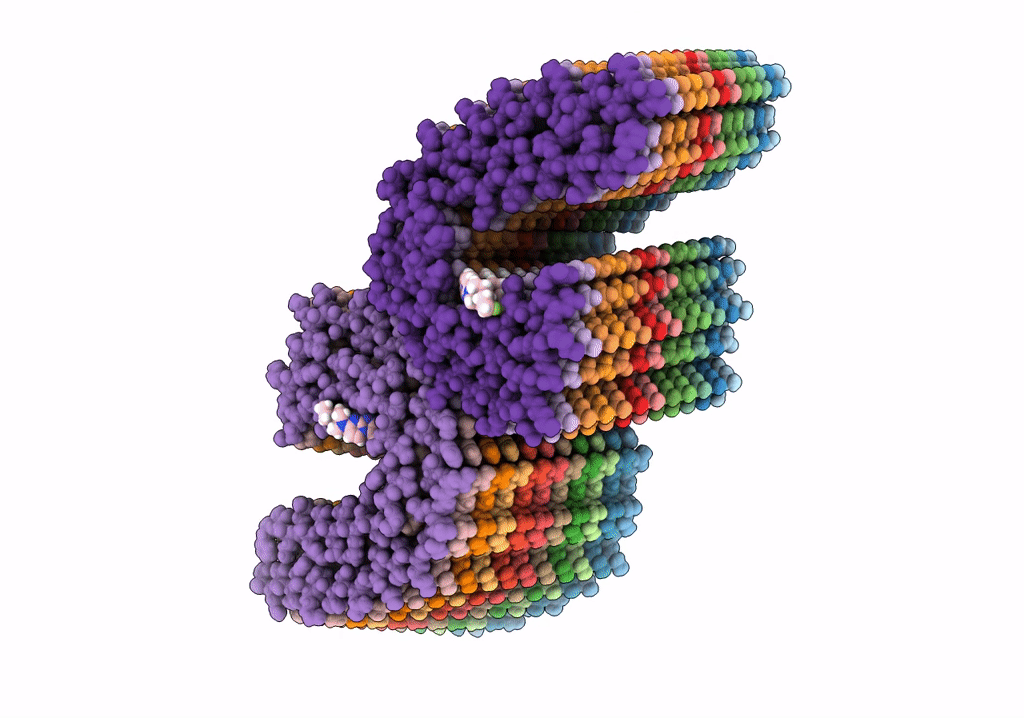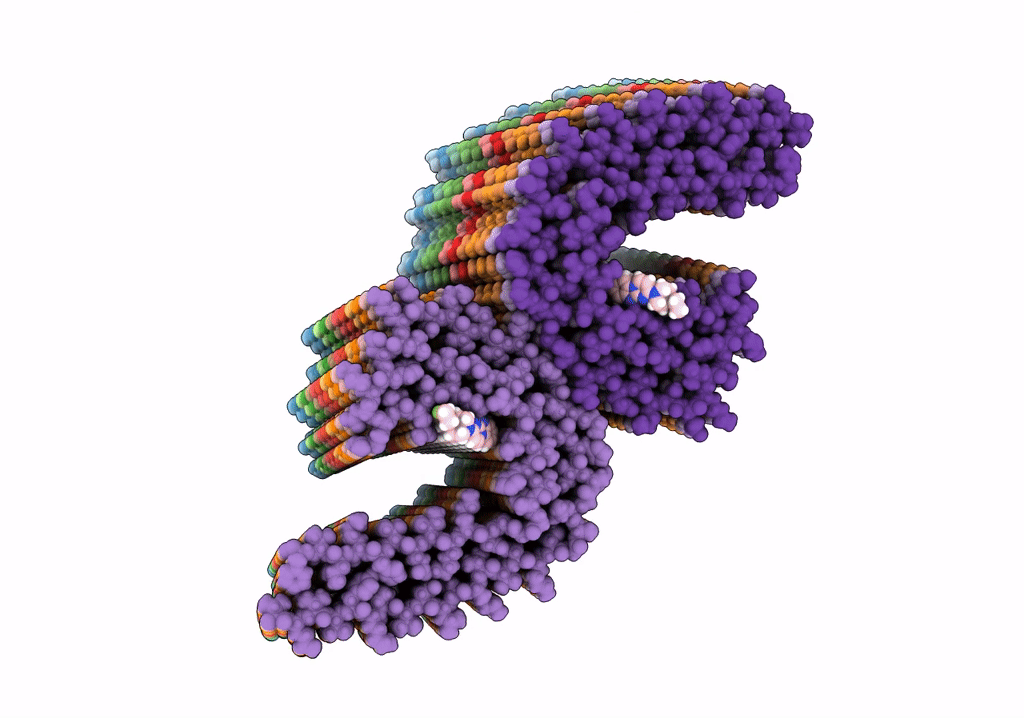
Alzheimer's disease paired-helical filament in complex with PET tracer GTP-1
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Homo sapiens (Taxon ID: 9606)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
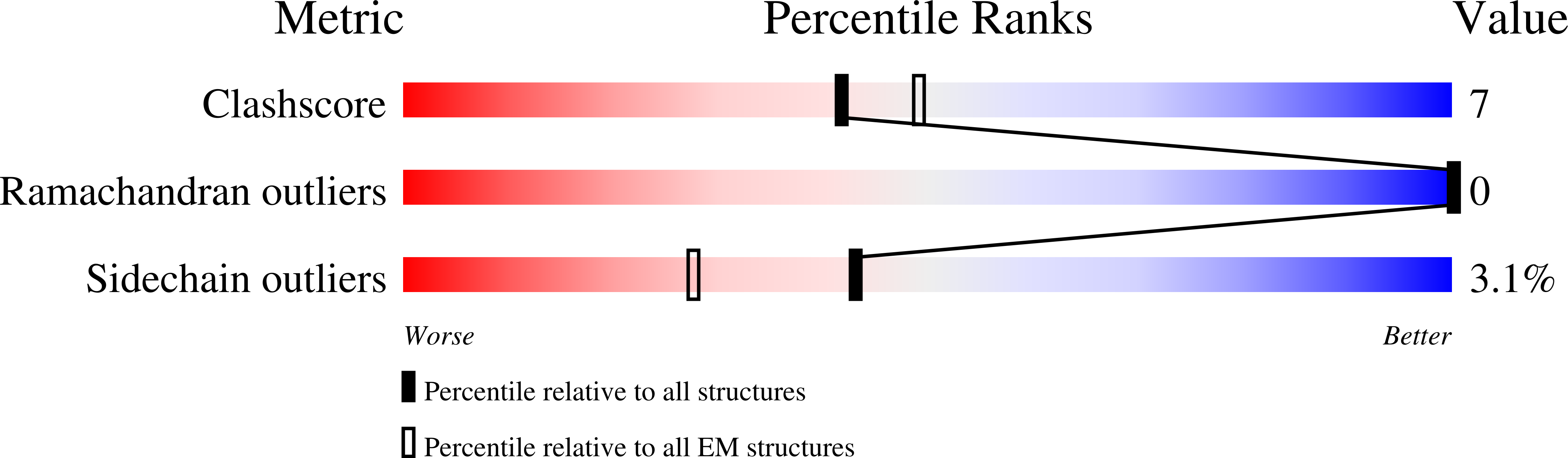
Resolution:
2.70 Å
Aggregation State:
FILAMENT
Reconstruction Method:
HELICAL