Deposition Date
2022-09-19
Release Date
2023-03-15
Last Version Date
2025-05-14
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
8EK1
Keywords:
Title:
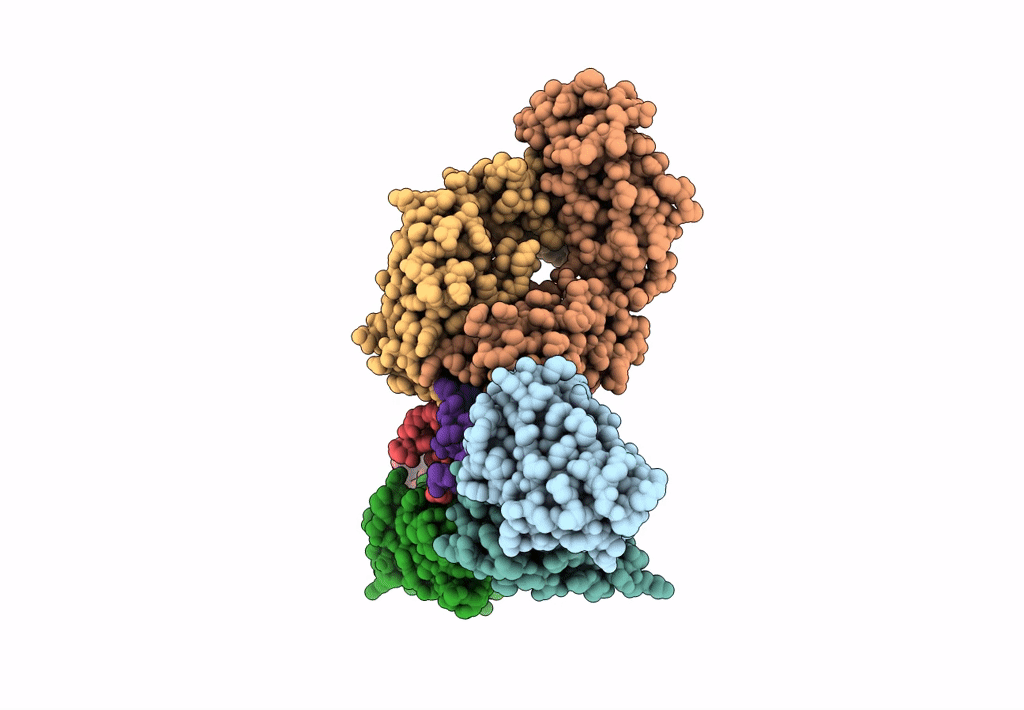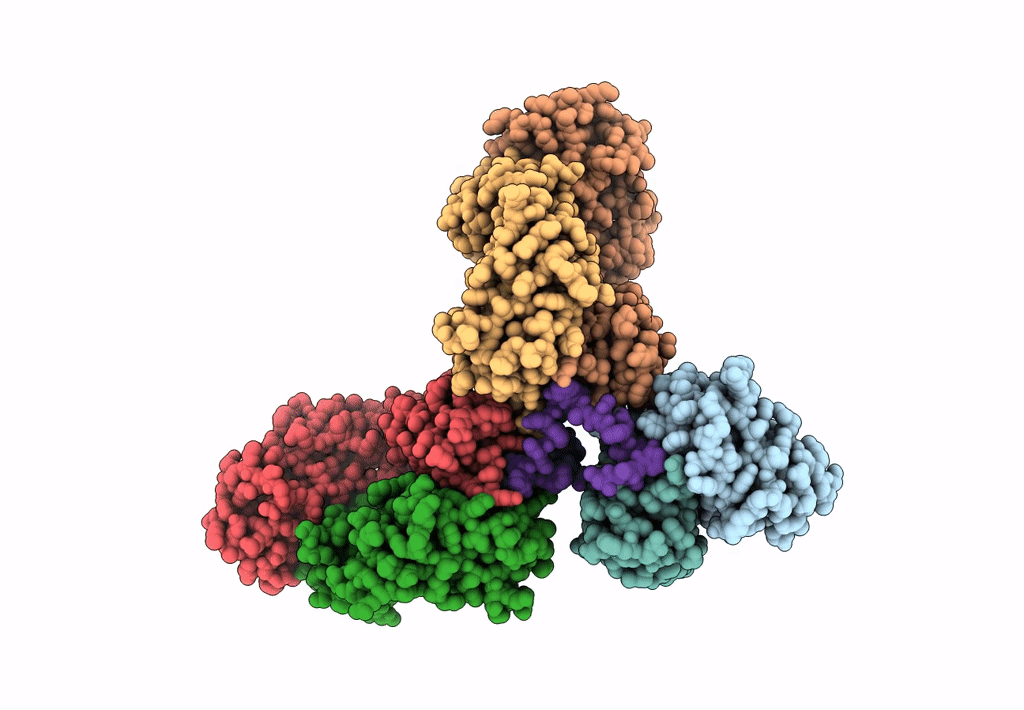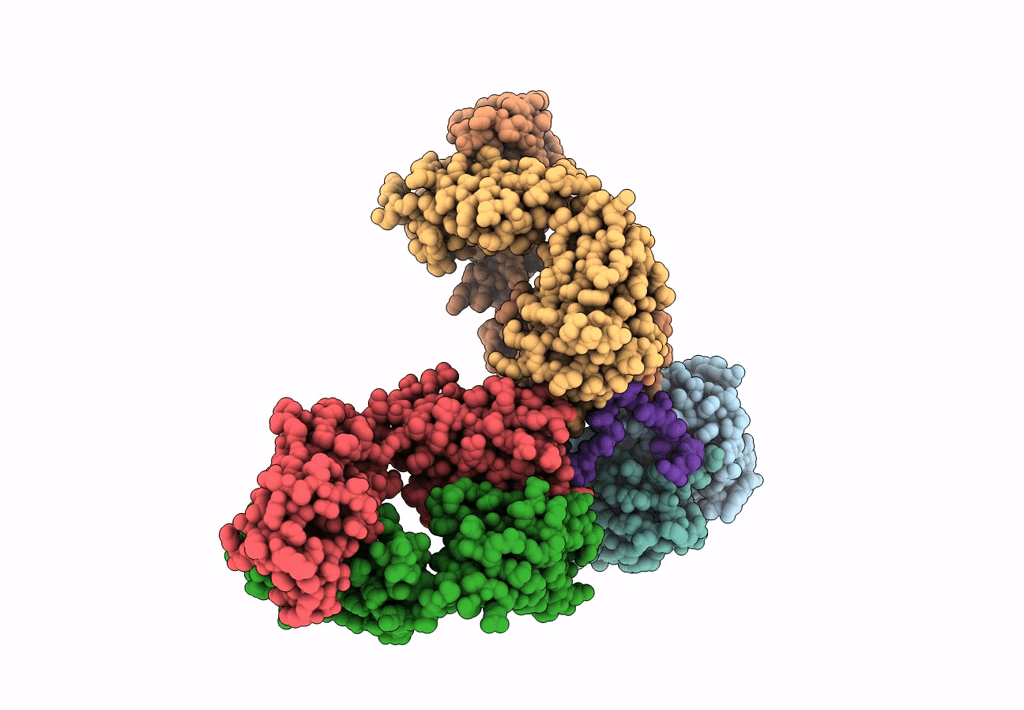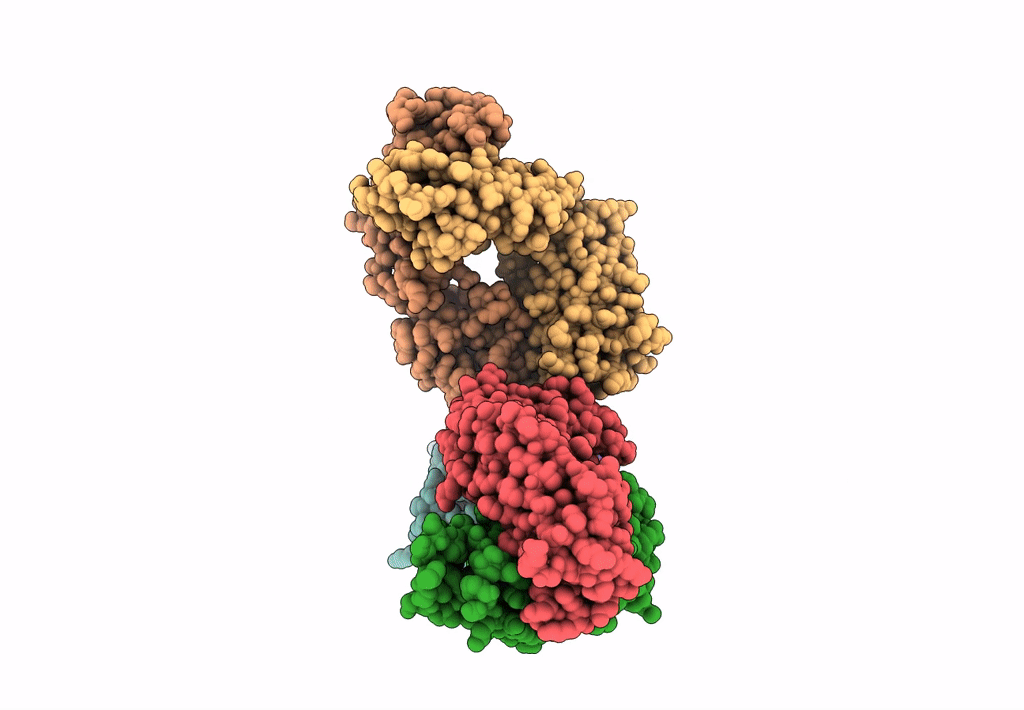
Cryo-EM structure of a potent anti-malarial antibody L9 in complex with Plasmodium falciparum circumsporozoite protein (PfCSP)(dominant class)
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
Homo sapiens (Taxon ID: 9606)
Plasmodium falciparum 3D7 (Taxon ID: 36329)
Plasmodium falciparum 3D7 (Taxon ID: 36329)
Host Organism:
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
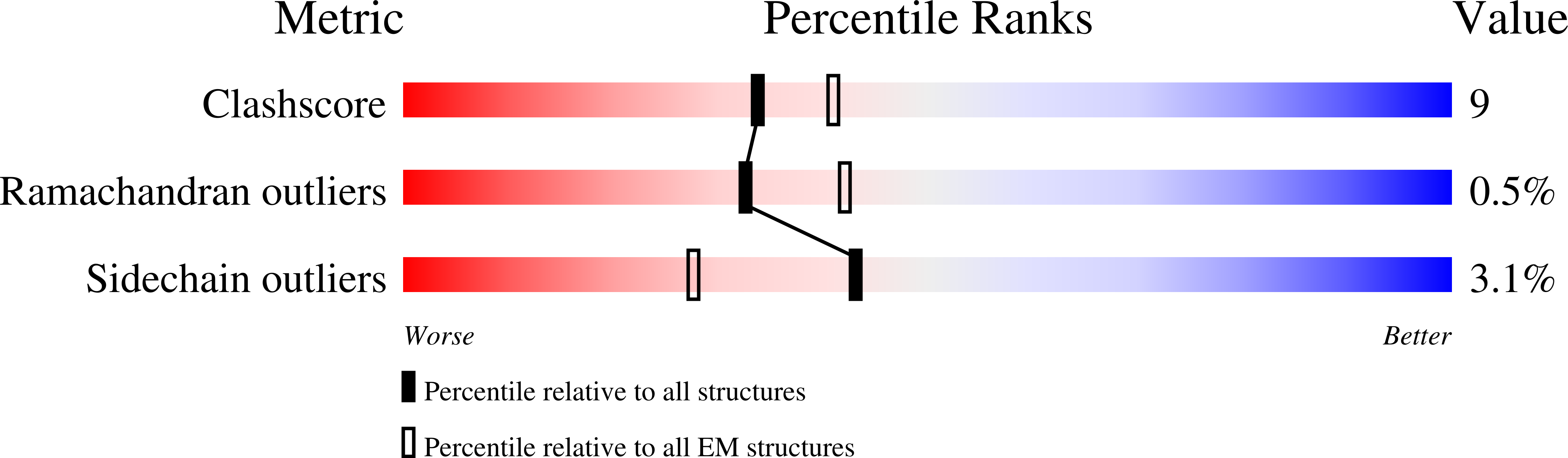
Resolution:
3.60 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE