Deposition Date
2022-09-06
Release Date
2024-01-03
Last Version Date
2025-05-14
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
8EE7
Keywords:
Title:
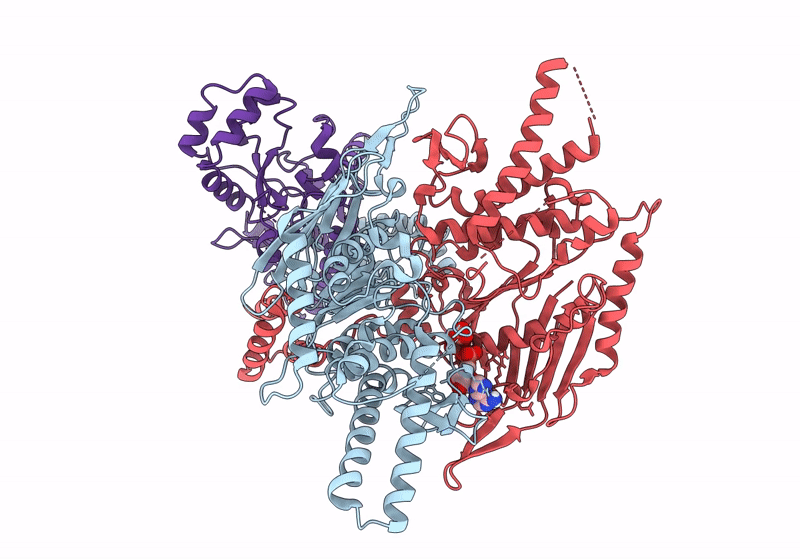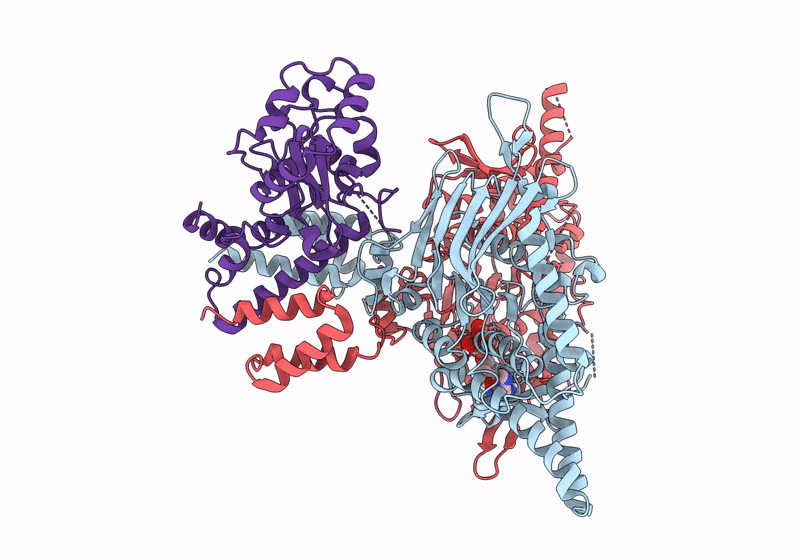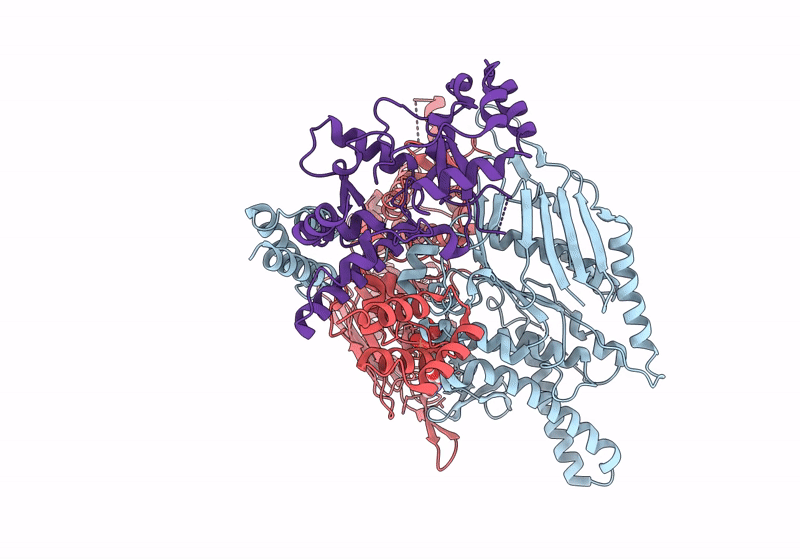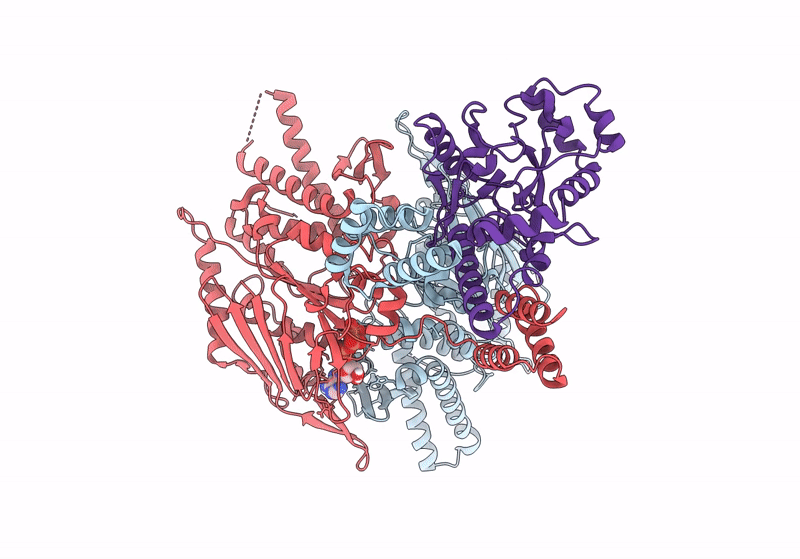
Structure of focused PtuA(dimer) and PtuB(monomer) complex
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Escherichia coli (Taxon ID: 562)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
2.72 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE


