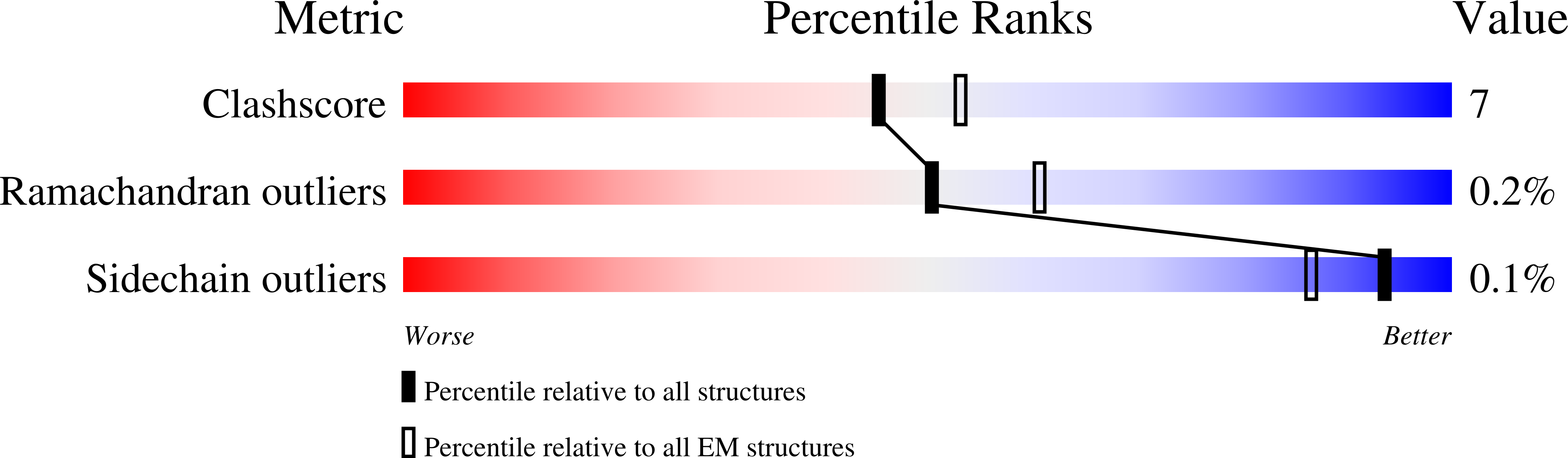
Deposition Date
2022-08-26
Release Date
2022-10-12
Last Version Date
2025-05-28
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
8E9G
Keywords:
Title:
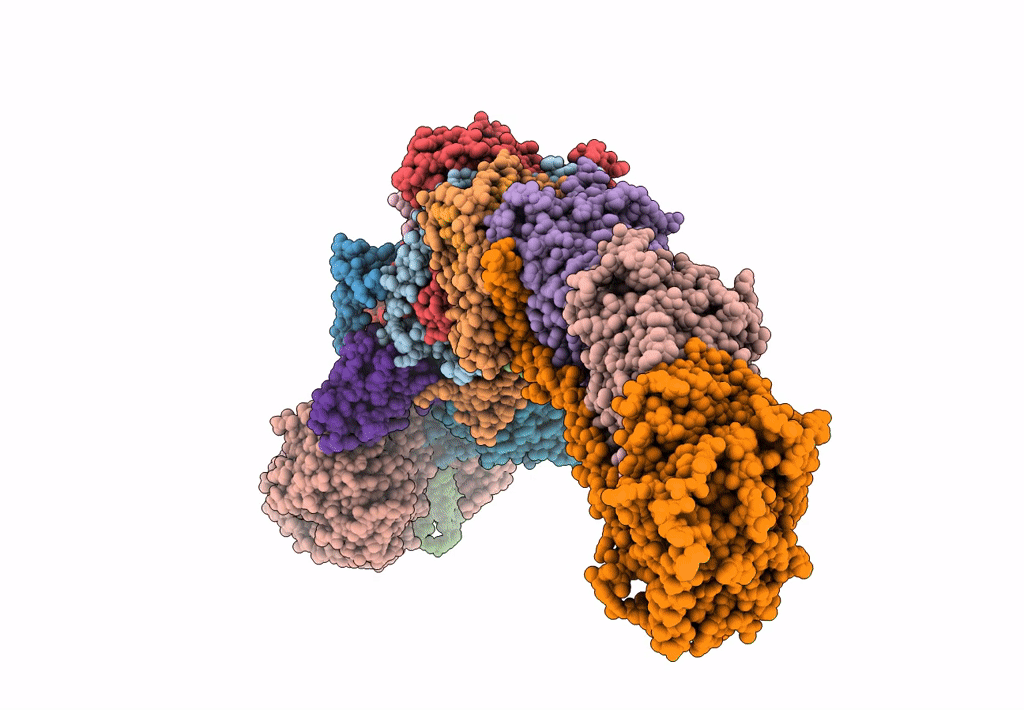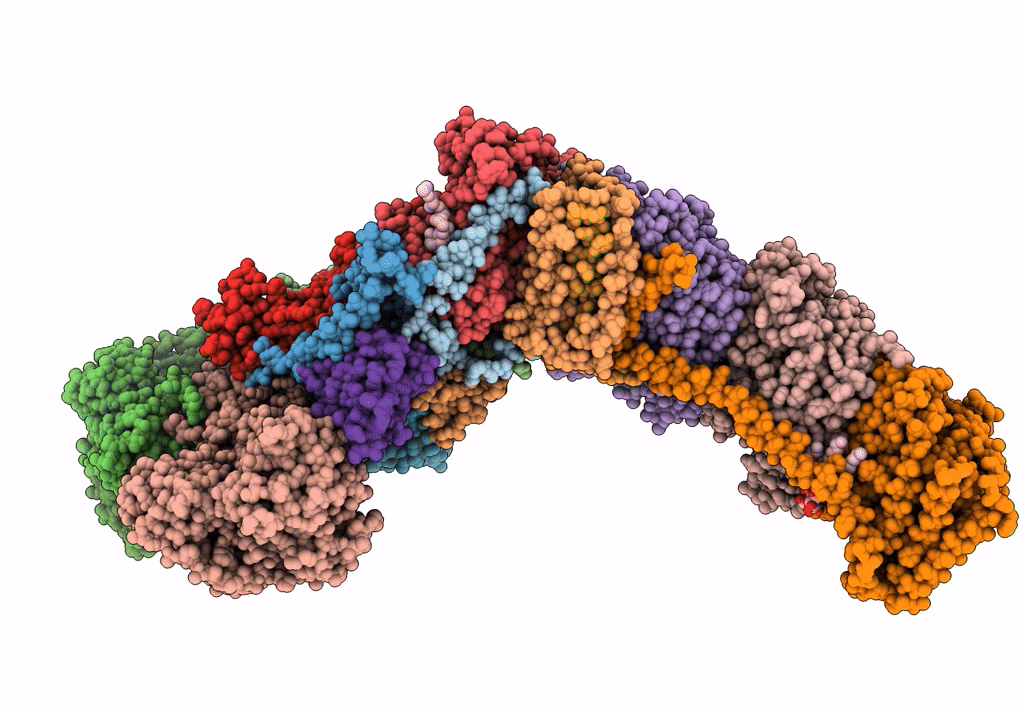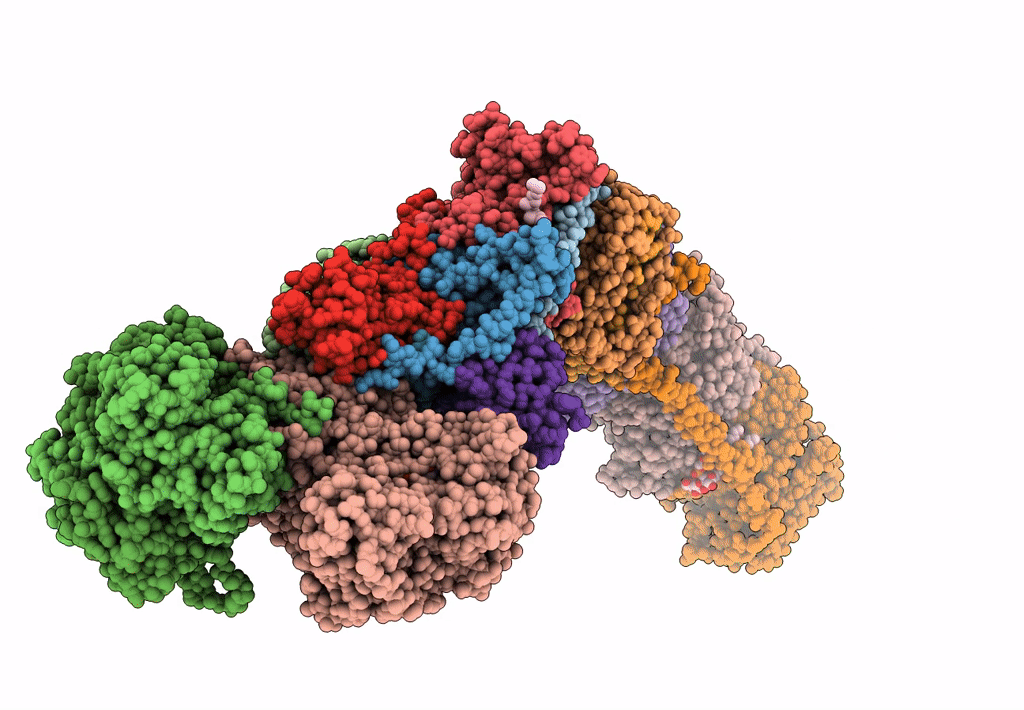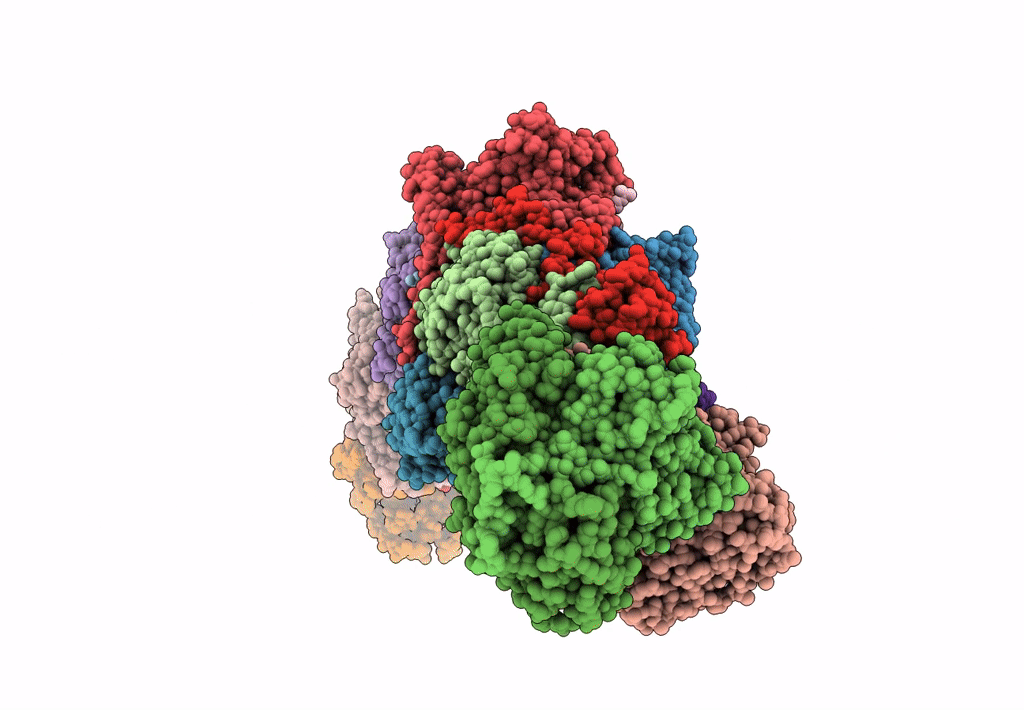
Mycobacterial respiratory complex I with both quinone positions modelled
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
Mycolicibacterium smegmatis MC2 155 (Taxon ID: 246196)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
2.60 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE