Deposition Date
2022-08-19
Release Date
2022-10-26
Last Version Date
2023-10-18
Entry Detail
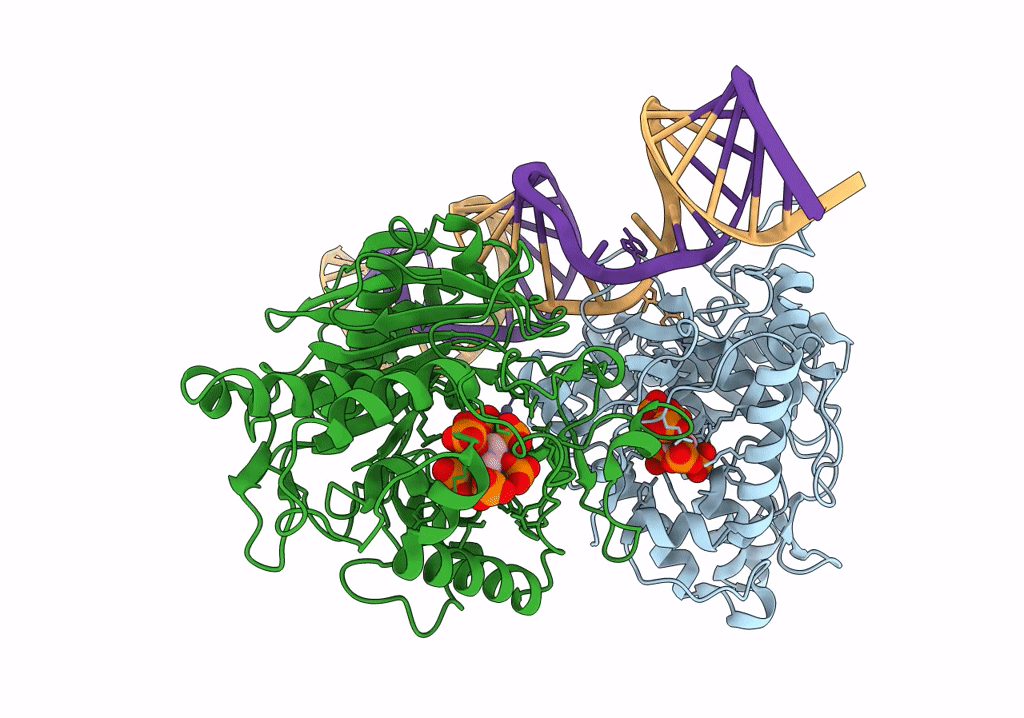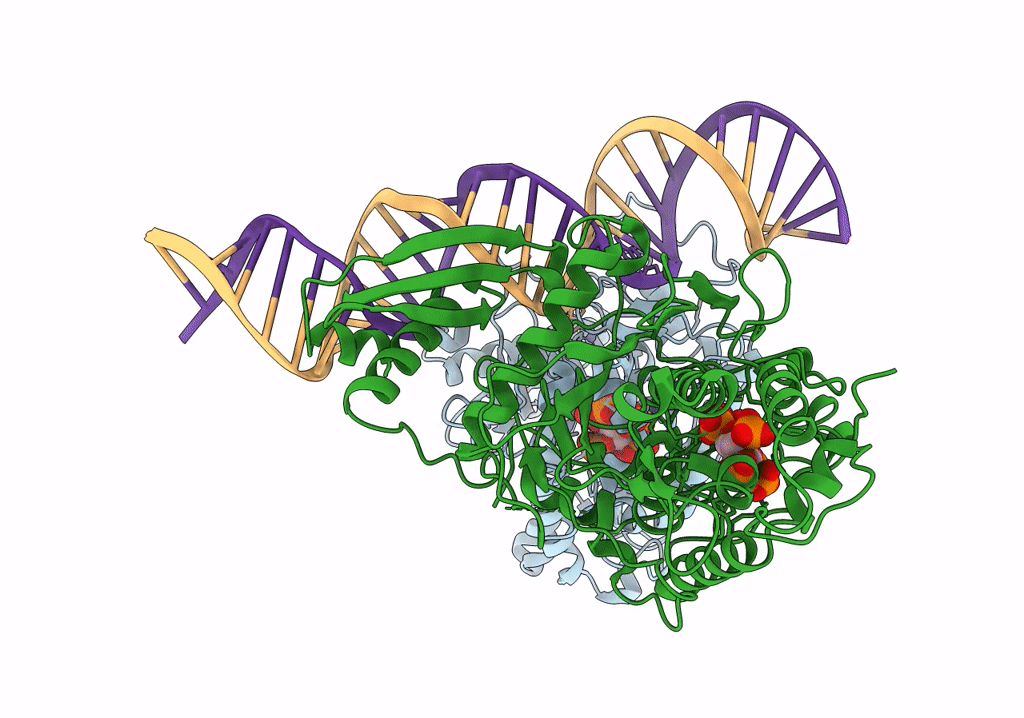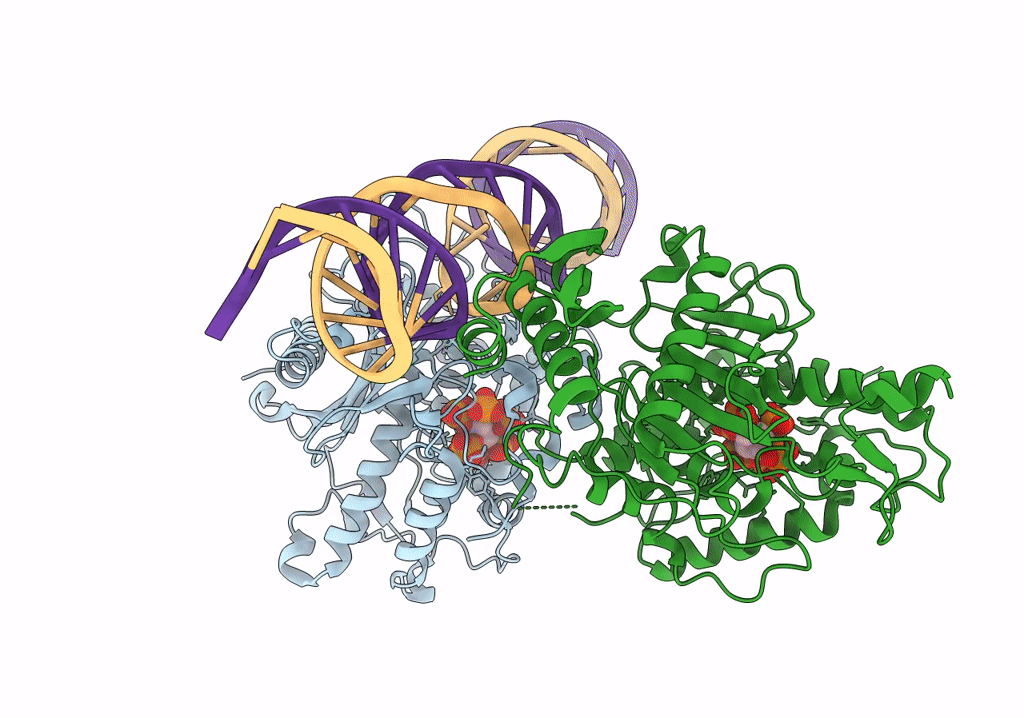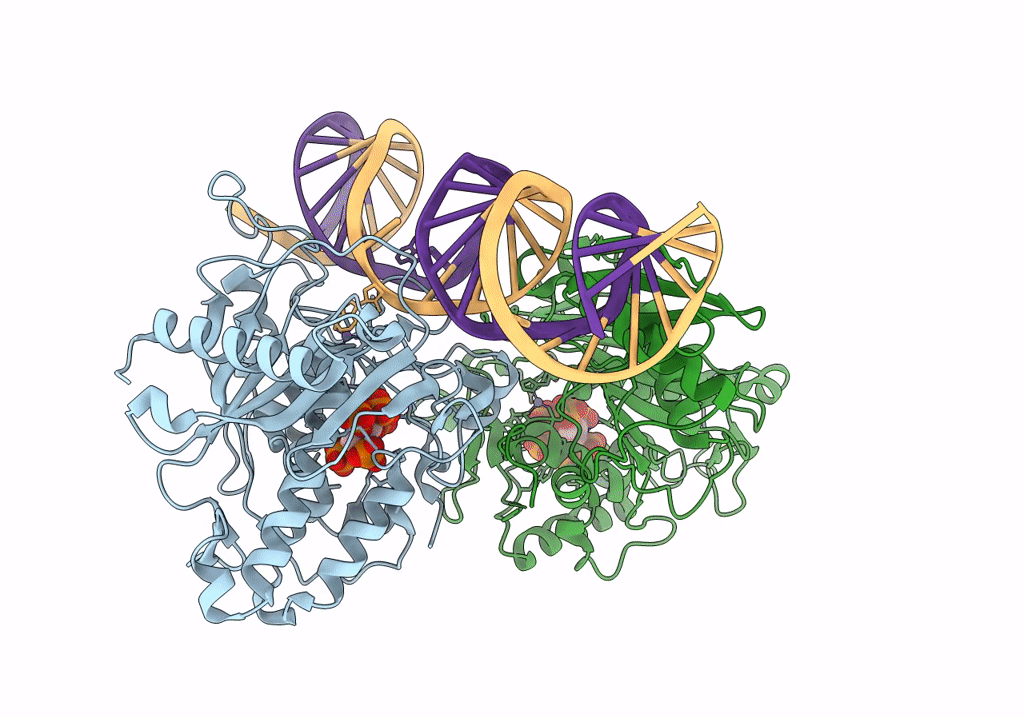
PDB ID:
8E4X
Keywords:
Title:
Human Adenosine Deaminase Acting on dsRNA (ADAR2-R2D) bound to dsRNA containing a G:3-deaza dA pair adjacent to the target site
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Homo sapiens (Taxon ID: 9606)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
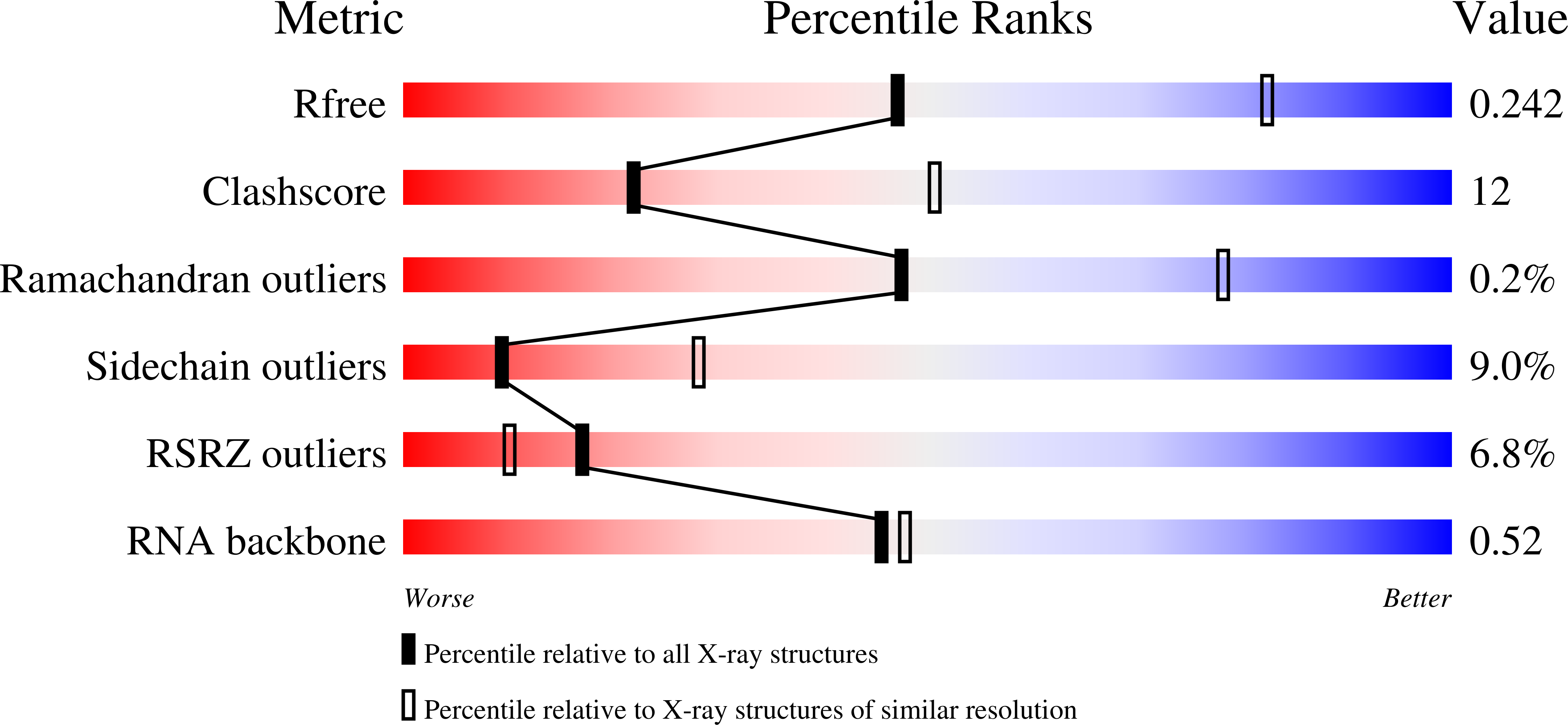
Resolution:
2.80 Å
R-Value Free:
0.23
R-Value Work:
0.19
R-Value Observed:
0.19
Space Group:
C 1 2 1