Deposition Date
2022-08-11
Release Date
2023-01-11
Last Version Date
2024-04-03
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
8E1W
Keywords:
Title:
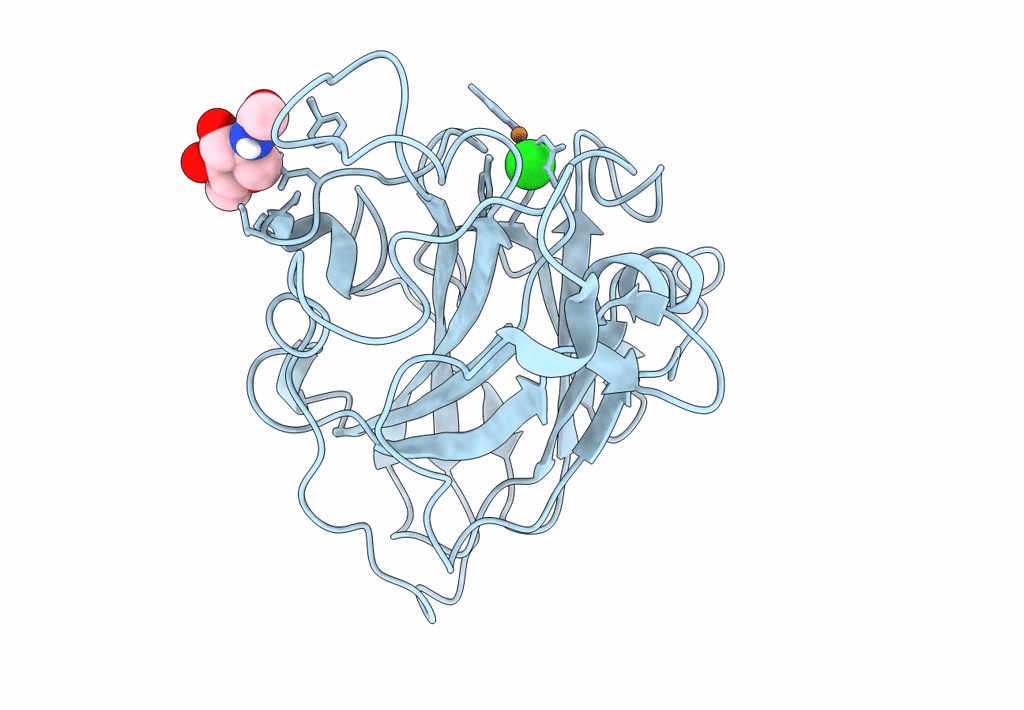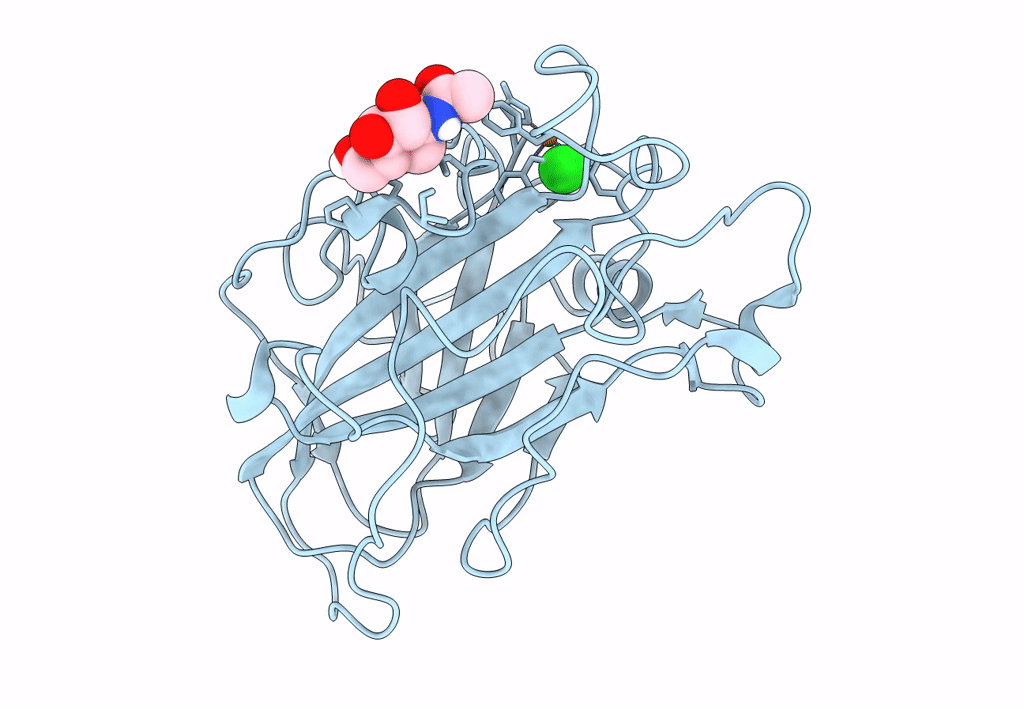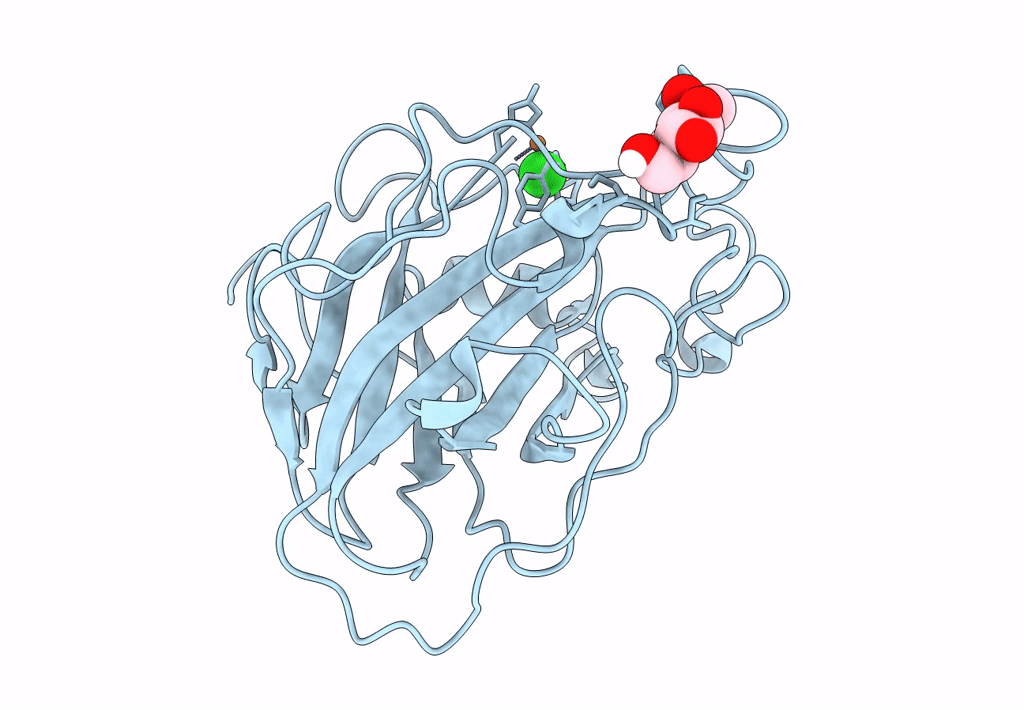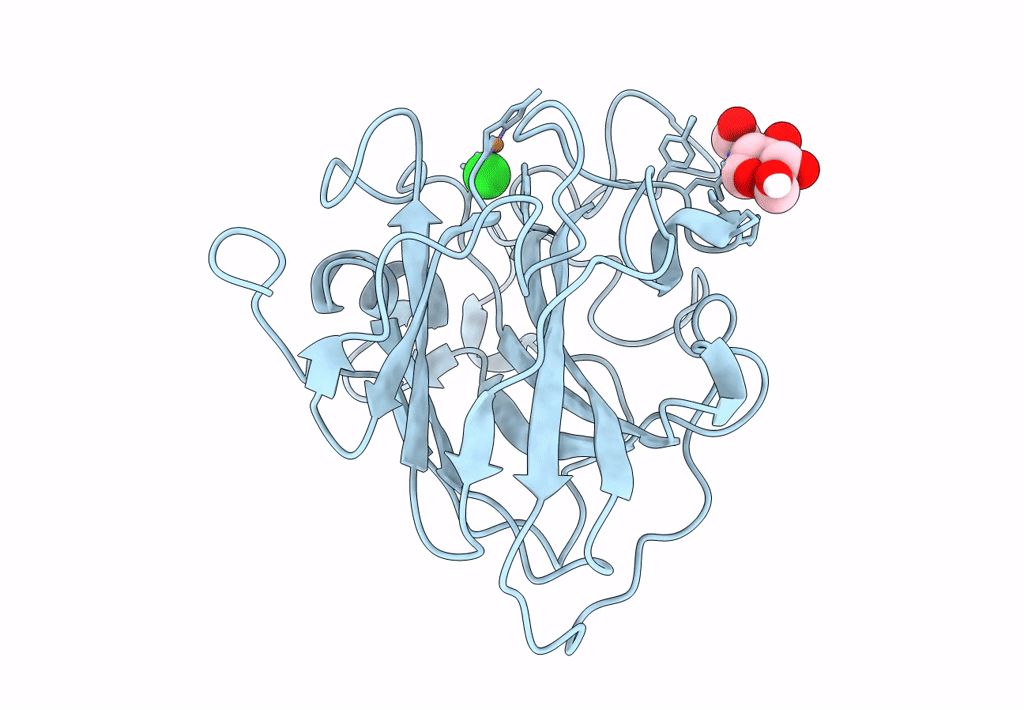
Neutron crystal structure of Panus similis AA9A at room temperature
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
Panus similis (Taxon ID: 292560)
Host Organism:
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
R-Value Free:
['0.17
R-Value Work:
['0.14
R-Value Observed:
['0.14
Space Group:
P 41 3 2


