Deposition Date
2022-07-07
Release Date
2023-07-12
Last Version Date
2024-07-24
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
8DLE
Keywords:
Title:
Crosslinked Crystal Structure of the 8-amino-7-oxonanoate synthase, BioF, and Benzene Sulfonyl Fluoride-crypto Acyl Carrier Protein, BSF-ACP
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Escherichia coli (Taxon ID: 562)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
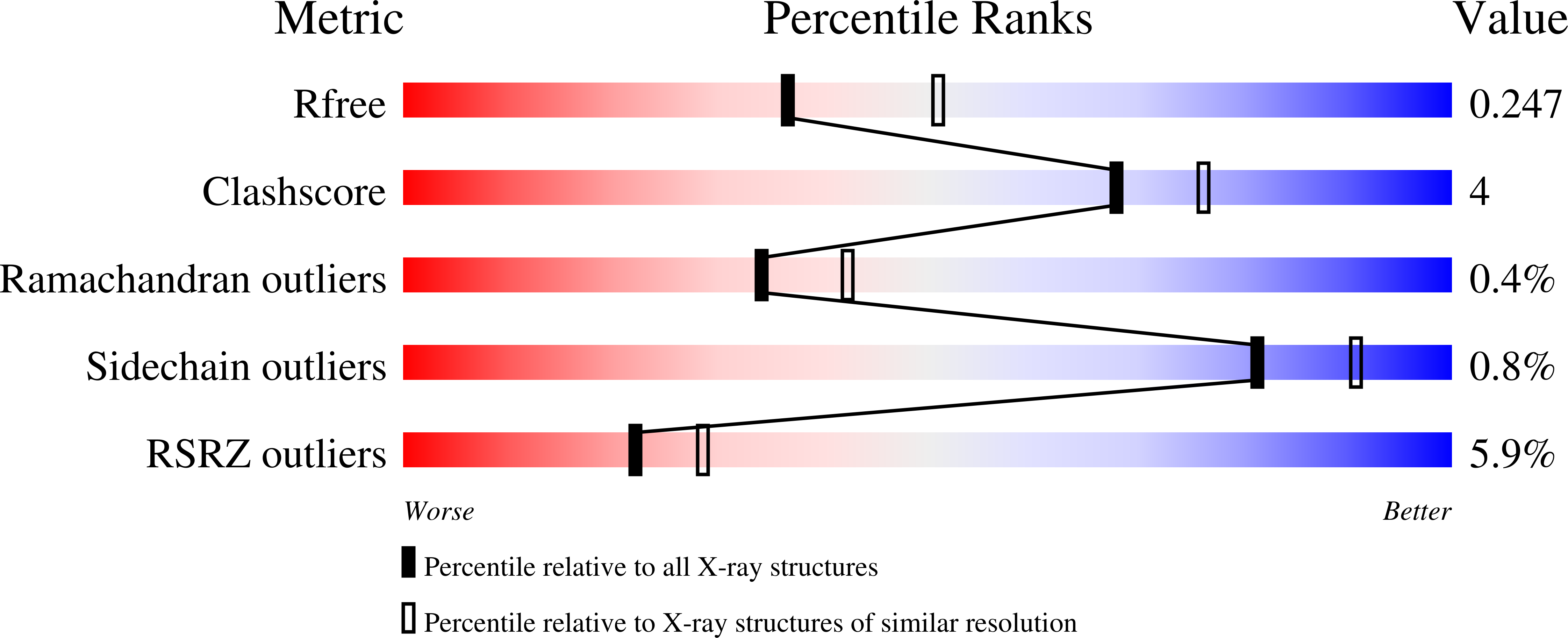
Resolution:
2.30 Å
R-Value Free:
0.24
R-Value Work:
0.20
R-Value Observed:
0.20
Space Group:
C 2 2 21