Deposition Date
2022-07-01
Release Date
2023-01-11
Last Version Date
2023-10-25
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
8DJZ
Keywords:
Title:
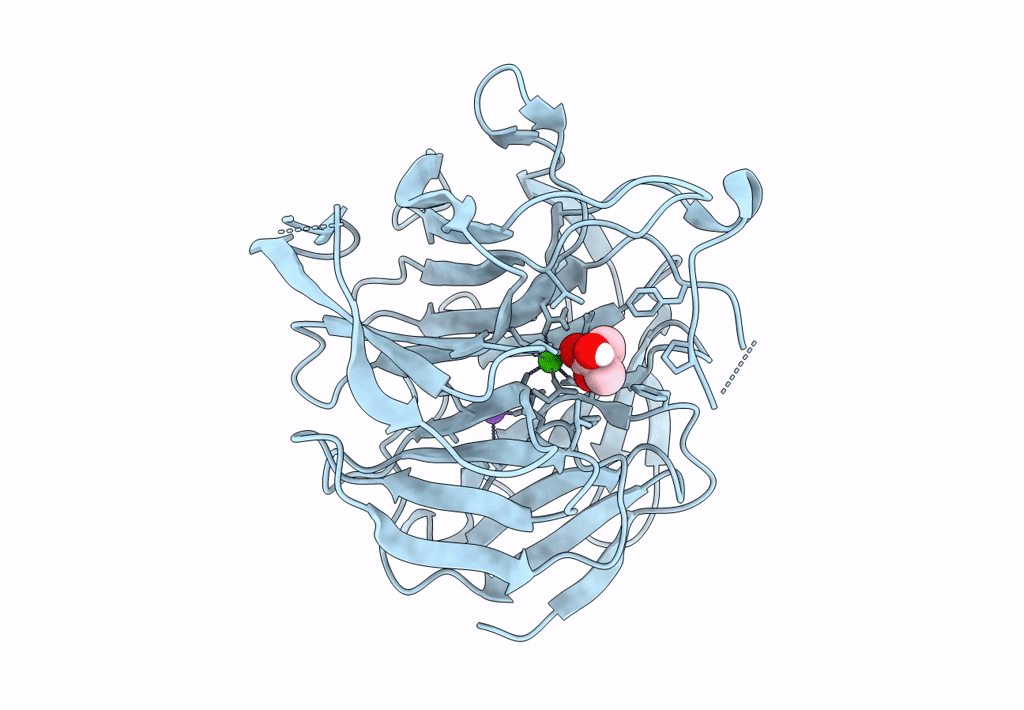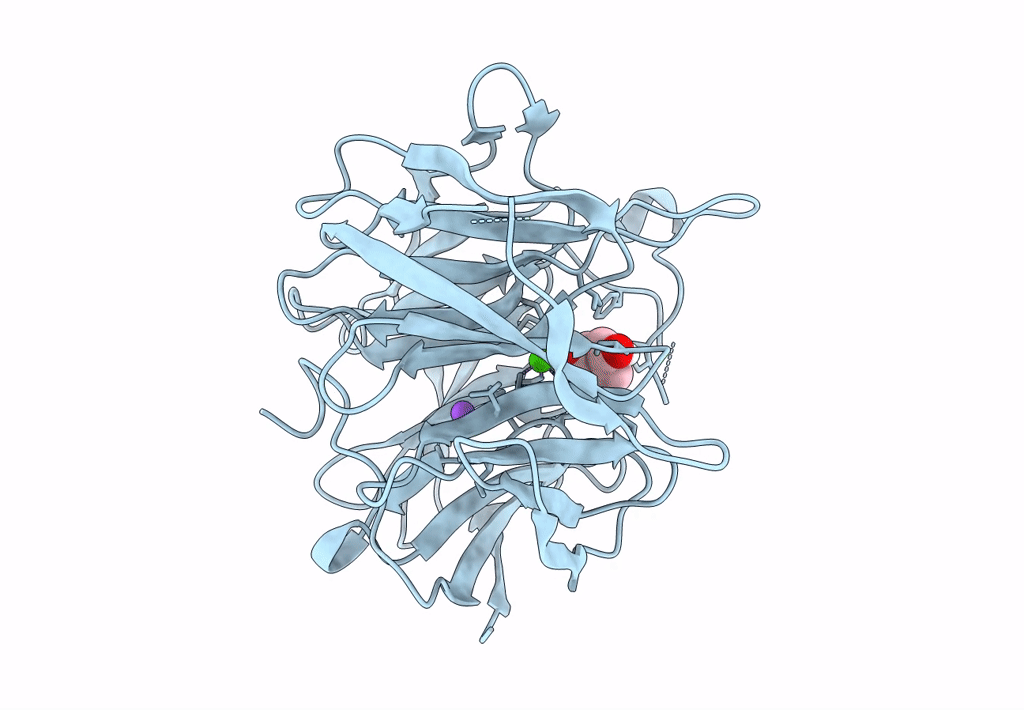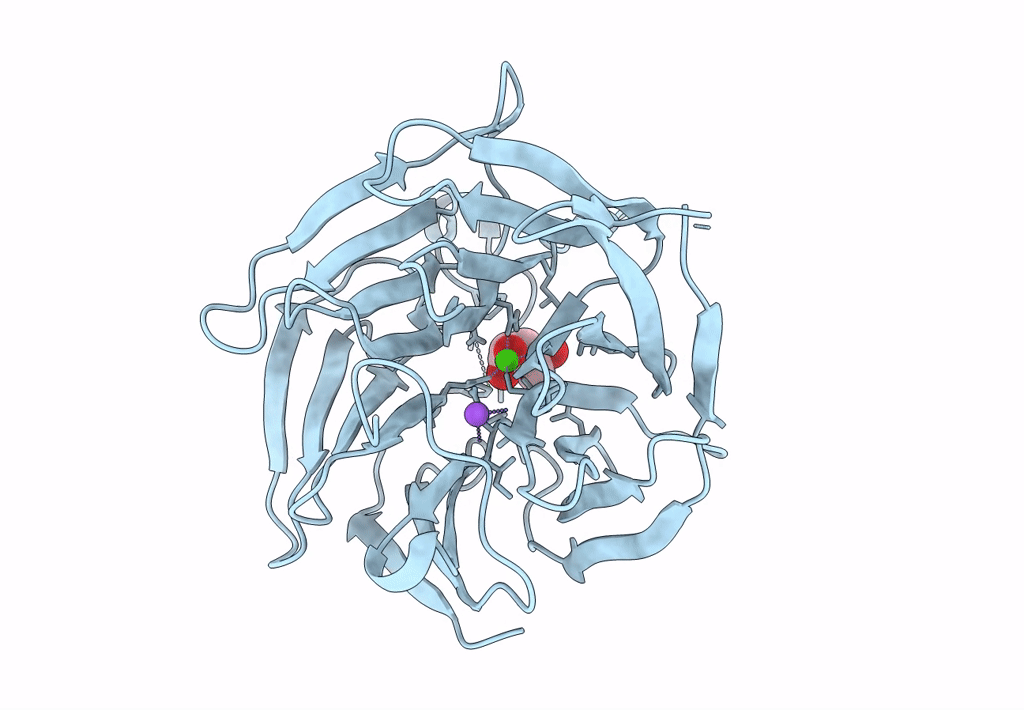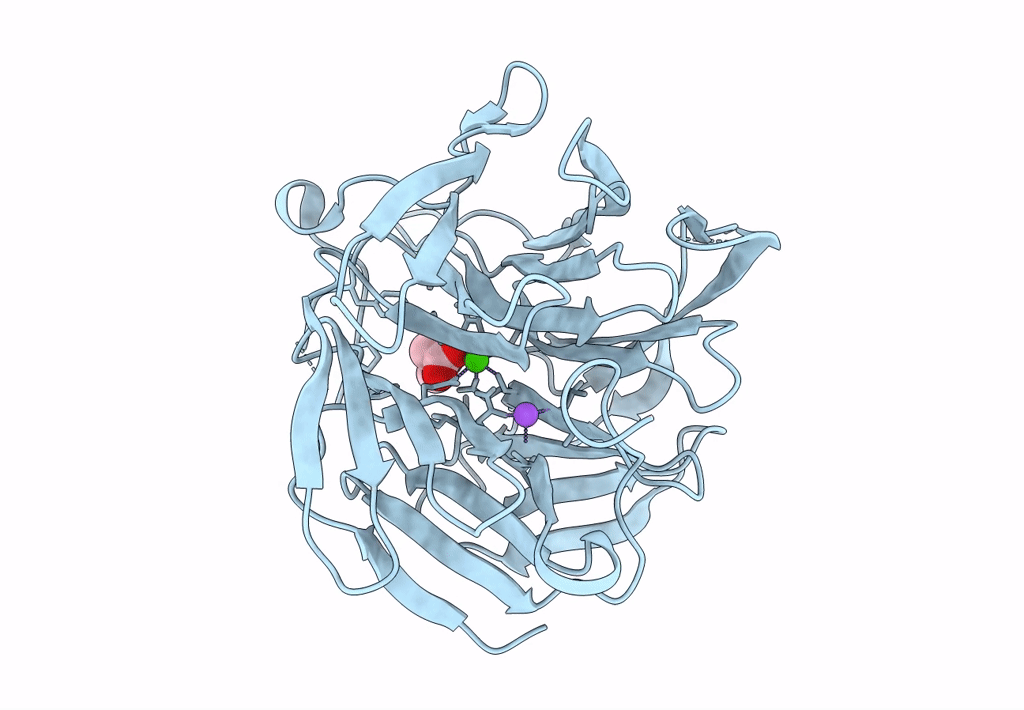
Crystal structure of RPA3624, a beta-propeller lactonase from Rhodopseudomonas palustris, with active-site bound product
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Rhodopseudomonas palustris CGA009 (Taxon ID: 258594)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
1.55 Å
R-Value Free:
0.21
R-Value Work:
0.17
R-Value Observed:
0.18
Space Group:
P 32 2 1


