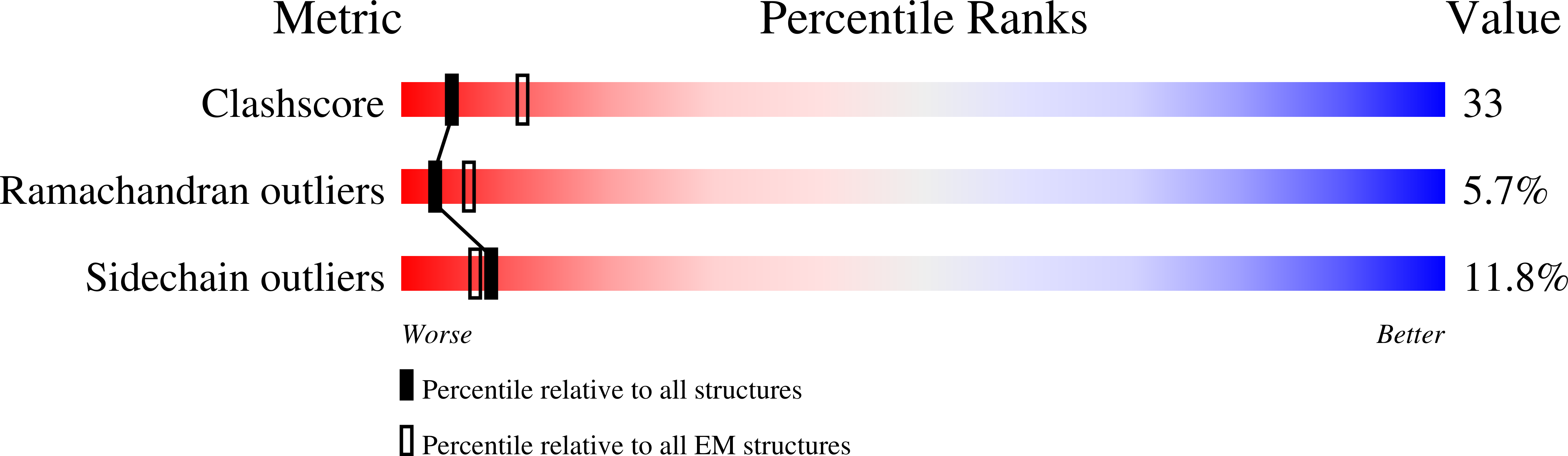Deposition Date
2022-06-08
Release Date
2022-08-31
Last Version Date
2024-10-23
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
8D87
Keywords:
Title:
Fitted crystal structure of the homotrimer of fusion glycoprotein E1 from SFV into subtomogram averaged CHIKV E1 glycoprotein density
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Chikungunya virus strain S27-African prototype (Taxon ID: 371094)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
27.20 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SUBTOMOGRAM AVERAGING