Deposition Date
2022-05-27
Release Date
2022-06-15
Last Version Date
2024-10-16
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
8D1U
Keywords:
Title:
E. coli beta-ketoacyl-[acyl carrier protein] synthase III (FabH) with an acetylated cysteine and in complex with oxa(dethia)-Coenzyme A
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Escherichia coli (Taxon ID: 562)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
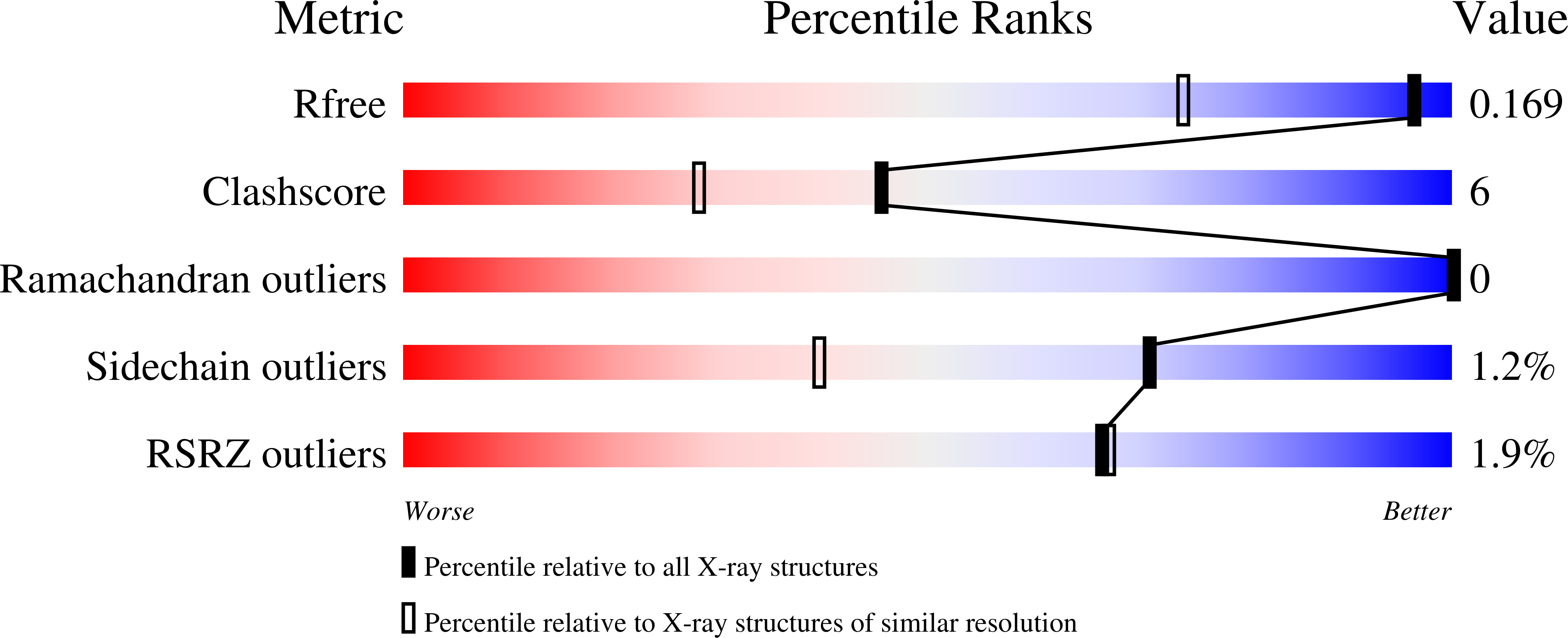
Resolution:
1.30 Å
R-Value Free:
0.16
R-Value Work:
0.14
Space Group:
P 41 21 2