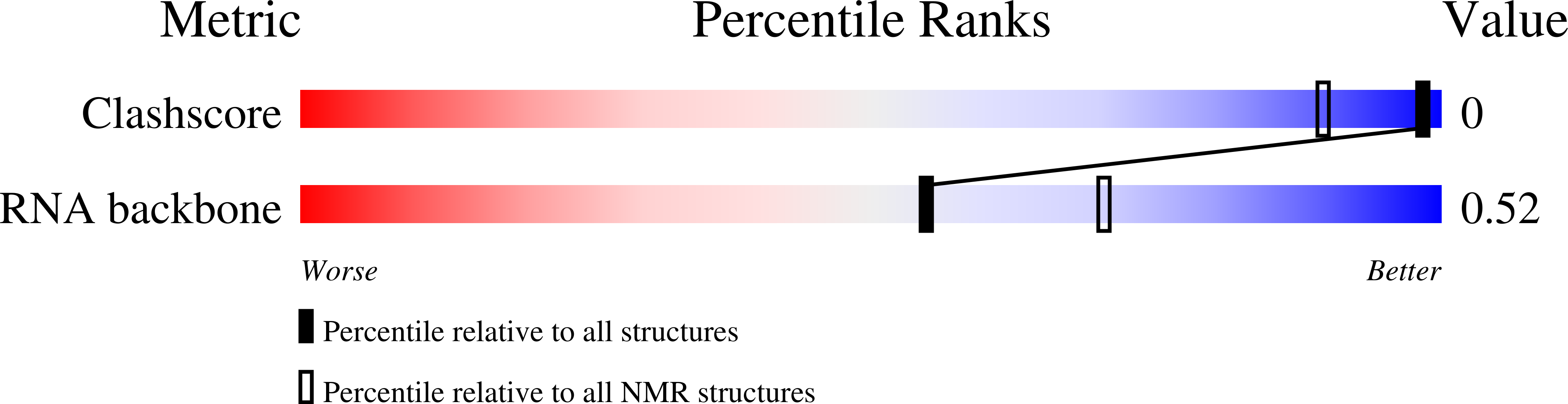Deposition Date
2023-02-02
Release Date
2024-02-21
Last Version Date
2024-05-22
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
8CF2
Keywords:
Title:
Solution structure of the RNA helix formed by the 5'-end of U1 snRNA and an A-1 bulged 5'-splice site in complex with SMN-CY
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
synthetic construct (Taxon ID: 32630)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Conformers Calculated:
20
Conformers Submitted:
14
Selection Criteria:
structures with acceptable covalent geometry