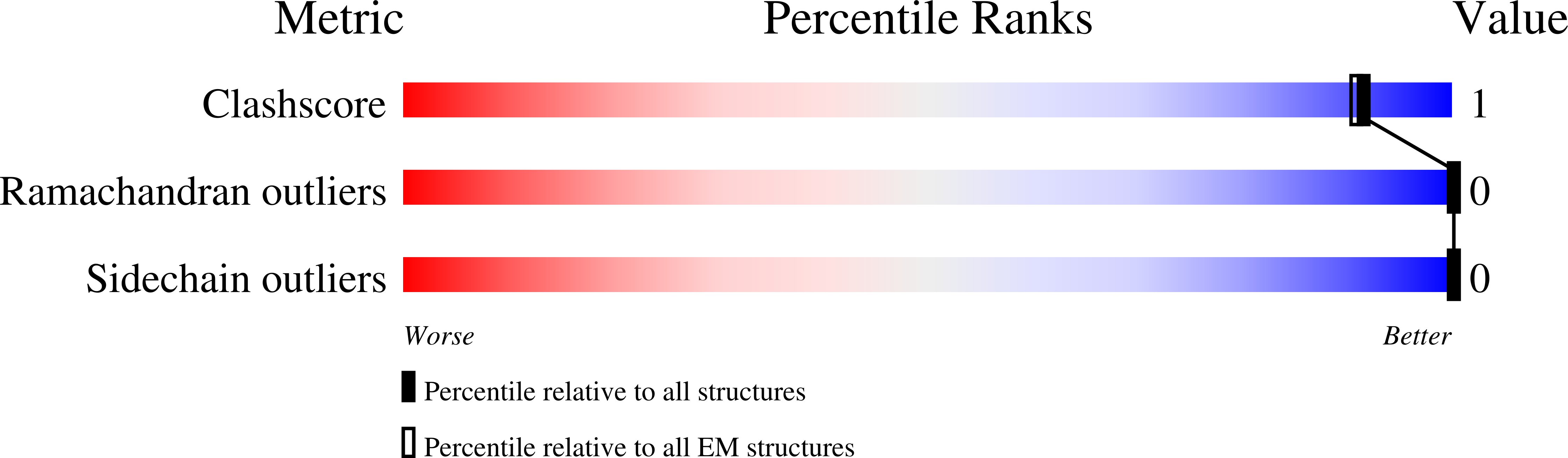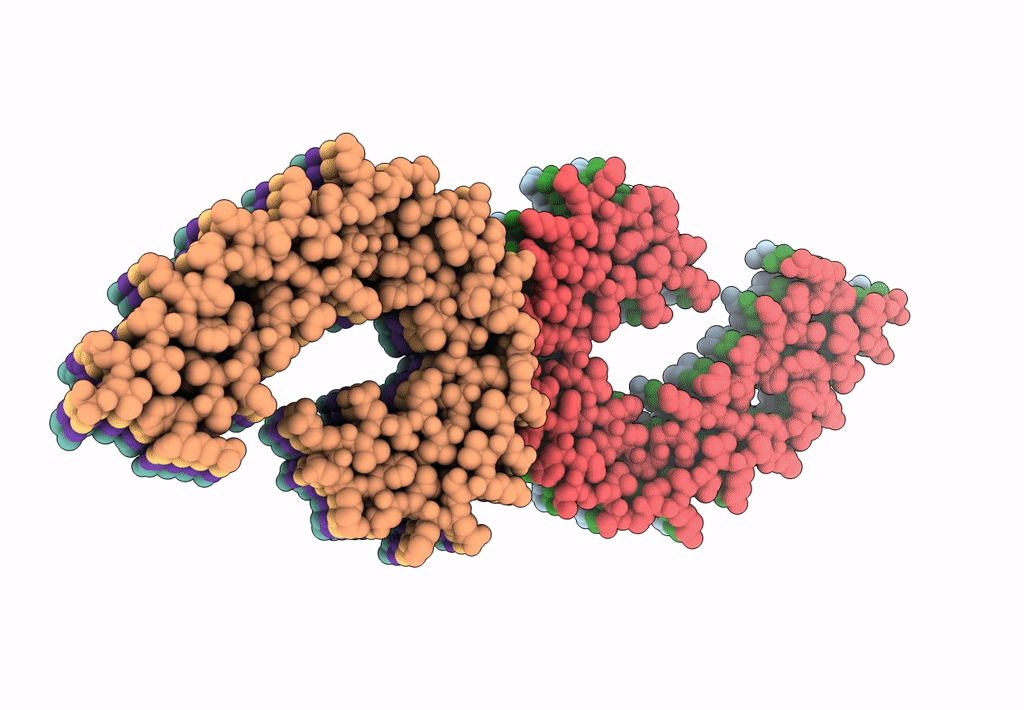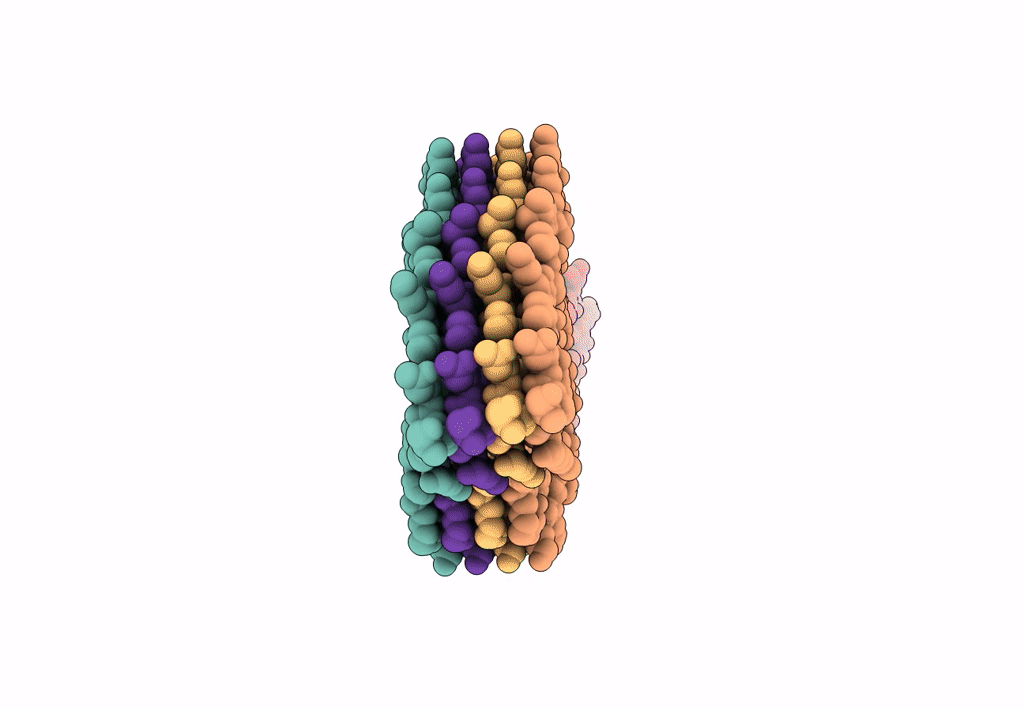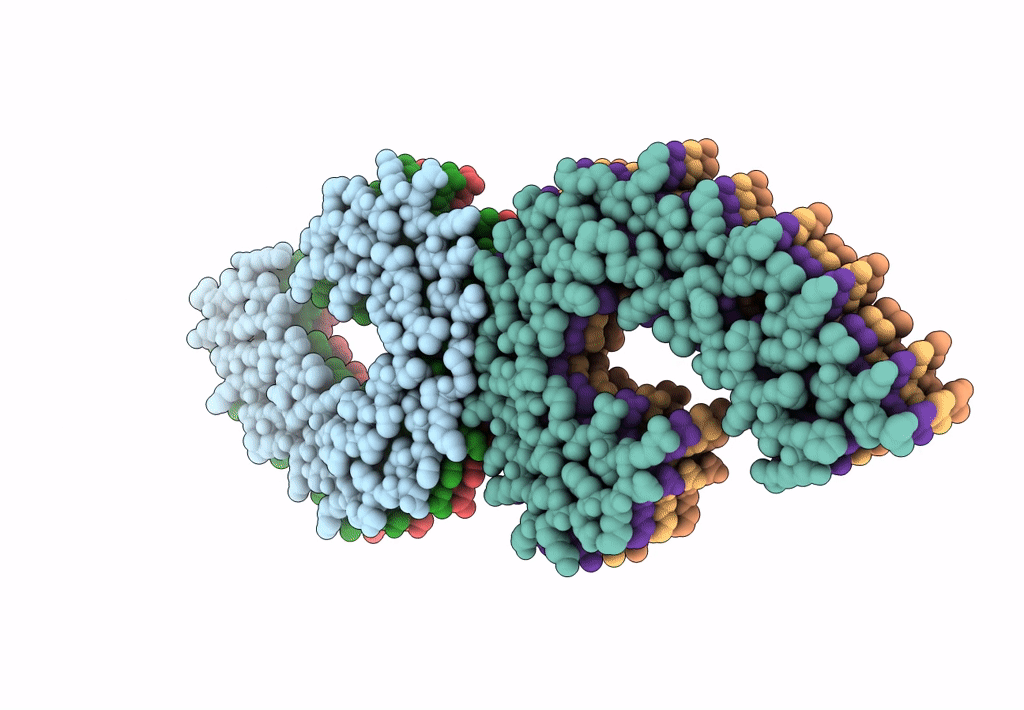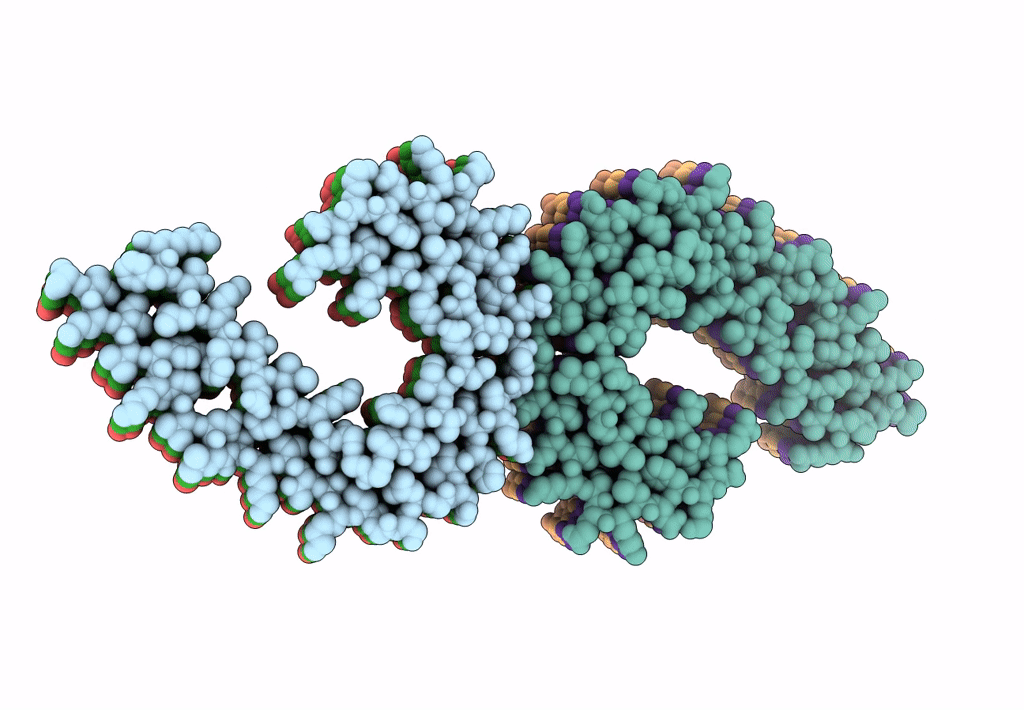
Deposition Date
2022-10-28
Release Date
2023-05-24
Last Version Date
2025-03-05
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
8BGS
Keywords:
Title:
Tau Paired Helical Filament from Extracellular Vesicles from Alzheimer's disease brain
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Homo sapiens (Taxon ID: 9606)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
3.16 Å
Aggregation State:
FILAMENT
Reconstruction Method:
HELICAL