Deposition Date
2022-06-22
Release Date
2022-10-05
Last Version Date
2024-11-20
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
8A8C
Keywords:
Title:
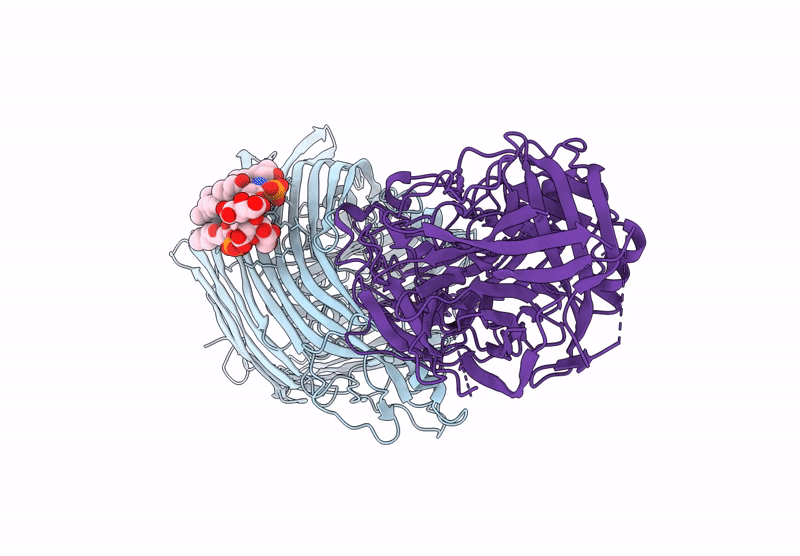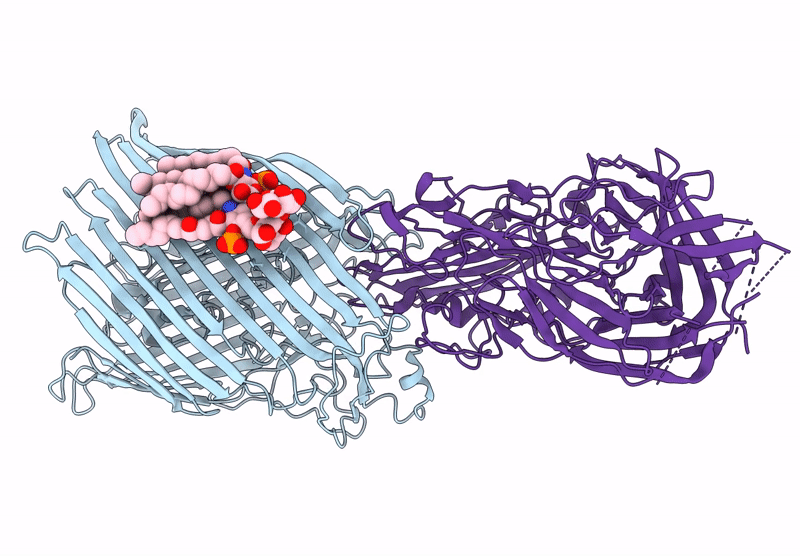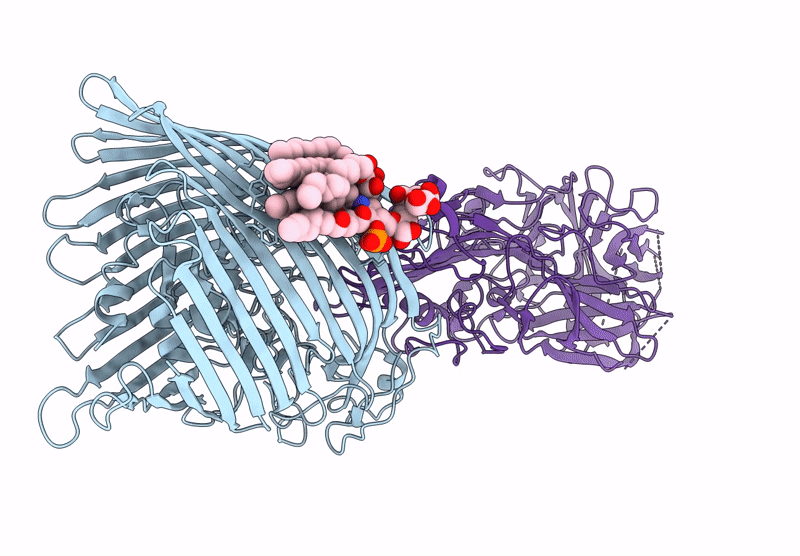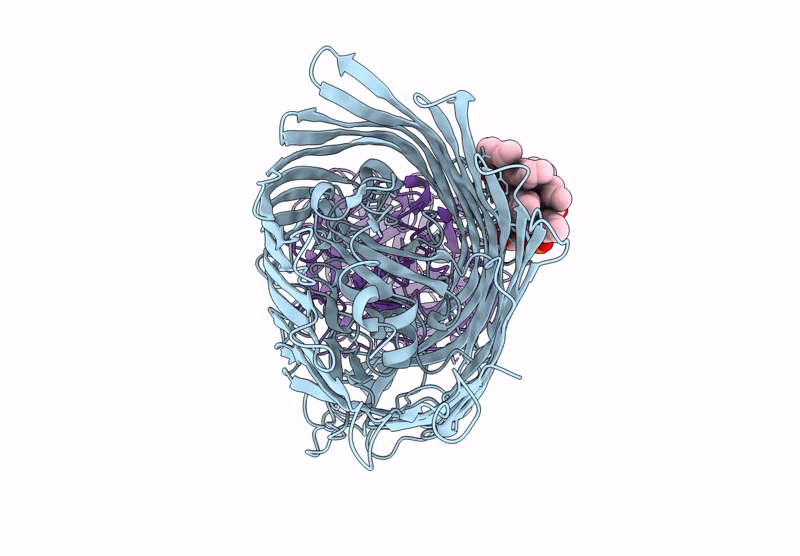
T5 phage receptor-binding protein pb5 bound to ferrichrome transporter FhuA
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Escherichia coli K-12 (Taxon ID: 83333)
Escherichia phage T5 (Taxon ID: 2695836)
Escherichia phage T5 (Taxon ID: 2695836)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
3.10 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE


