Deposition Date
2022-06-14
Release Date
2022-12-28
Last Version Date
2024-07-24
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
8A5D
Keywords:
Title:
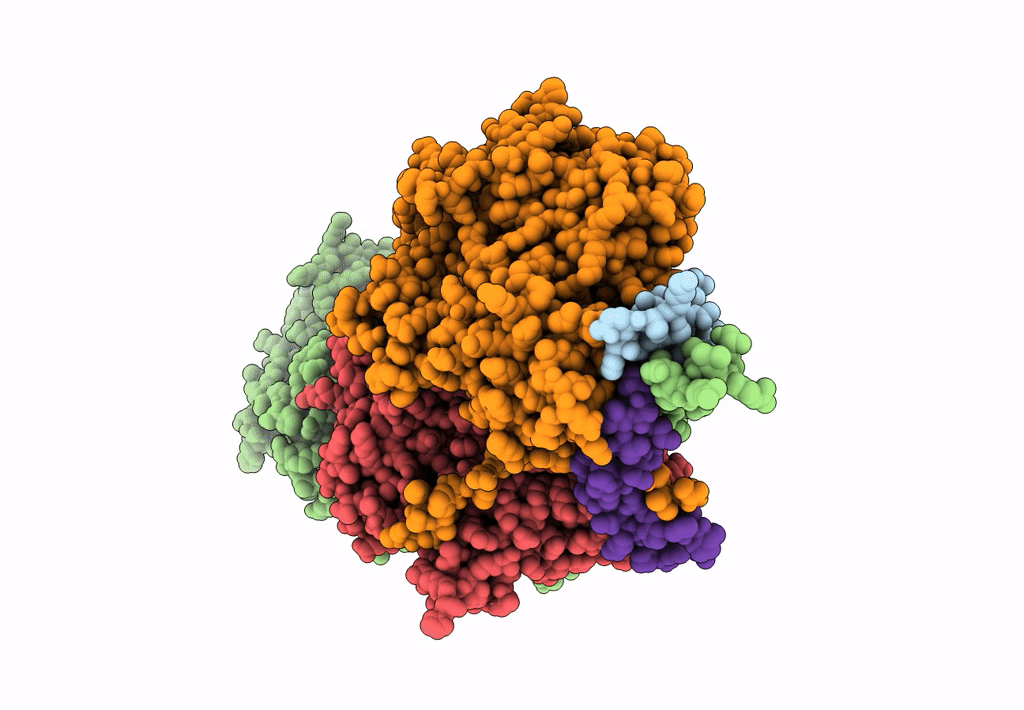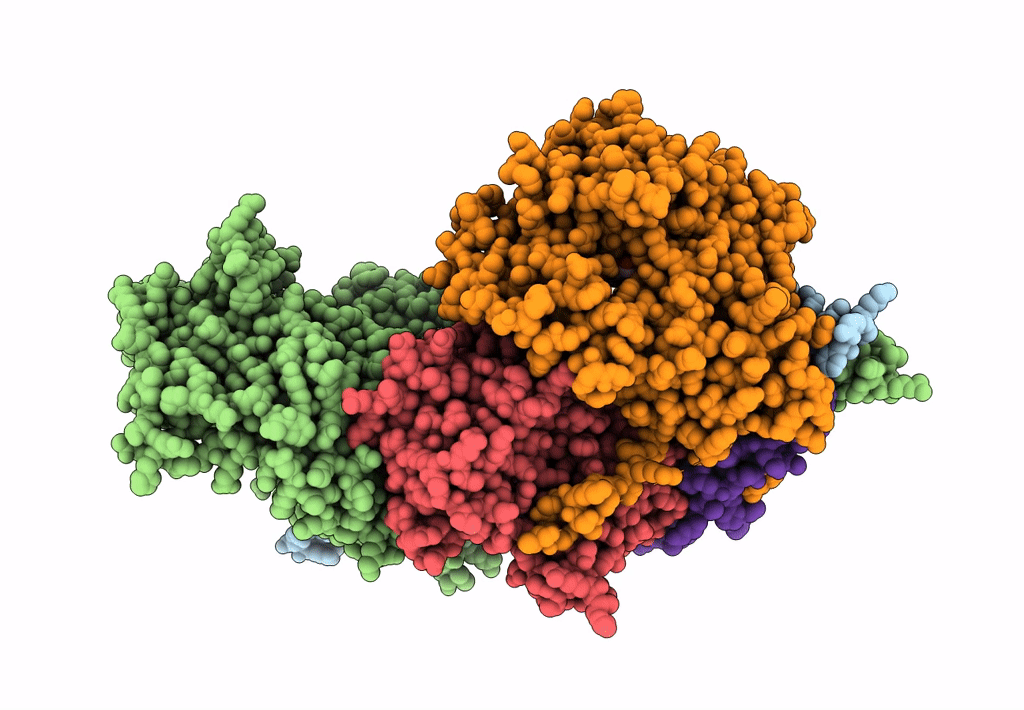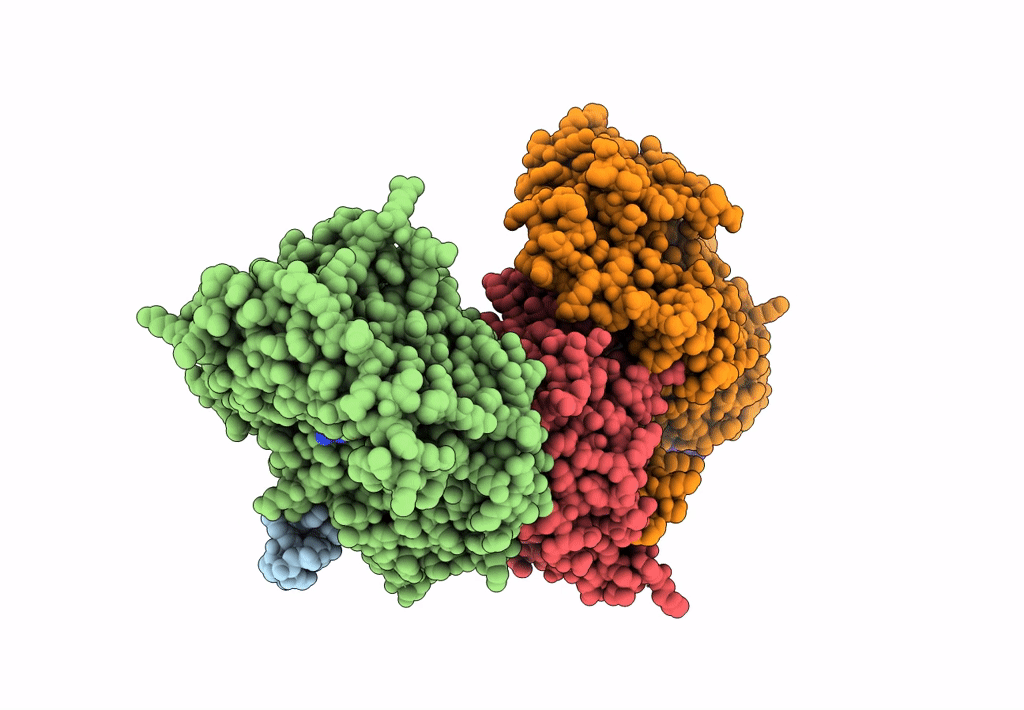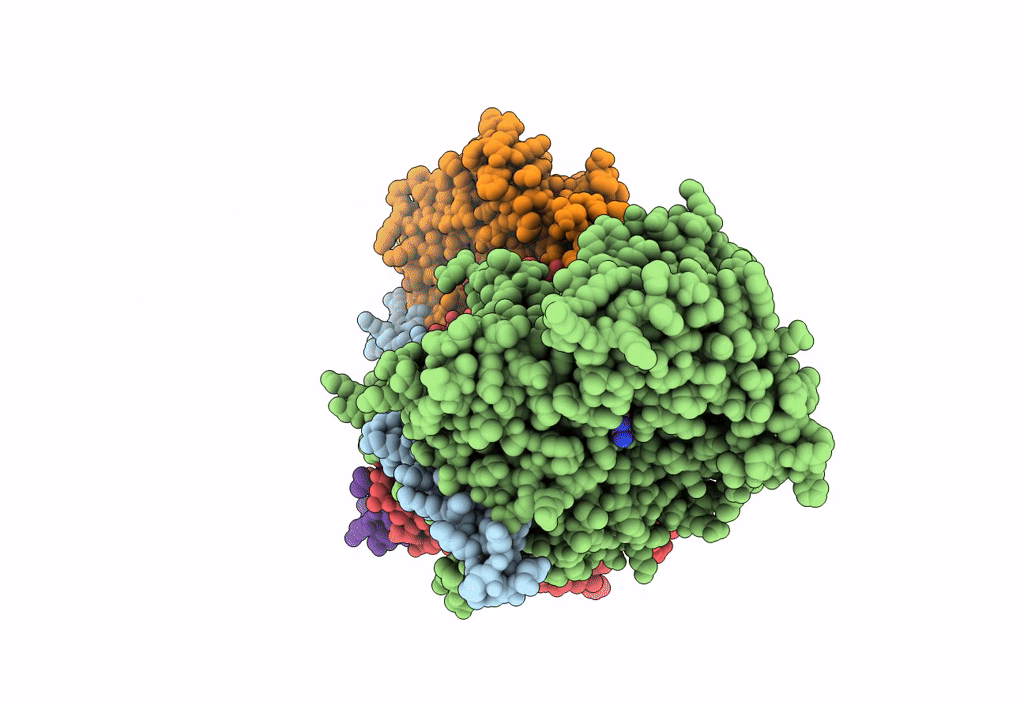
Structure of Arp4-Ies4-N-actin-Arp8-Ino80HSA subcomplex (A-module) of Chaetomium thermophilum INO80
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Thermochaetoides thermophila (Taxon ID: 209285)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
2.90 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE


