Deposition Date
2021-06-25
Release Date
2021-11-24
Last Version Date
2024-11-20
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
7OZ6
Keywords:
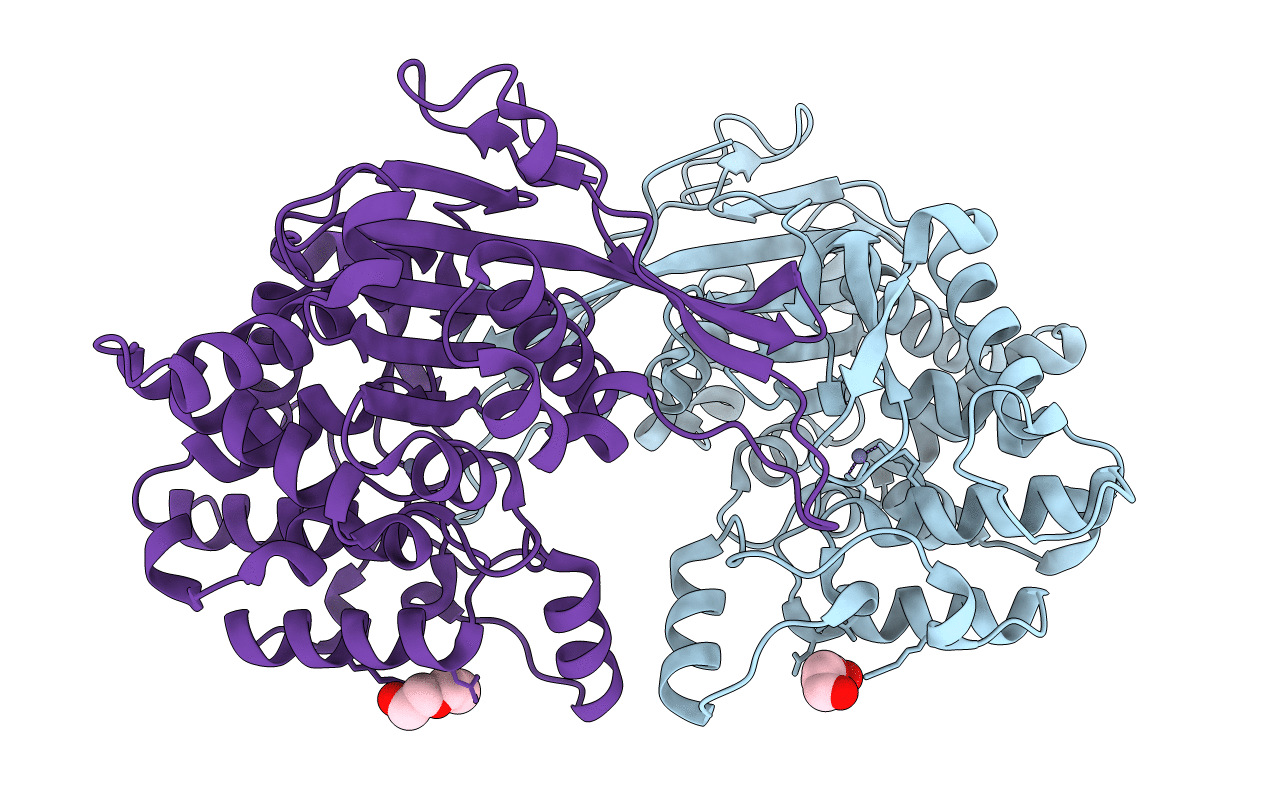
Title:
Crystal structure of Rhizobium etli inducible L-asparaginase ReAV (monoclinic form MC)
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Rhizobium etli (strain CFN 42 / ATCC 51251) (Taxon ID: 347834)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
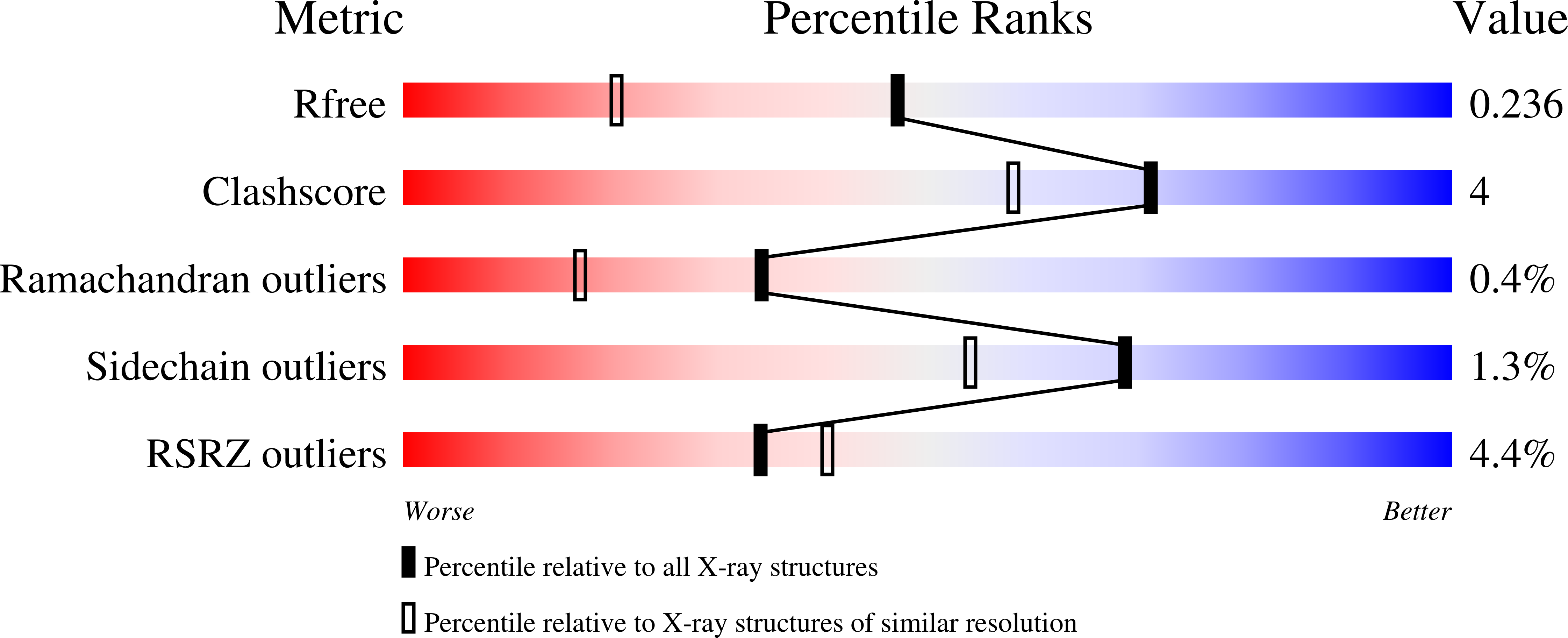
Resolution:
1.76 Å
R-Value Free:
0.22
R-Value Work:
0.18
Space Group:
C 1 2 1