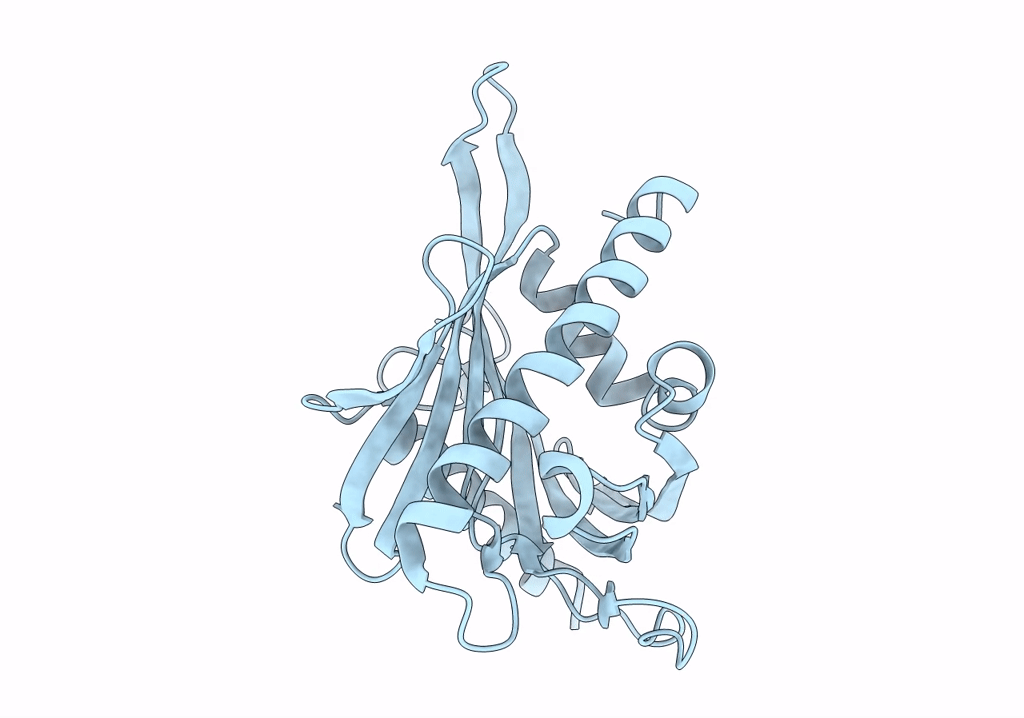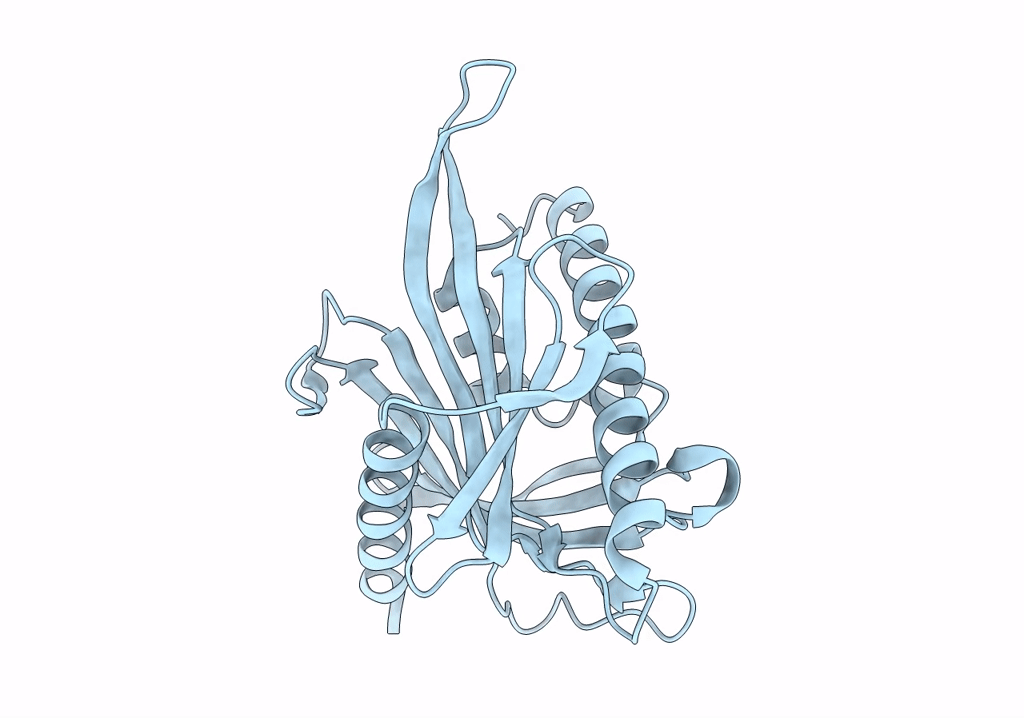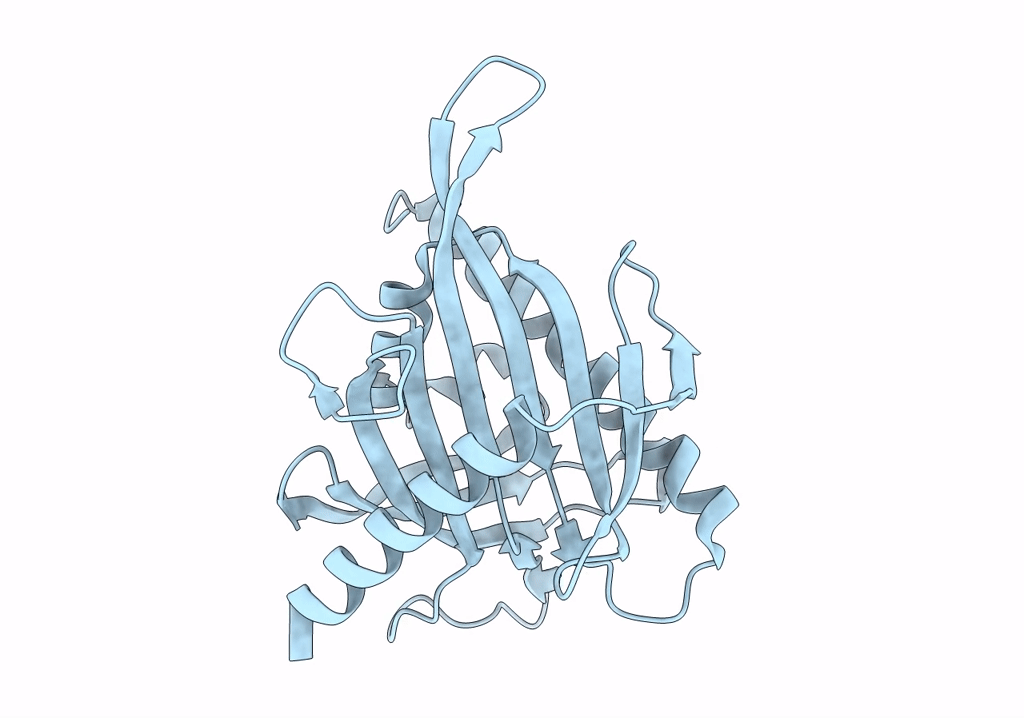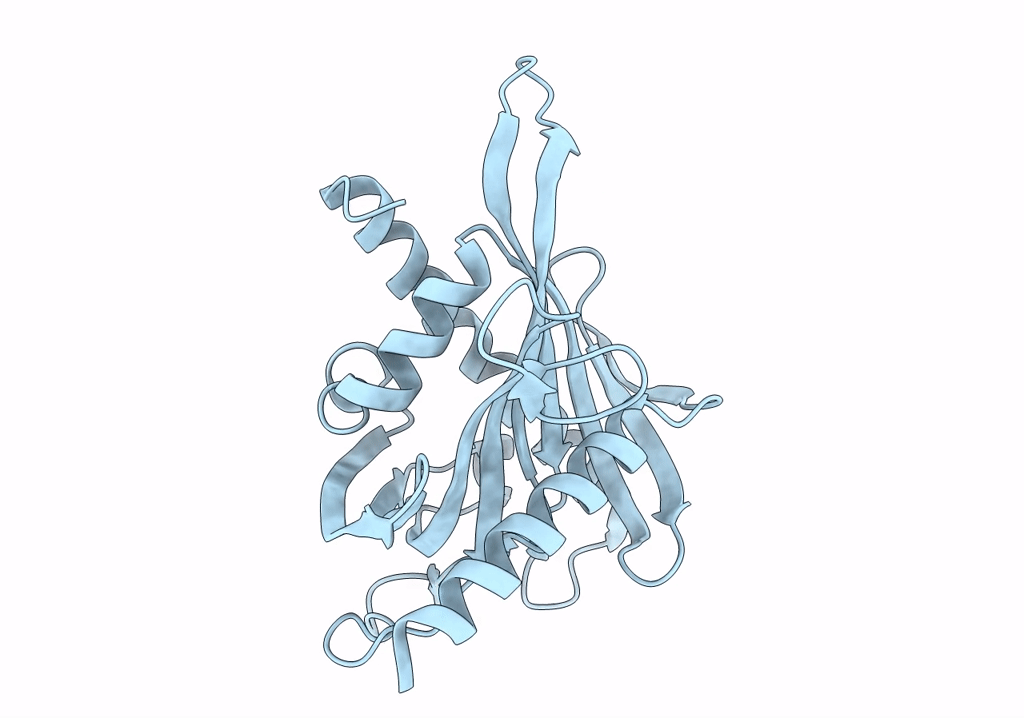
Deposition Date
2022-05-17
Release Date
2022-10-26
Last Version Date
2024-01-31
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
7ZVQ
Keywords:
Title:
Crystal structure of the carotenoid-binding protein domain from silkworm Bombyx mori (BmCBP) in the apoform, S206V mutant
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
Bombyx mori (Taxon ID: 7091)
Host Organism:
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
2.50 Å
R-Value Free:
0.25
R-Value Work:
0.19
R-Value Observed:
0.20
Space Group:
C 2 2 21