Deposition Date
2022-04-26
Release Date
2023-05-10
Last Version Date
2024-11-06
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
7ZON
Keywords:
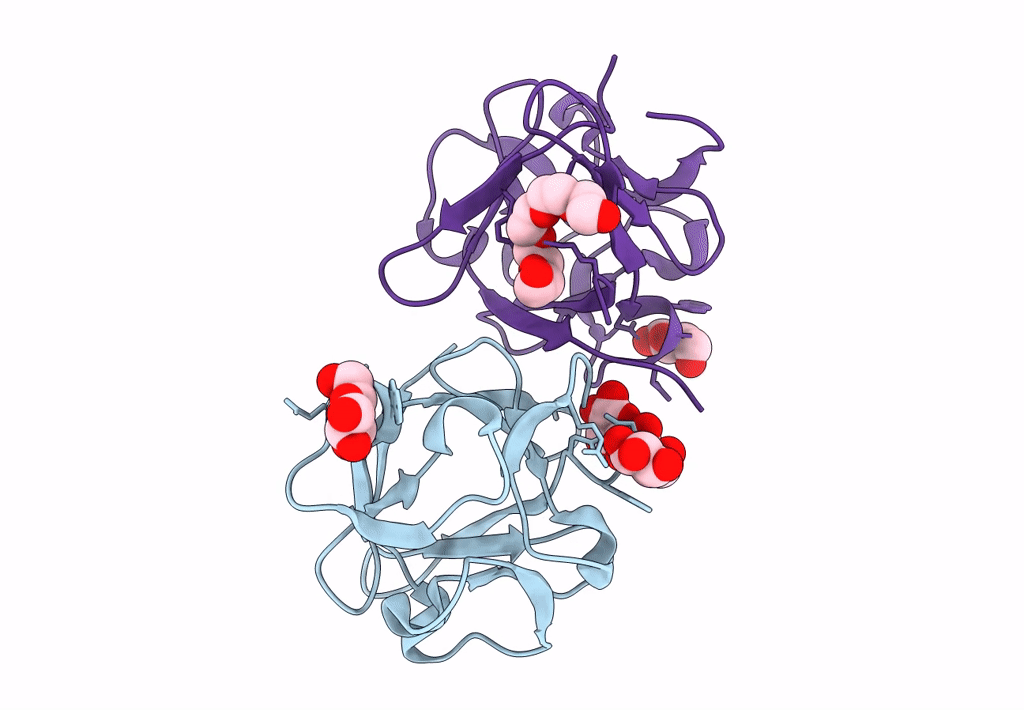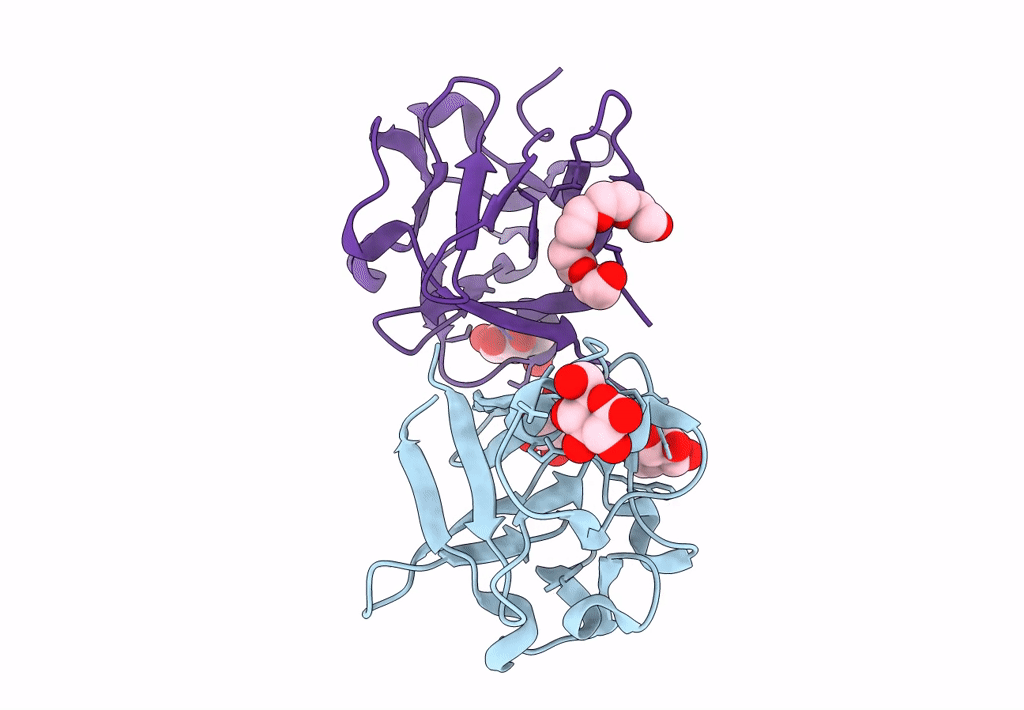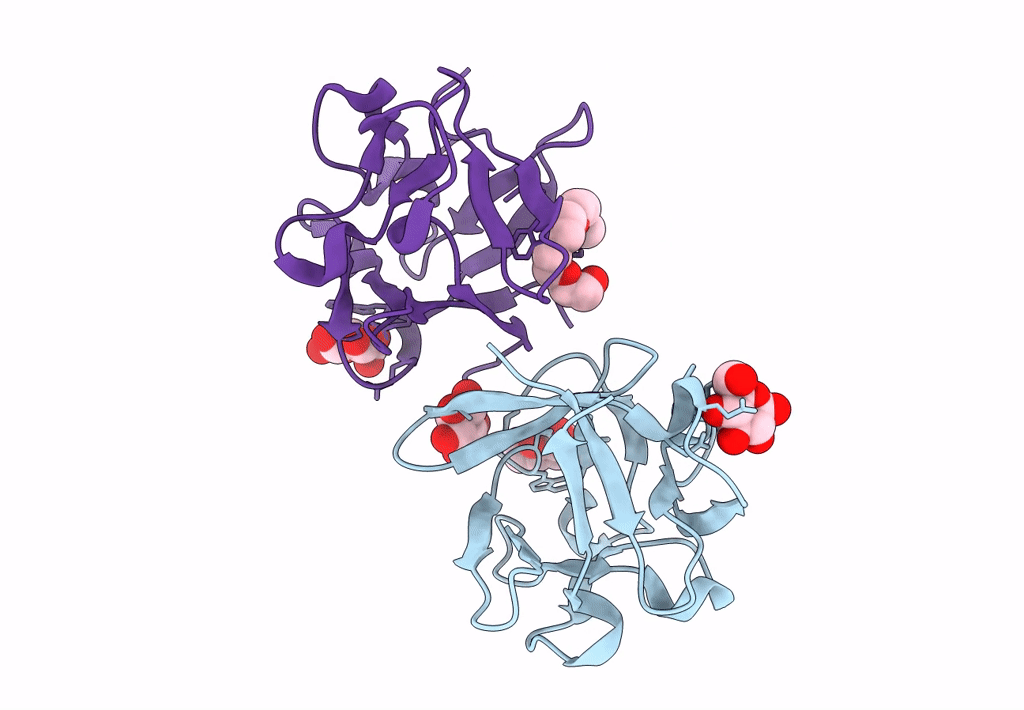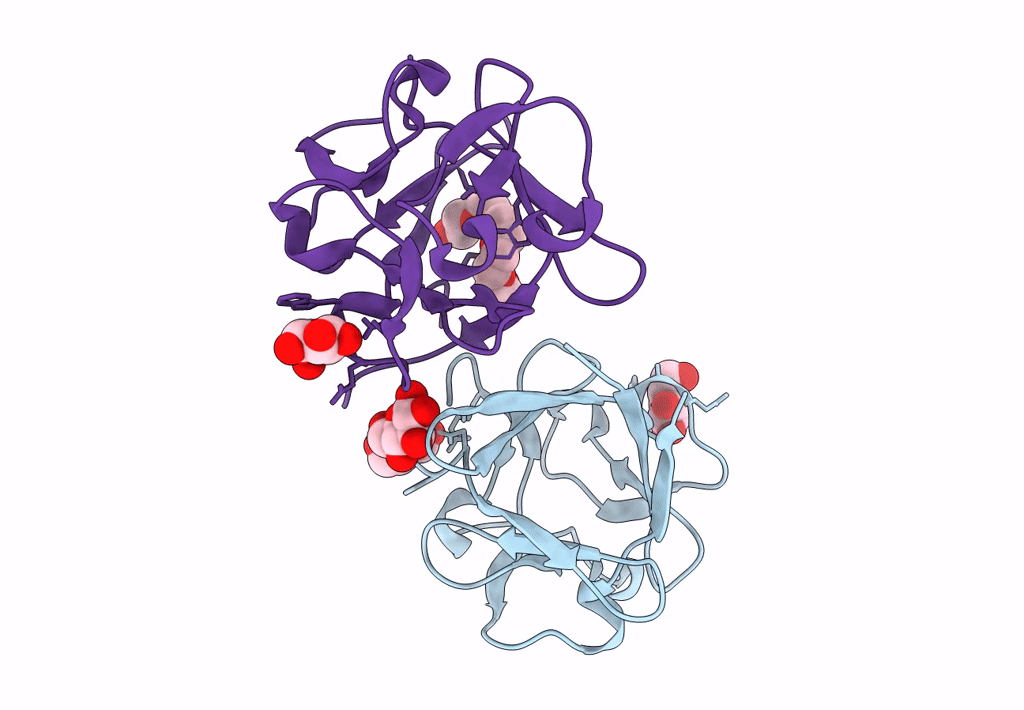
Title:
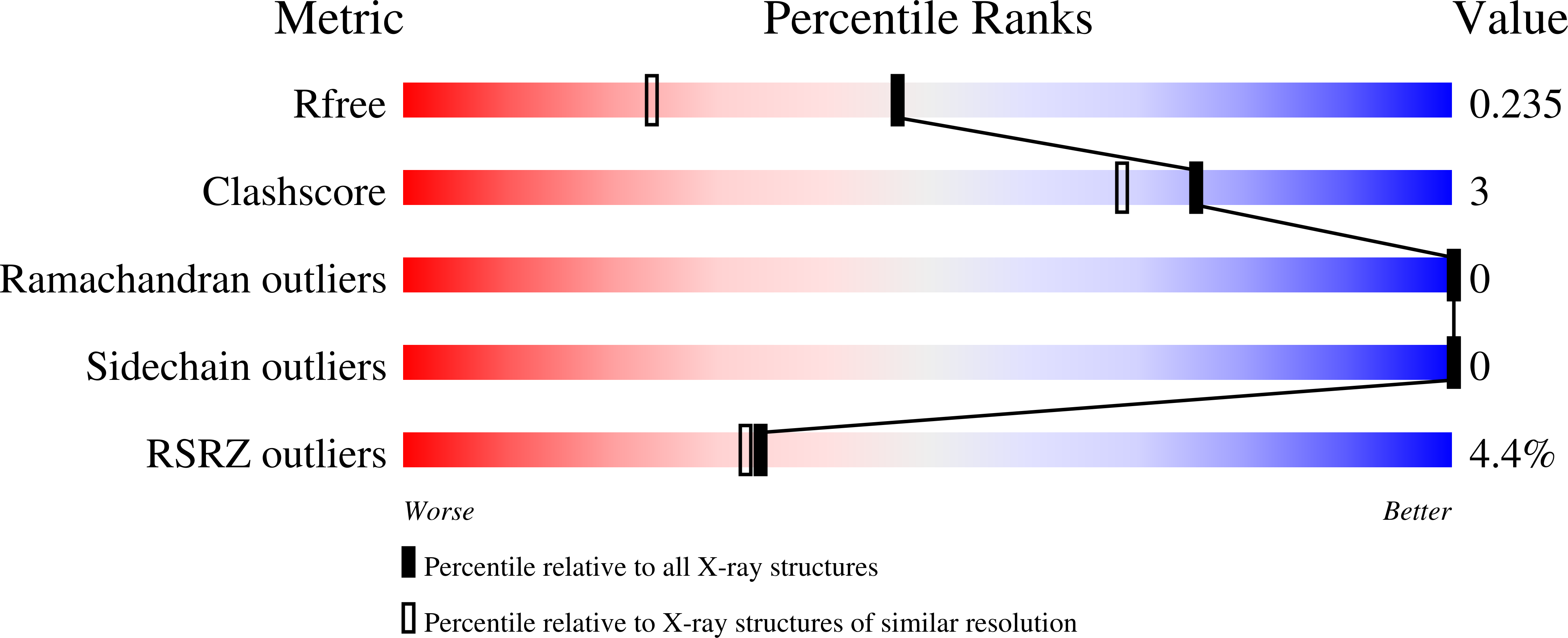
Carbohydrate binding domain CBM92-B from a multi-catalytic glucanase-chitinase from Chitinophaga pinensis DSM 2588 in complex with glucose
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Chitinophaga pinensis DSM 2588 (Taxon ID: 485918)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
1.77 Å
R-Value Free:
0.23
R-Value Work:
0.19
R-Value Observed:
0.20
Space Group:
C 1 2 1