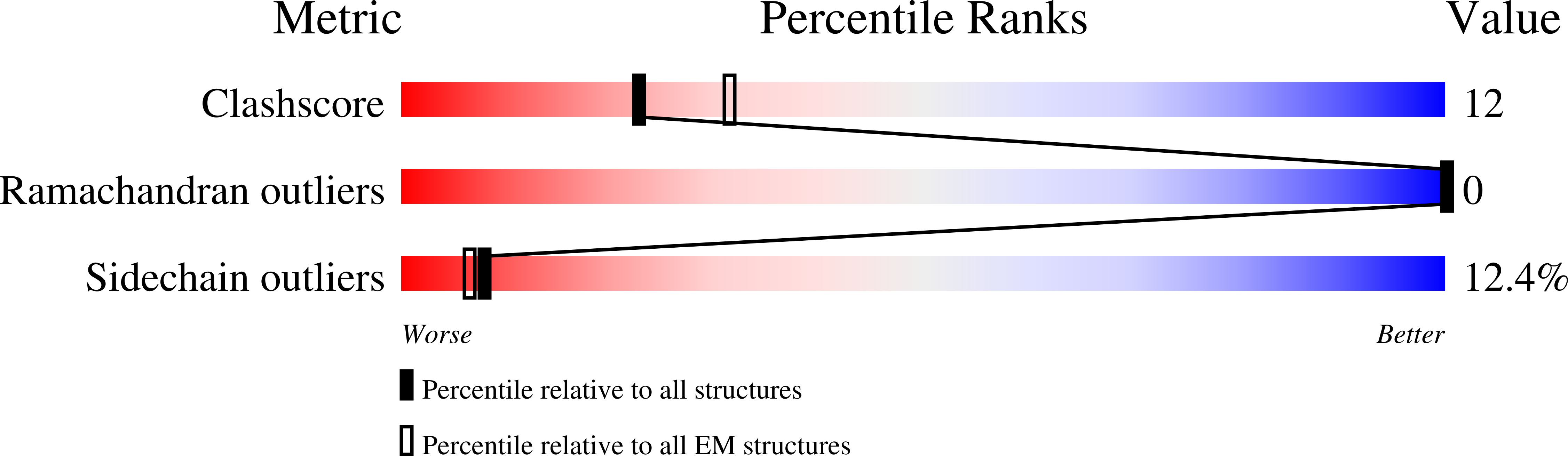
Deposition Date
2022-02-18
Release Date
2023-01-25
Last Version Date
2025-10-01
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
7YYO
Keywords:
Title:
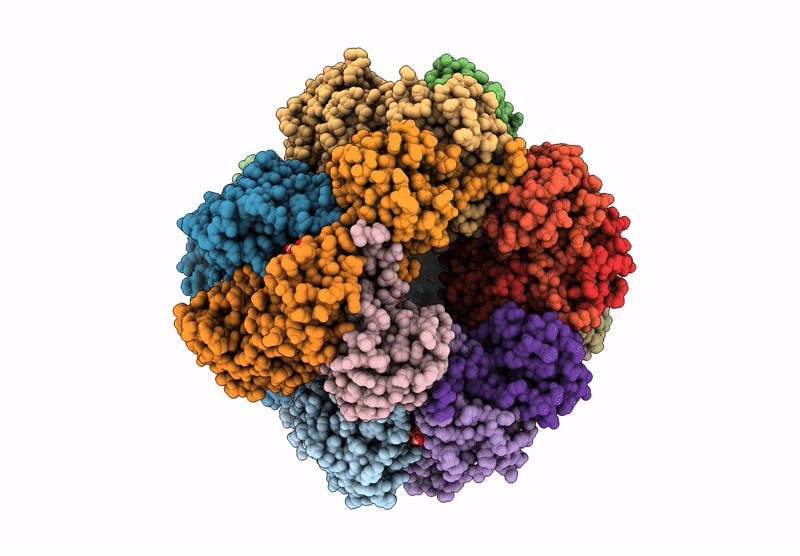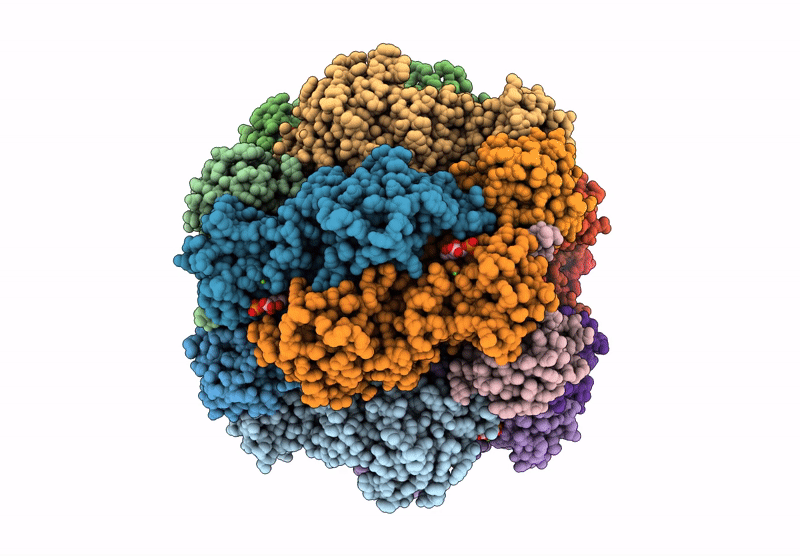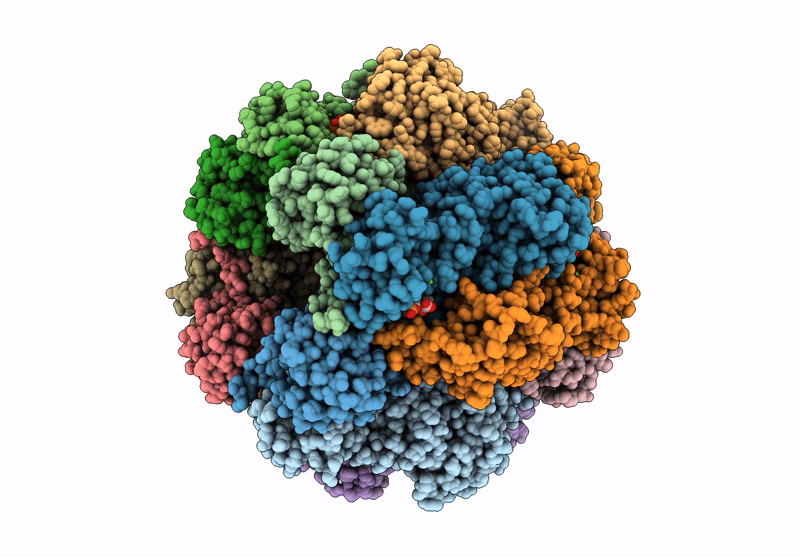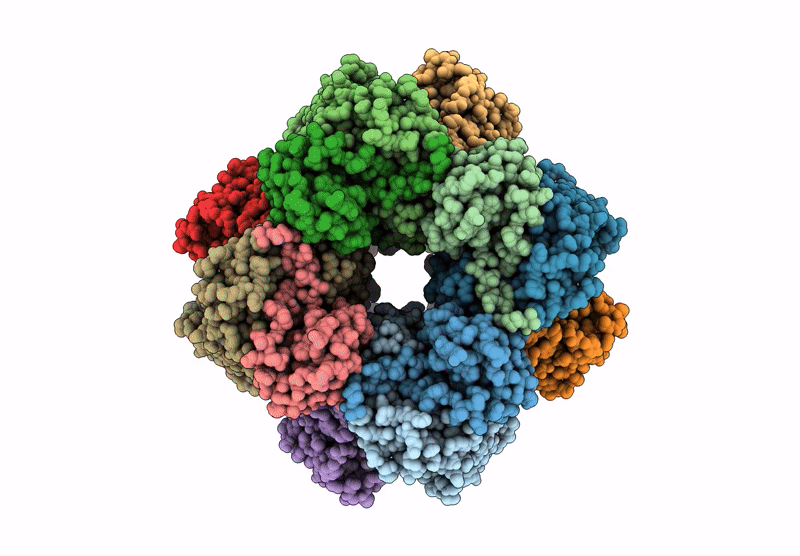
Cryo-EM structure of an a-carboxysome RuBisCO enzyme at 2.9 A resolution
Biological Source:
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
2.87 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE