Deposition Date
2022-02-14
Release Date
2022-11-16
Last Version Date
2024-11-06
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
7YWV
Keywords:
Title:
Eugenol oxidase from rhodococcus jostii: mutant S81H, D151E, A423M, H434Y, S394V, Q425S, I445D, S518P
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Rhodococcus jostii RHA1 (Taxon ID: 101510)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
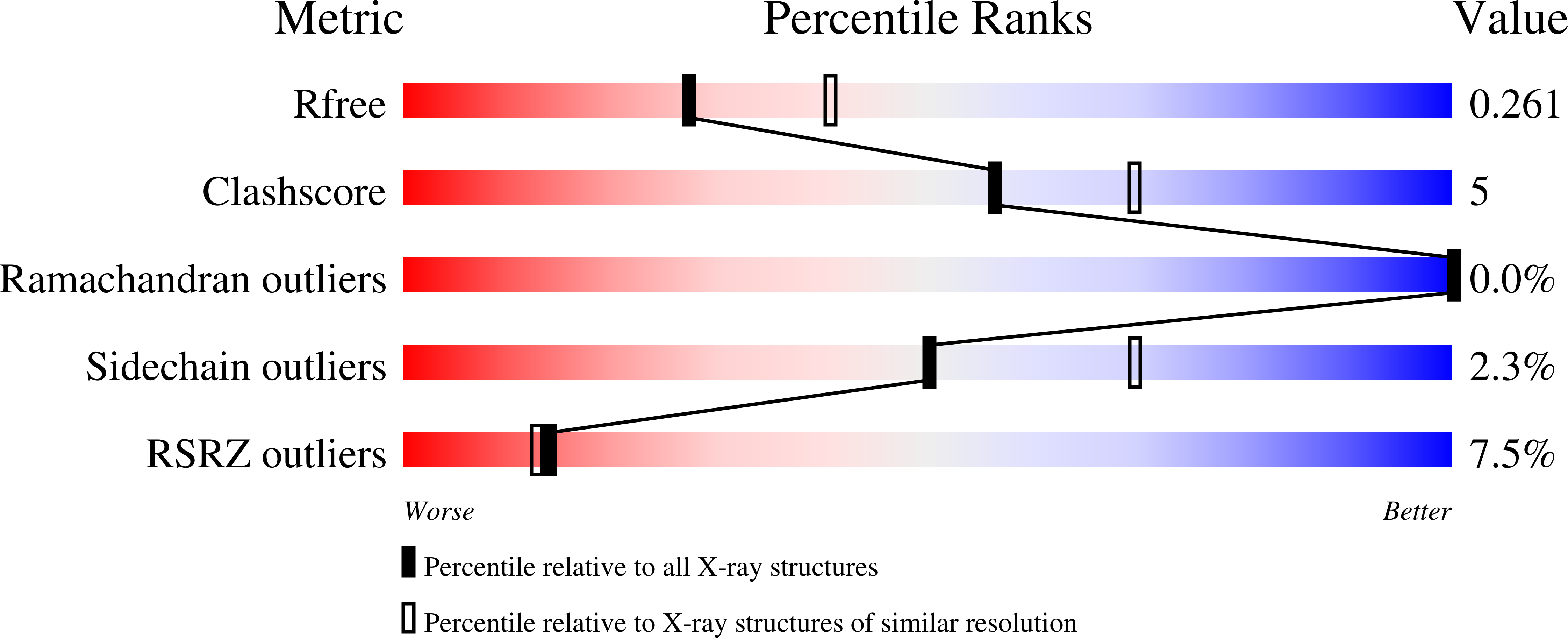
Resolution:
2.40 Å
R-Value Free:
0.26
R-Value Work:
0.22
R-Value Observed:
0.22
Space Group:
I 1 2 1