Deposition Date
2022-07-04
Release Date
2023-11-22
Last Version Date
2024-03-13
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
7YD8
Keywords:
Title:
TR-SFX MmCPDII-DNA complex: 2 ns snapshot. Includes 2 ns, dark, and extrapolated structure factors
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Methanosarcina mazei (Taxon ID: 192952)
synthetic construct (Taxon ID: 32630)
synthetic construct (Taxon ID: 32630)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
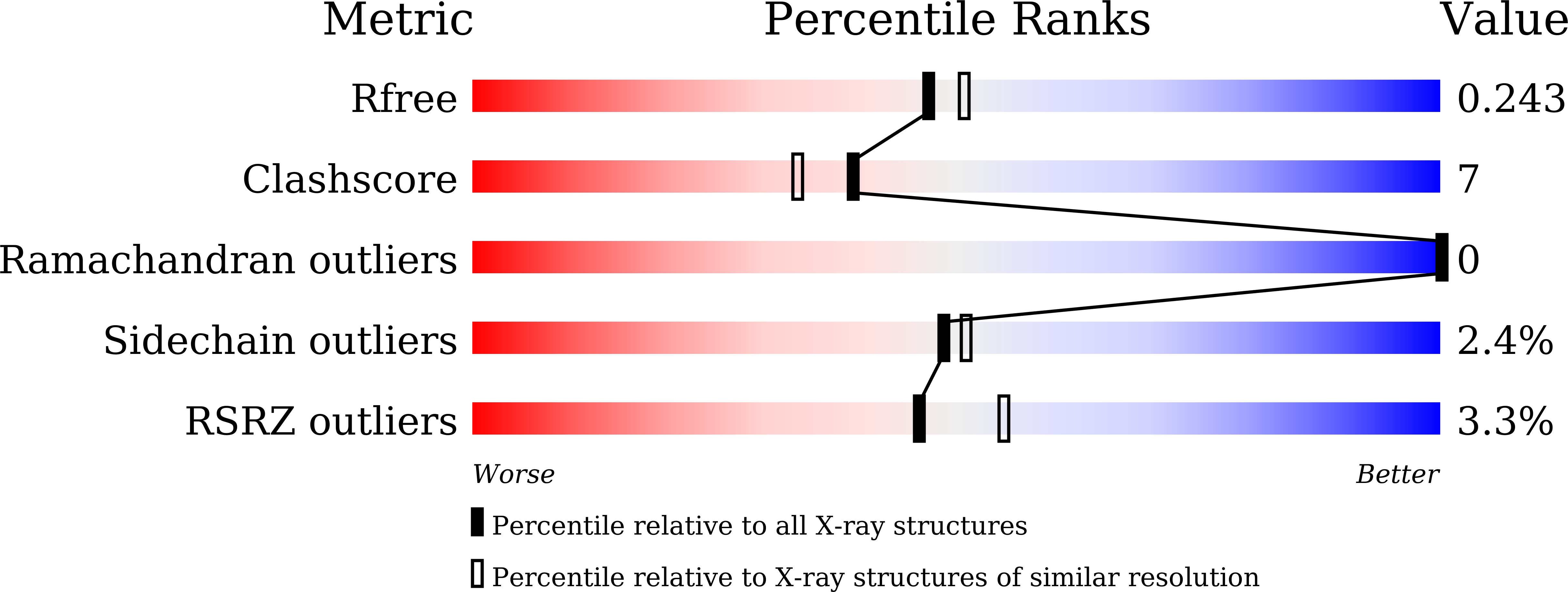
Resolution:
2.15 Å
R-Value Free:
0.24
R-Value Work:
0.23
R-Value Observed:
0.23
Space Group:
P 21 21 21