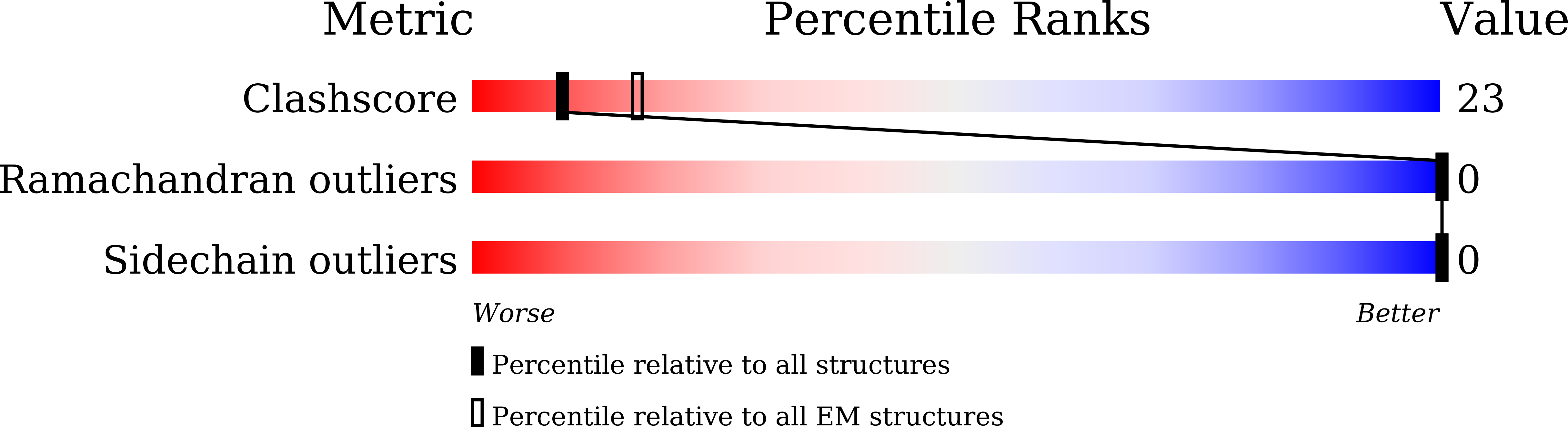
Deposition Date
2022-02-09
Release Date
2022-04-27
Last Version Date
2025-06-25
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
7WUQ
Keywords:
Title:
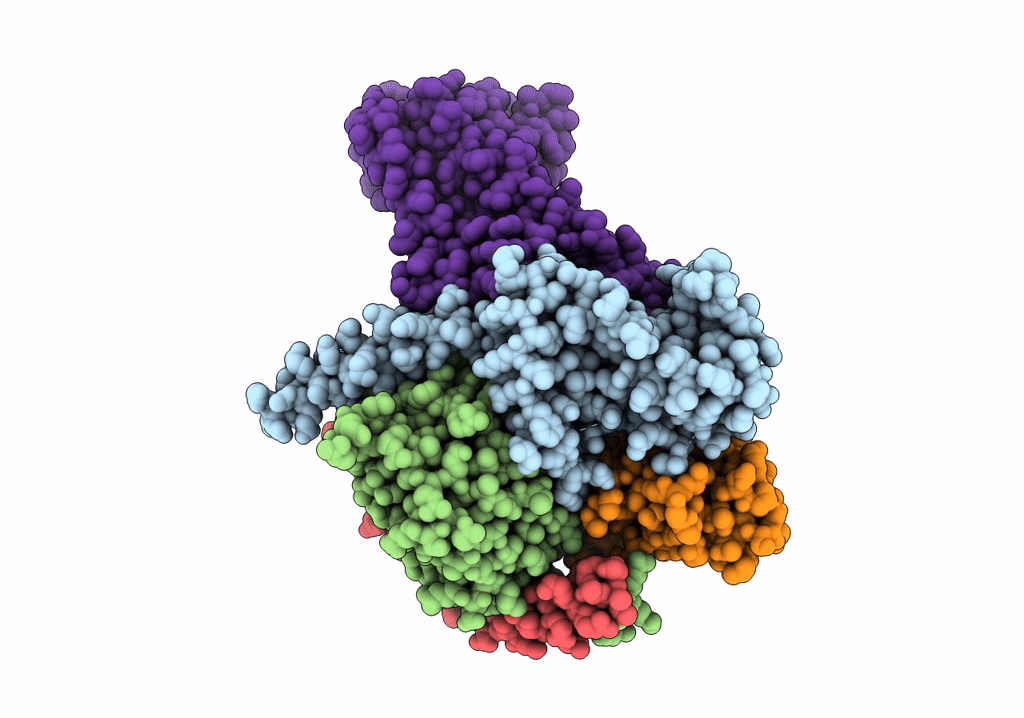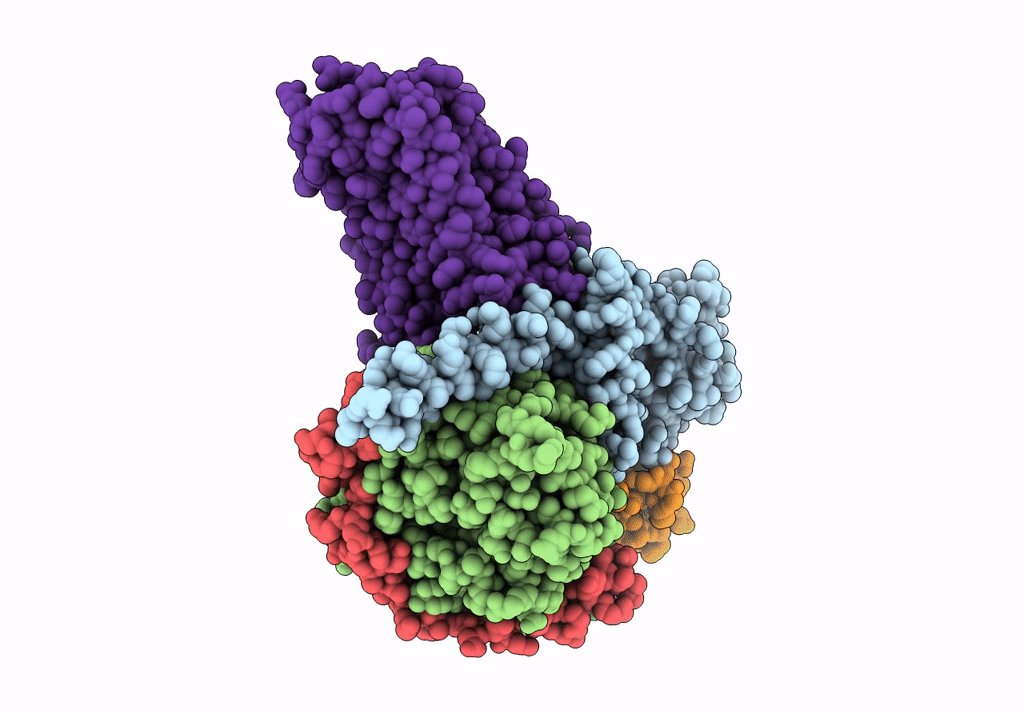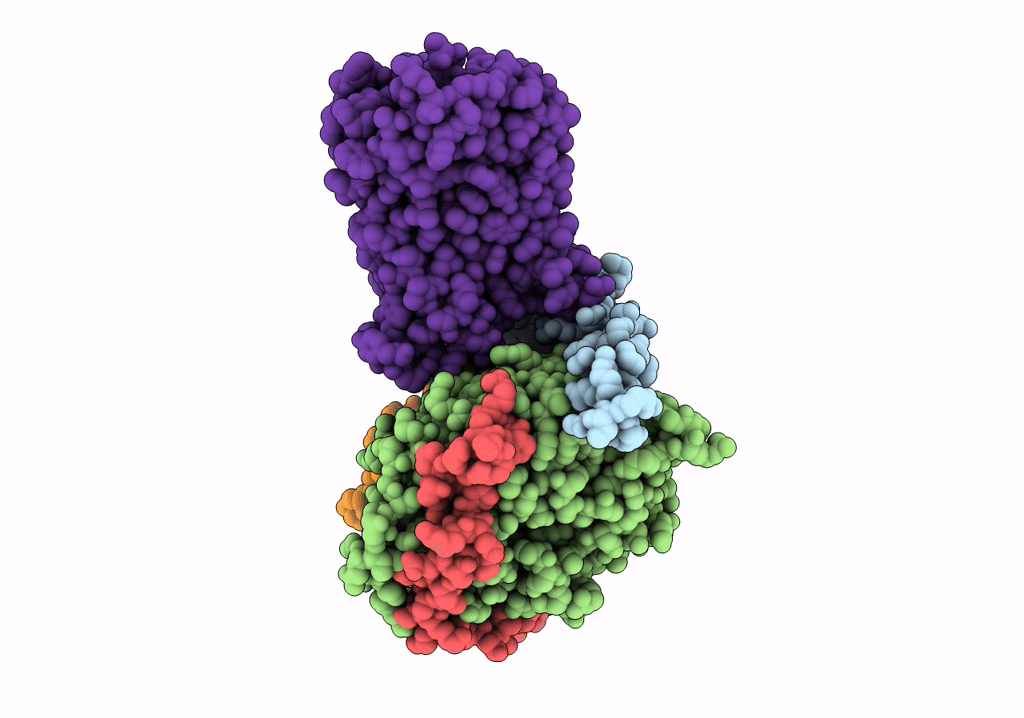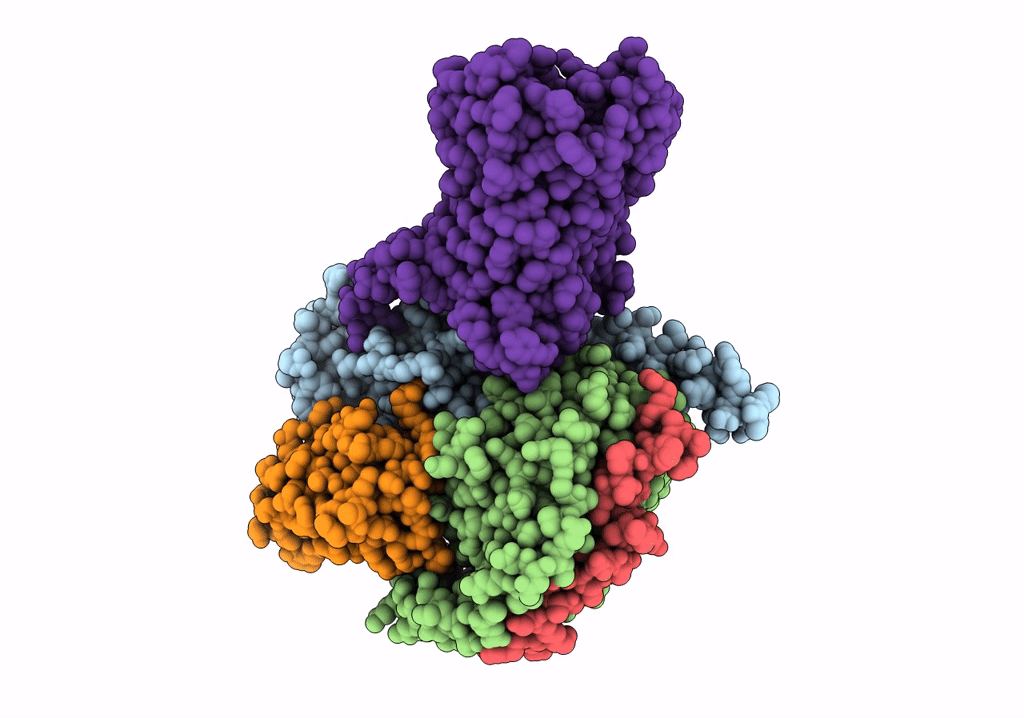
Tethered peptide activation mechanism of adhesion GPCRs ADGRG2 and ADGRG4
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Homo sapiens (Taxon ID: 9606)
Lama glama (Taxon ID: 9844)
Mus musculus (Taxon ID: 10090)
Lama glama (Taxon ID: 9844)
Mus musculus (Taxon ID: 10090)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
2.90 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE