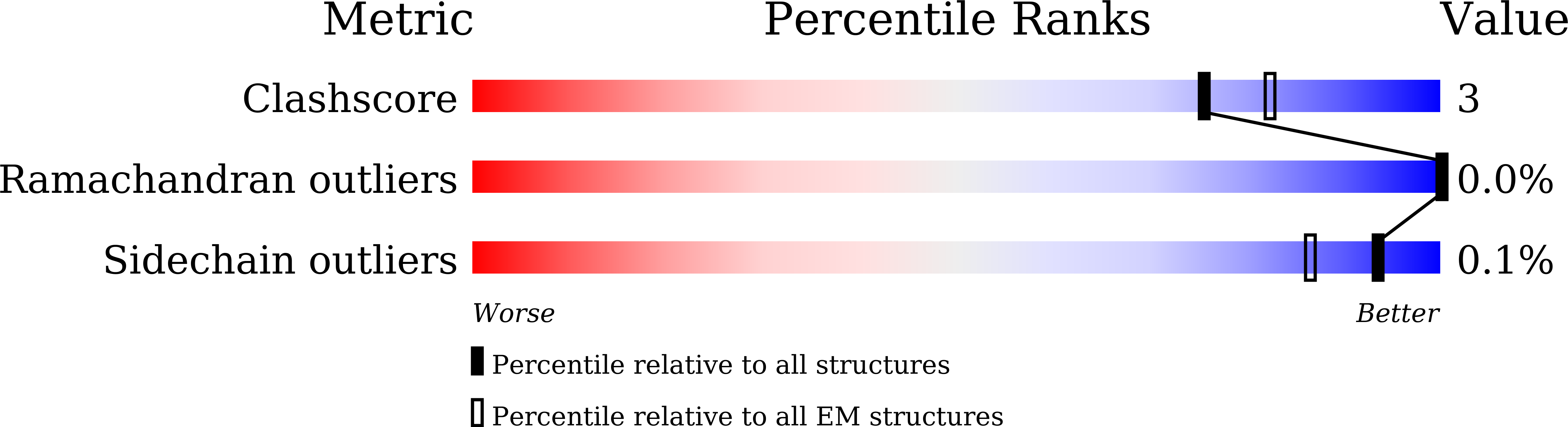
Deposition Date
2022-02-08
Release Date
2022-06-08
Last Version Date
2024-06-26
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
7WUG
Keywords:
Title:
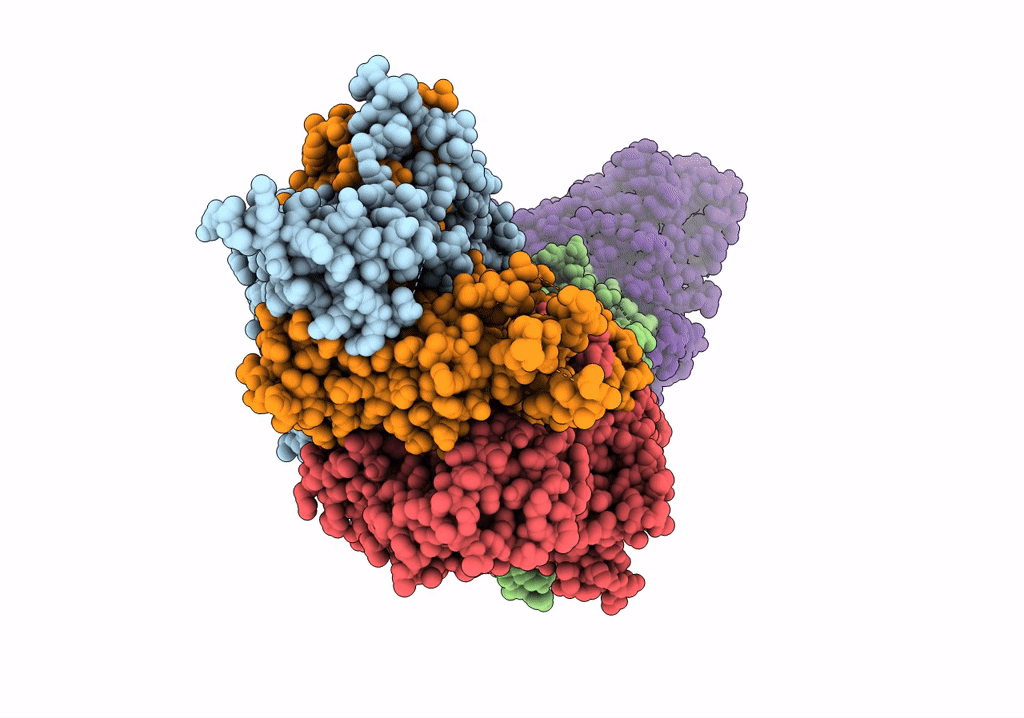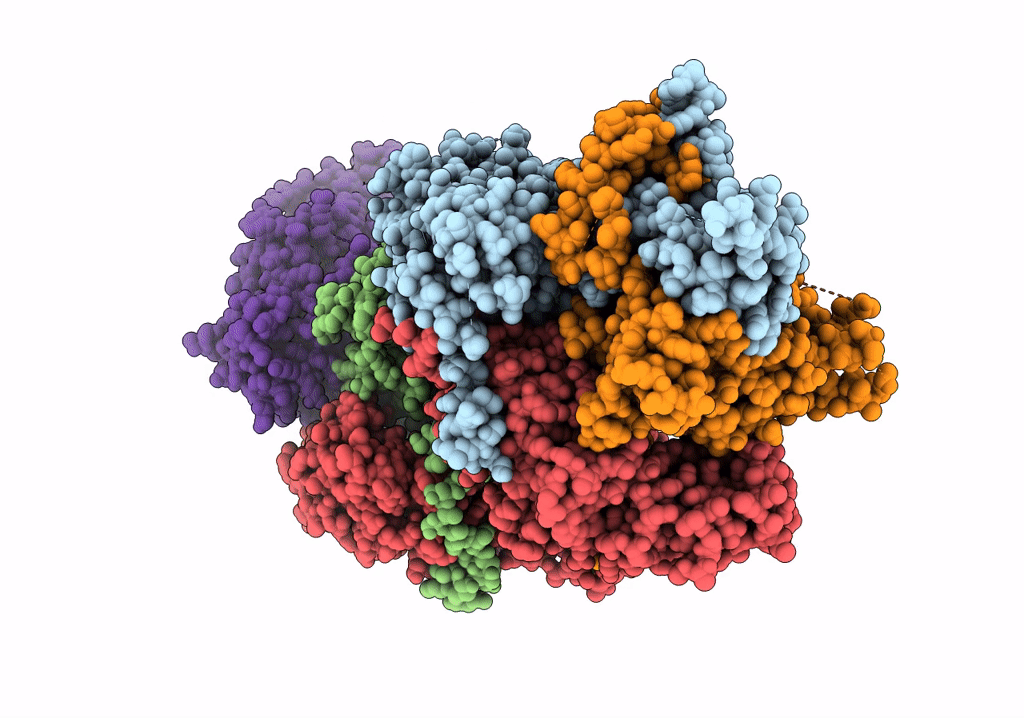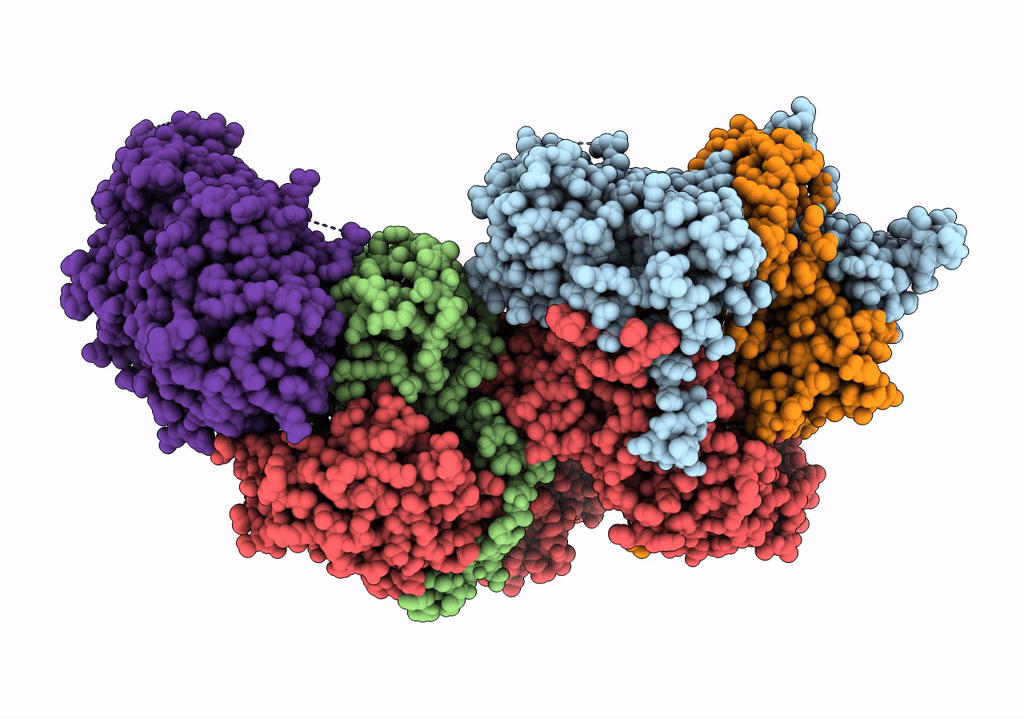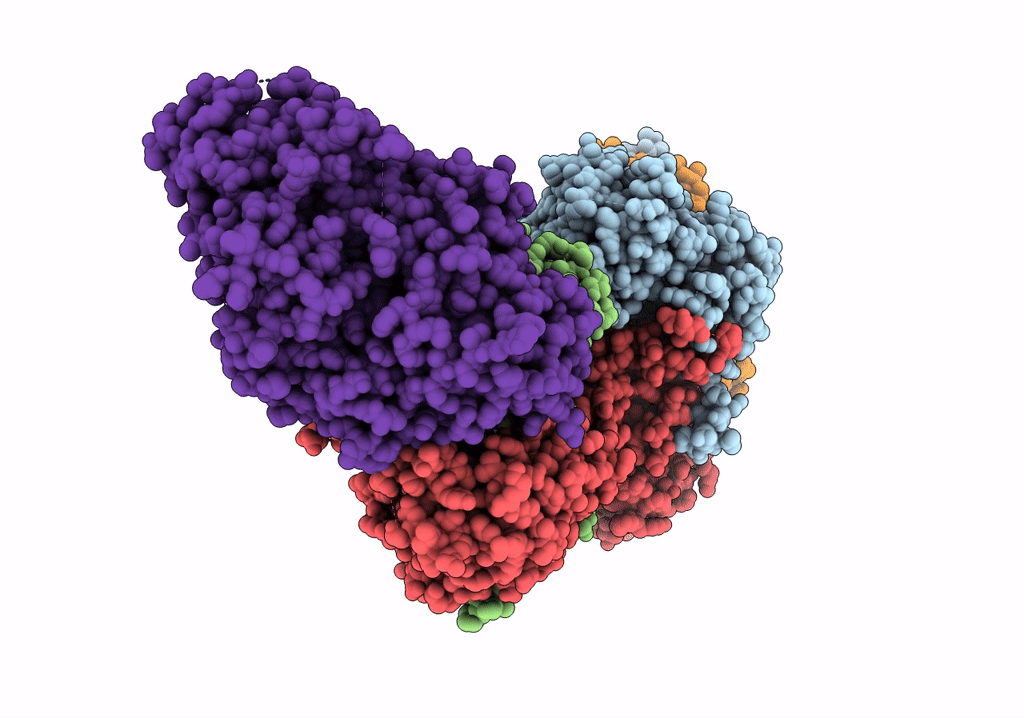
GID subcomplex: Gid12 bound Substrate Receptor Scaffolding module
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Saccharomyces cerevisiae YJM1133 (Taxon ID: 1294333)
Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Taxon ID: 4932)
Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Taxon ID: 4932)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
3.30 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE