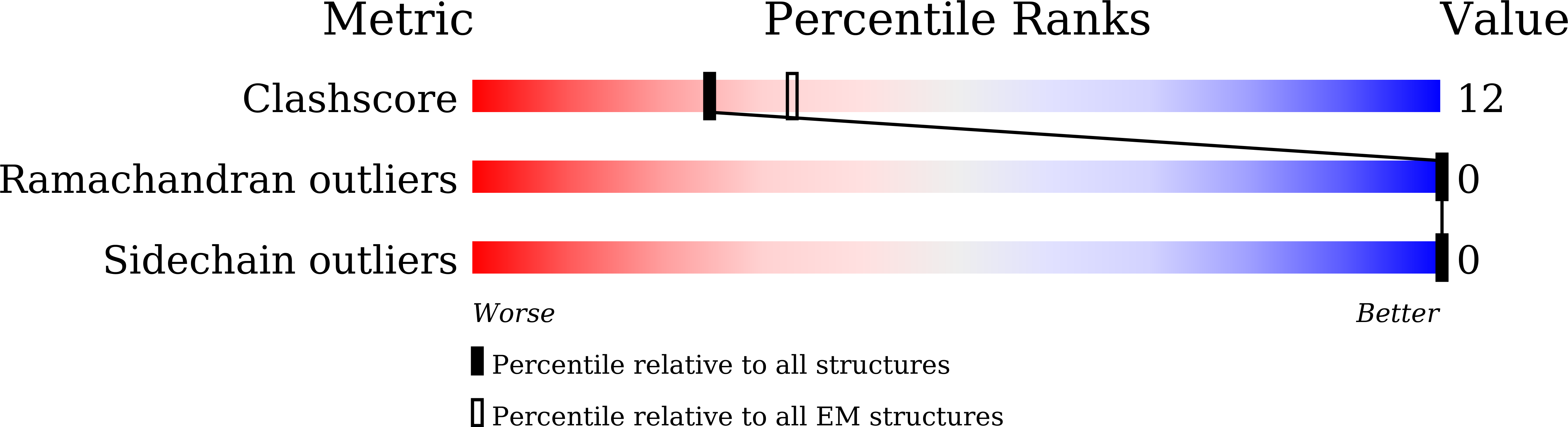Deposition Date
2022-01-28
Release Date
2022-06-01
Last Version Date
2025-06-25
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
7WS6
Keywords:
Title:
Structures of Omicron Spike complexes illuminate broad-spectrum neutralizing antibody development
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (Taxon ID: 2697049)
Homo sapiens (Taxon ID: 9606)
Homo sapiens (Taxon ID: 9606)
Host Organism:
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
3.80 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE