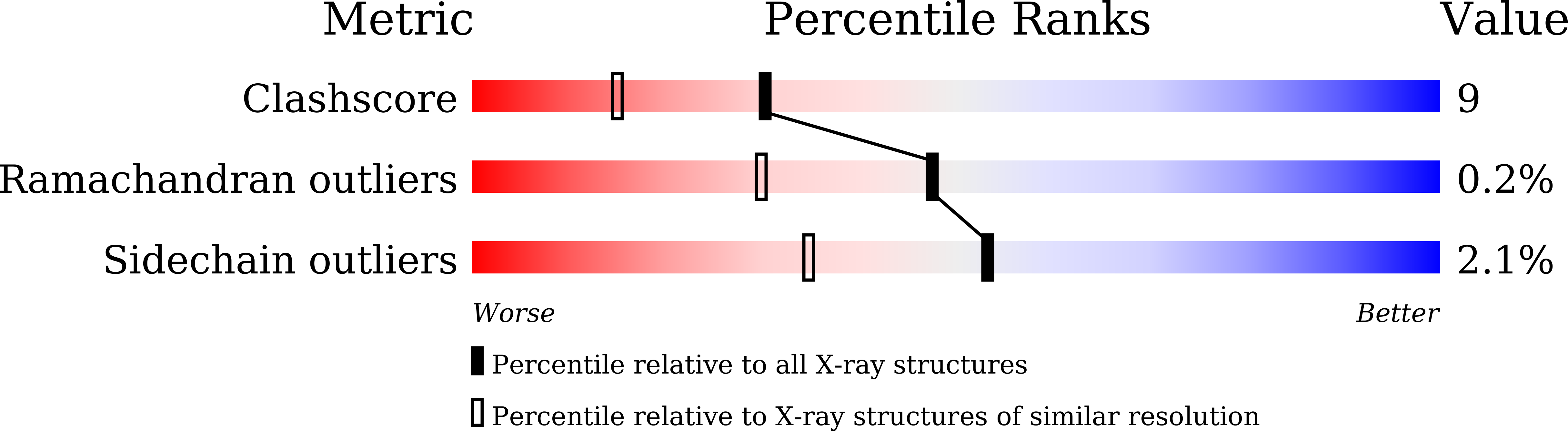Deposition Date
2022-01-19
Release Date
2022-04-20
Last Version Date
2022-05-25
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
7WNO
Keywords:
Title:
Crystallographic structure of copper amine oxidase from Arthrobacter glibiformis at pD 7.4 determined by only neutron diffraction data.
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Arthrobacter globiformis (Taxon ID: 1665)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
1.72 Å
R-Value Free:
0.25
R-Value Work:
0.16
R-Value Observed:
0.16
Space Group:
C 1 2 1