Deposition Date
2022-01-13
Release Date
2022-11-16
Last Version Date
2023-11-29
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
7WLP
Keywords:
Title:
Epstein-Barr virus protein BKRF4 restricts nucleosome assembly to suppress host antiviral responses
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Homo sapiens (Taxon ID: 9606)
Human gammaherpesvirus 4 (Taxon ID: 10376)
Human gammaherpesvirus 4 (Taxon ID: 10376)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
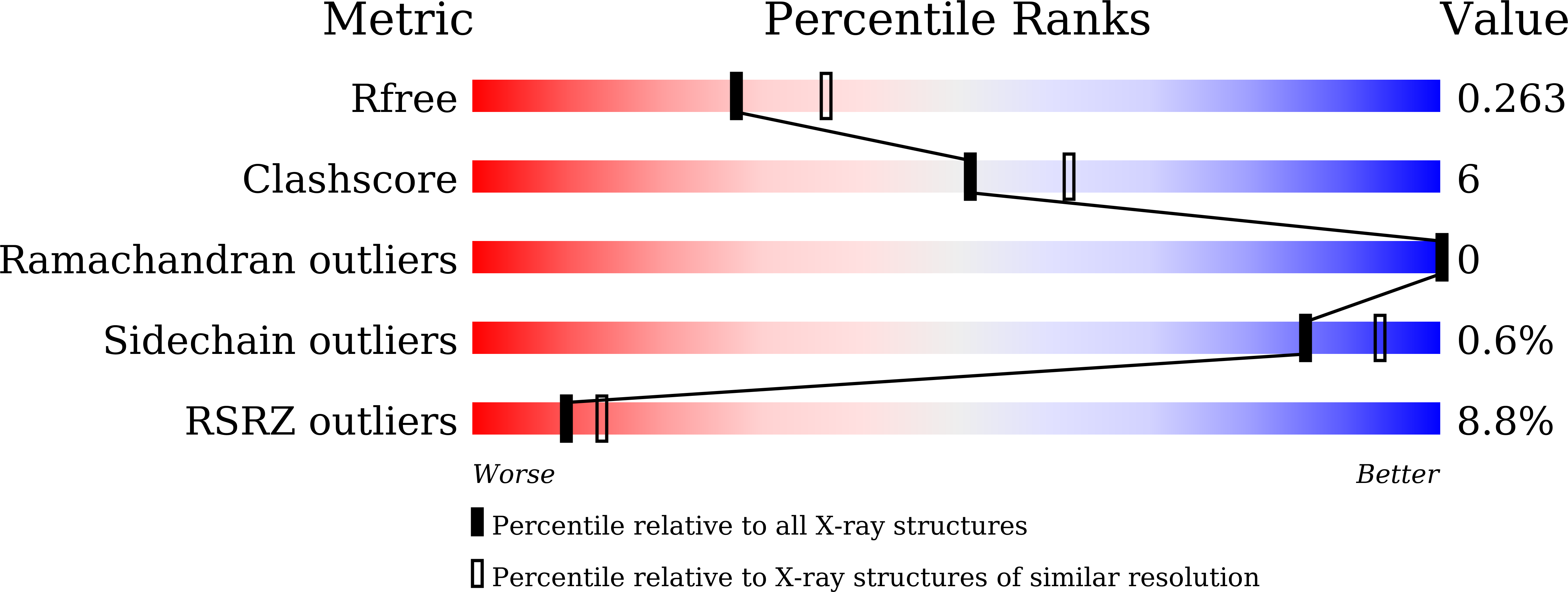
Resolution:
2.29 Å
R-Value Free:
0.24
R-Value Work:
0.22
R-Value Observed:
0.22
Space Group:
P 63 2 2