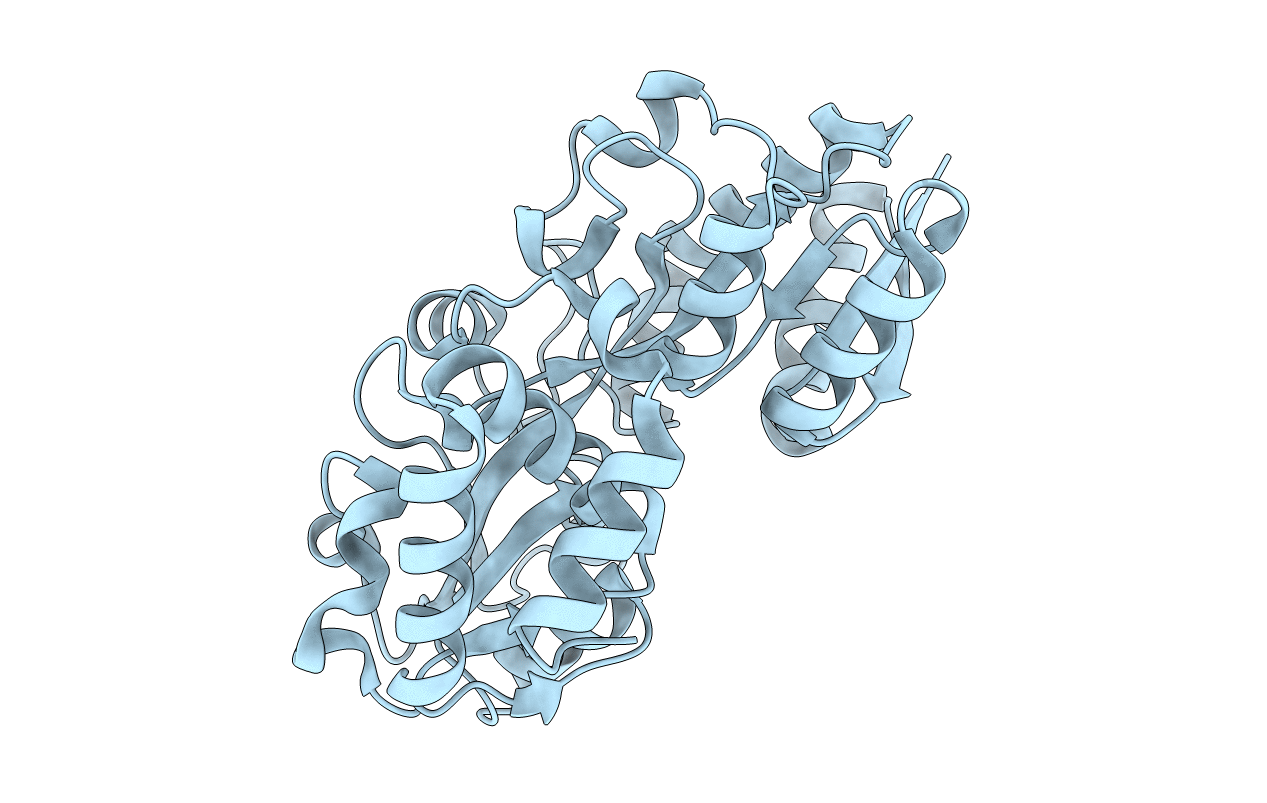
Deposition Date
2021-11-26
Release Date
2021-12-15
Last Version Date
2023-11-29
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
7W3W
Keywords:
Title:
X-ray structure of apo-VmFbpA, a ferric ion-binding protein from Vibrio metschnikovii
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
Vibrio metschnikovii (Taxon ID: 28172)
Host Organism:
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
1.86 Å
R-Value Free:
0.20
R-Value Work:
0.18
Space Group:
P 63 2 2


