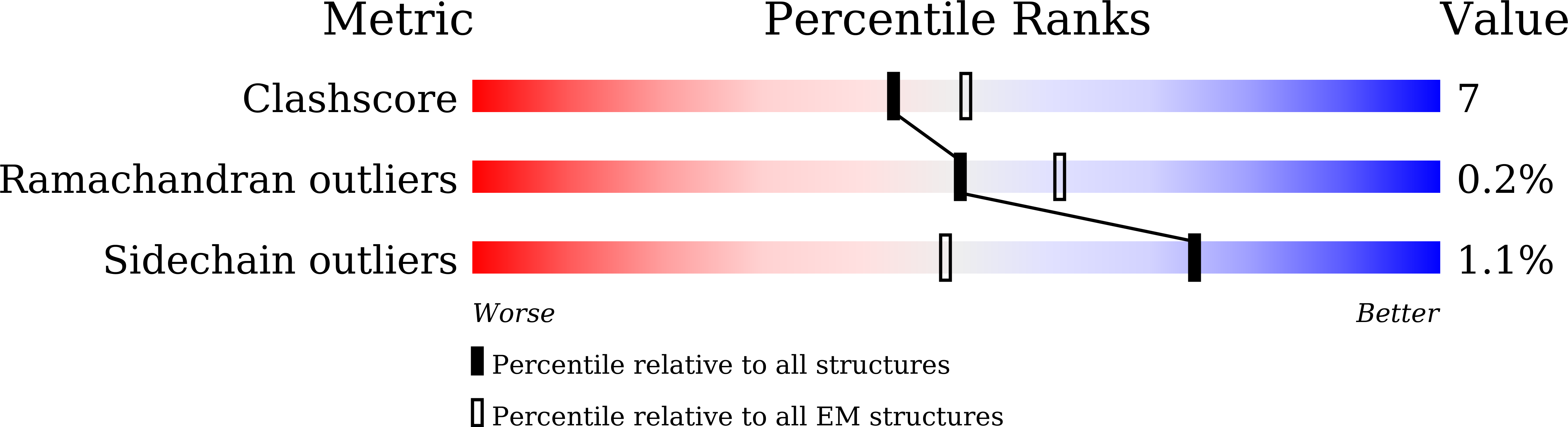Deposition Date
2021-09-18
Release Date
2021-09-29
Last Version Date
2024-10-30
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
7VGQ
Keywords:
Title:
Cryo-EM structure of Machupo virus polymerase L in complex with matrix protein Z
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Machupo virus (Taxon ID: 11628)
Escherichia coli (strain K12) (Taxon ID: 83333)
Escherichia coli (strain K12) (Taxon ID: 83333)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
4.00 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE