Deposition Date
2022-04-10
Release Date
2022-10-19
Last Version Date
2024-10-23
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
7UNC
Keywords:
Title:
Pol II-DSIF-SPT6-PAF1c-TFIIS complex with rewrapped nucleosome
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Homo sapiens (Taxon ID: 9606)
Xenopus laevis (Taxon ID: 8355)
synthetic construct (Taxon ID: 32630)
Sus scrofa (Taxon ID: 9823)
Xenopus laevis (Taxon ID: 8355)
synthetic construct (Taxon ID: 32630)
Sus scrofa (Taxon ID: 9823)
Expression System(s):
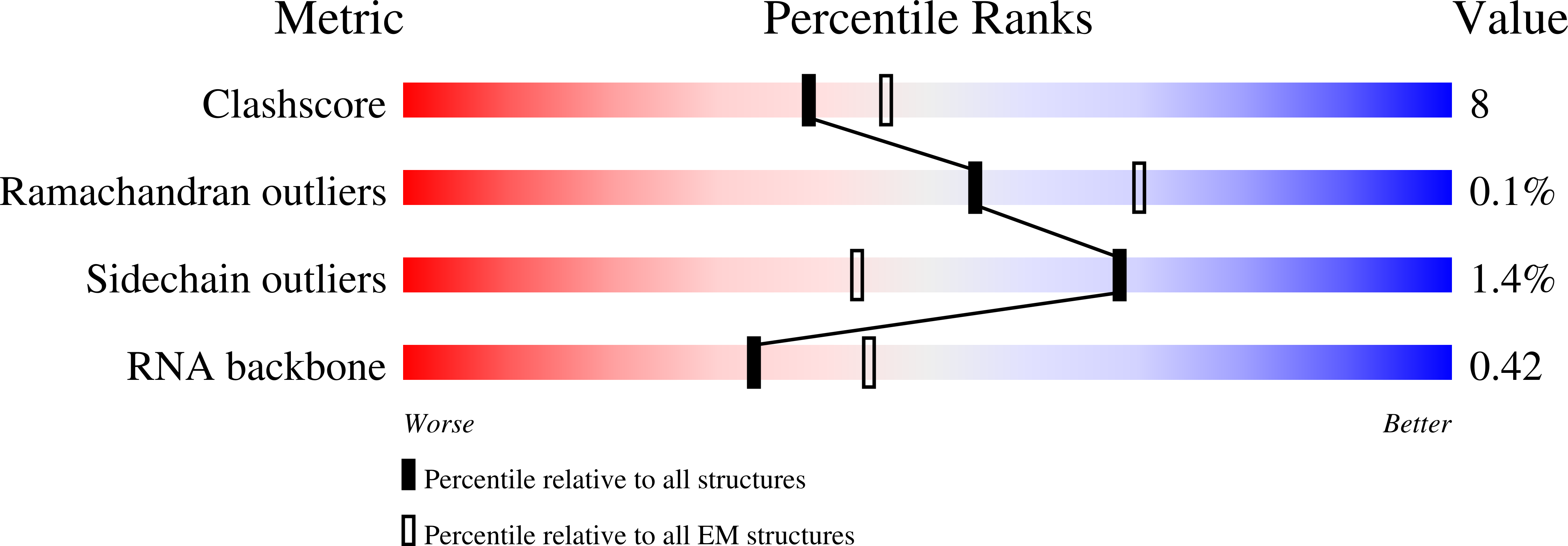
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
3.00 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE