Deposition Date
2022-02-20
Release Date
2022-03-23
Last Version Date
2025-05-14
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
7U18
Keywords:
Title:
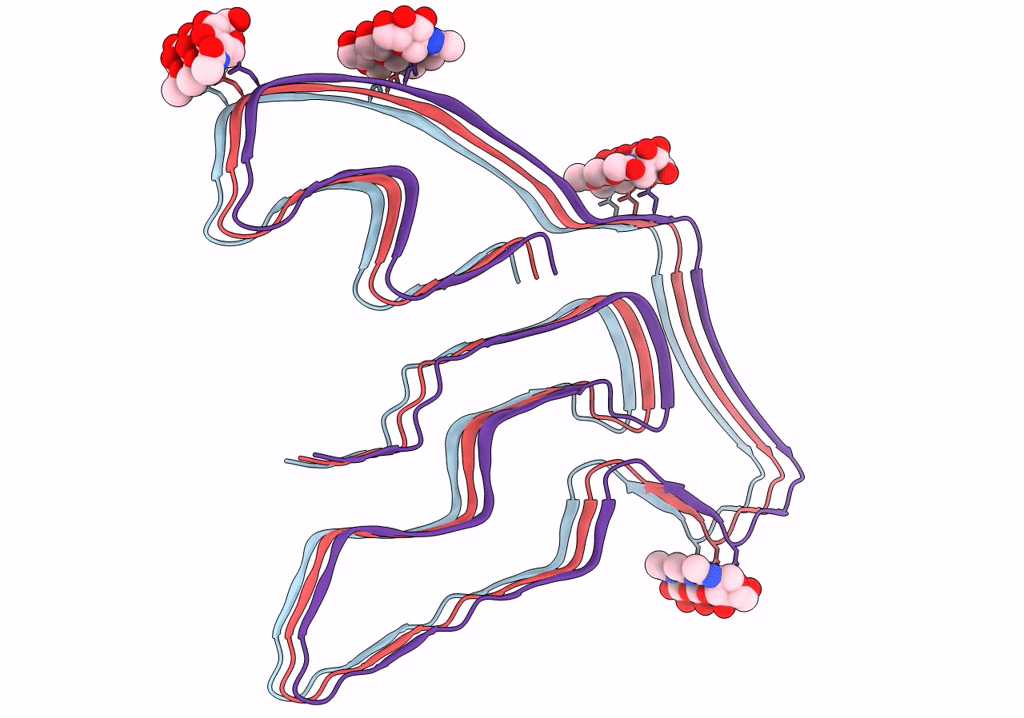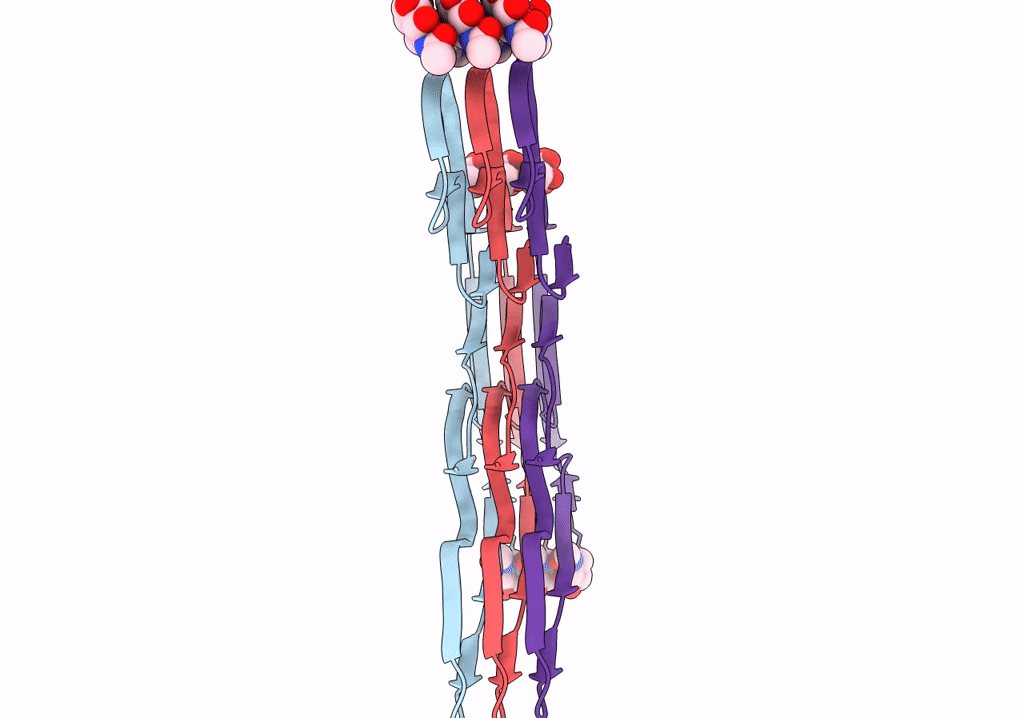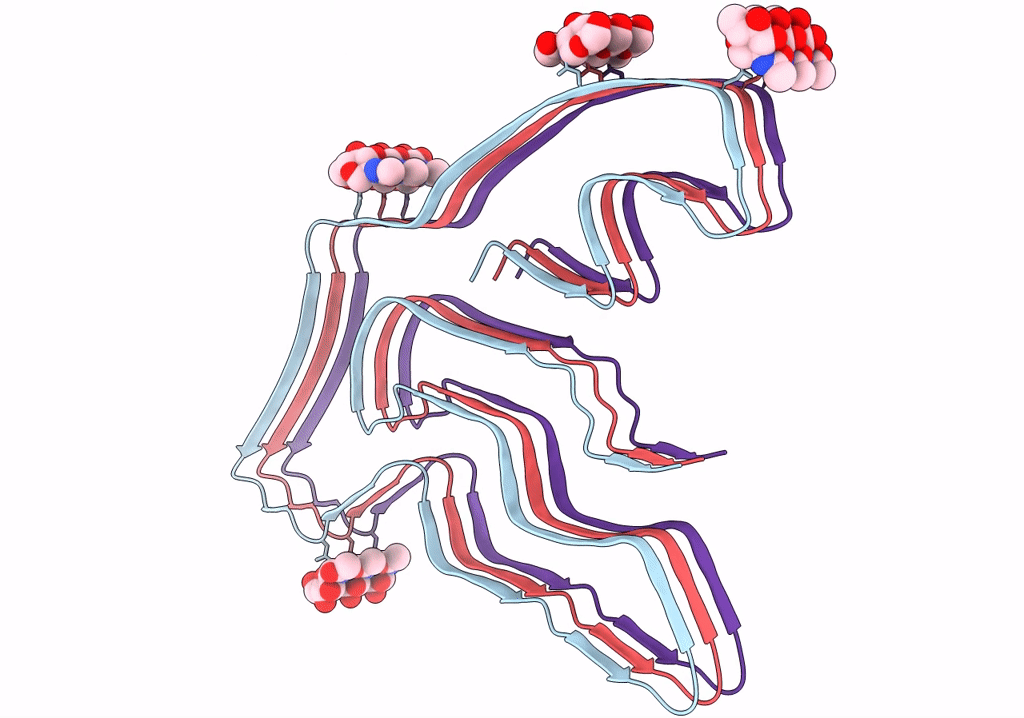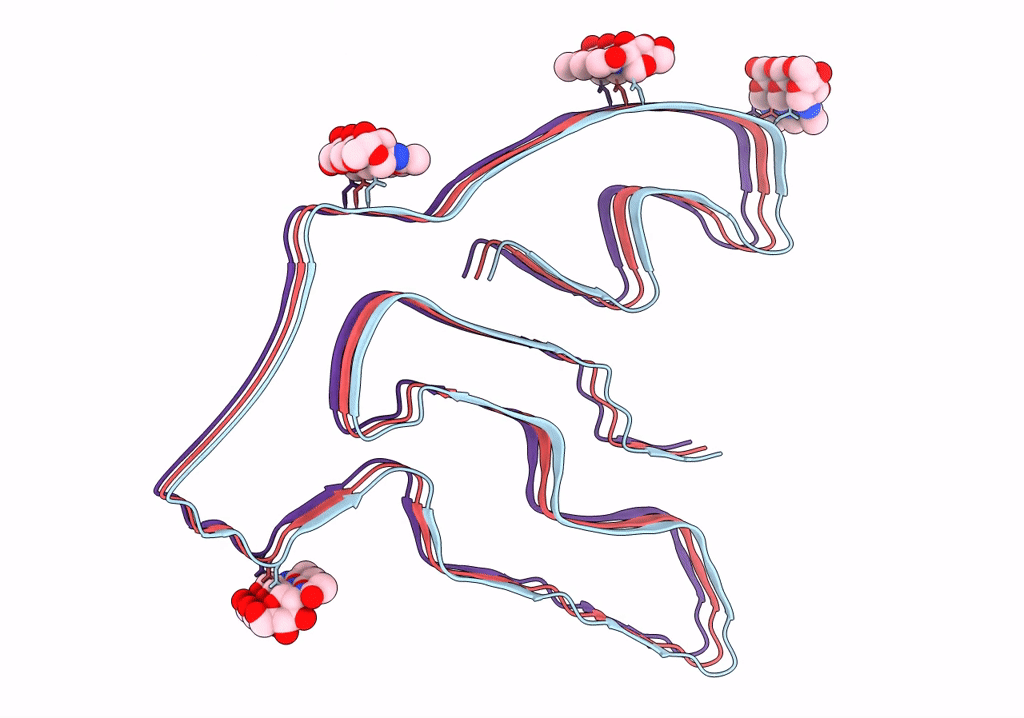
TMEM106B(120-254) T185S protofilament from frontotemporal lobar degeneration with TDP-43 pathology (FTLD-TDP) type A (all cases combined).
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Homo sapiens (Taxon ID: 9606)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
2.70 Å
Aggregation State:
FILAMENT
Reconstruction Method:
HELICAL


