Deposition Date
2022-01-27
Release Date
2022-07-20
Last Version Date
2024-02-21
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
7TR3
Keywords:
Title:
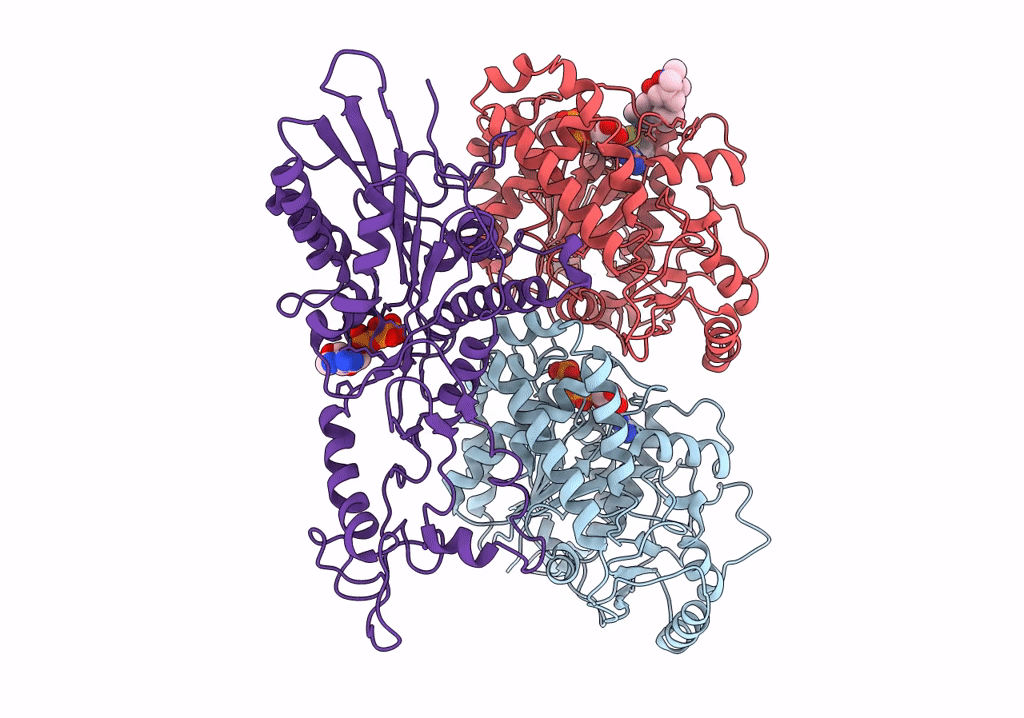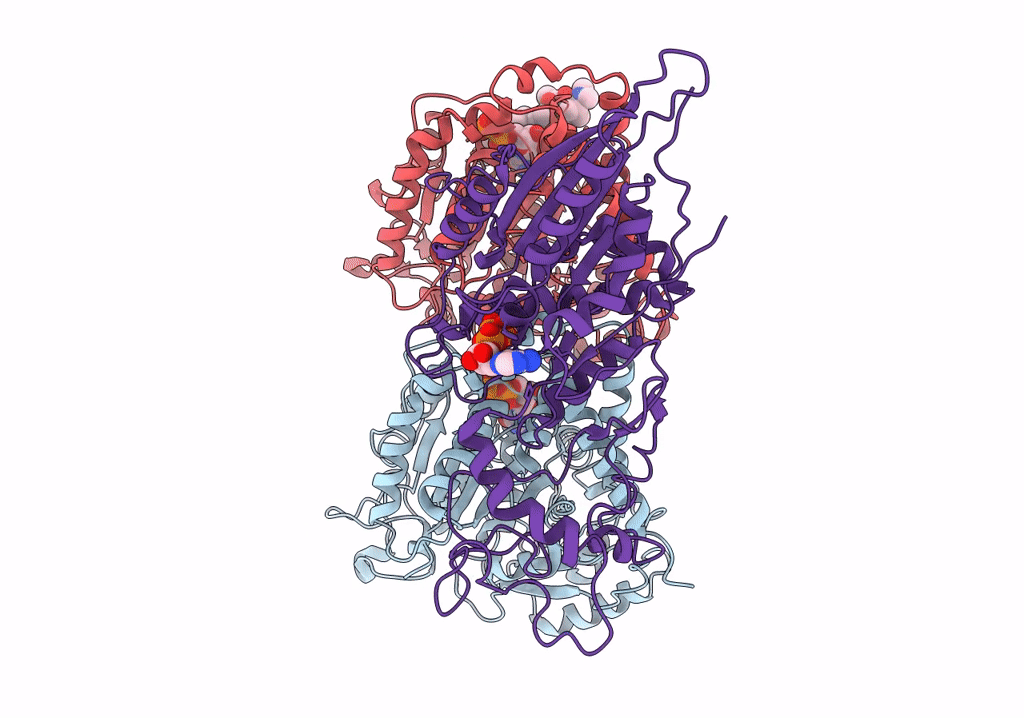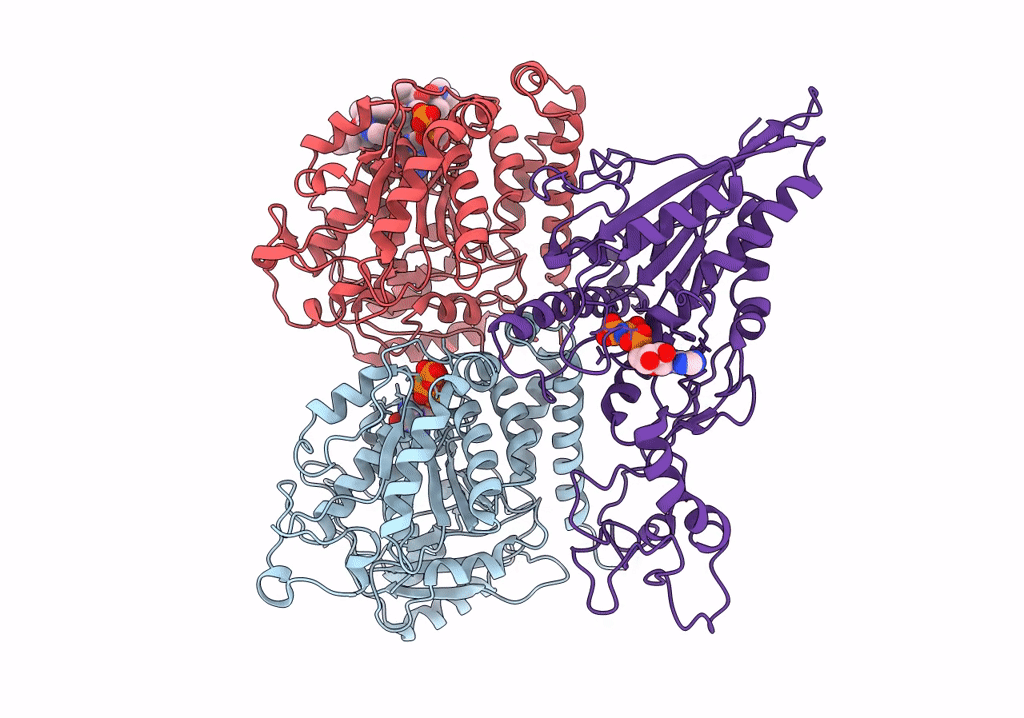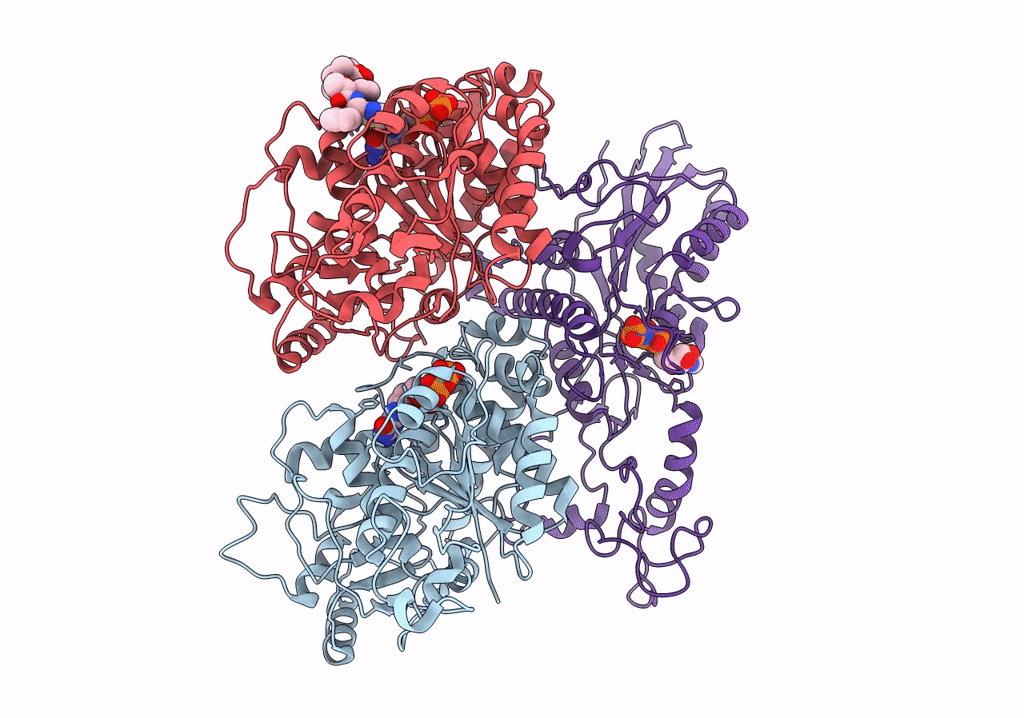
CaKip3[2-482] - AMP-PNP in complex with a dolastatin-10-stabilized tubulin ring
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Candida albicans (Taxon ID: 5476)
Sus scrofa (Taxon ID: 9823)
Sus scrofa (Taxon ID: 9823)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
3.90 Å
Aggregation State:
FILAMENT
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE


