Deposition Date
2022-01-26
Release Date
2022-05-25
Last Version Date
2022-06-08
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
7TPT
Keywords:
Title:
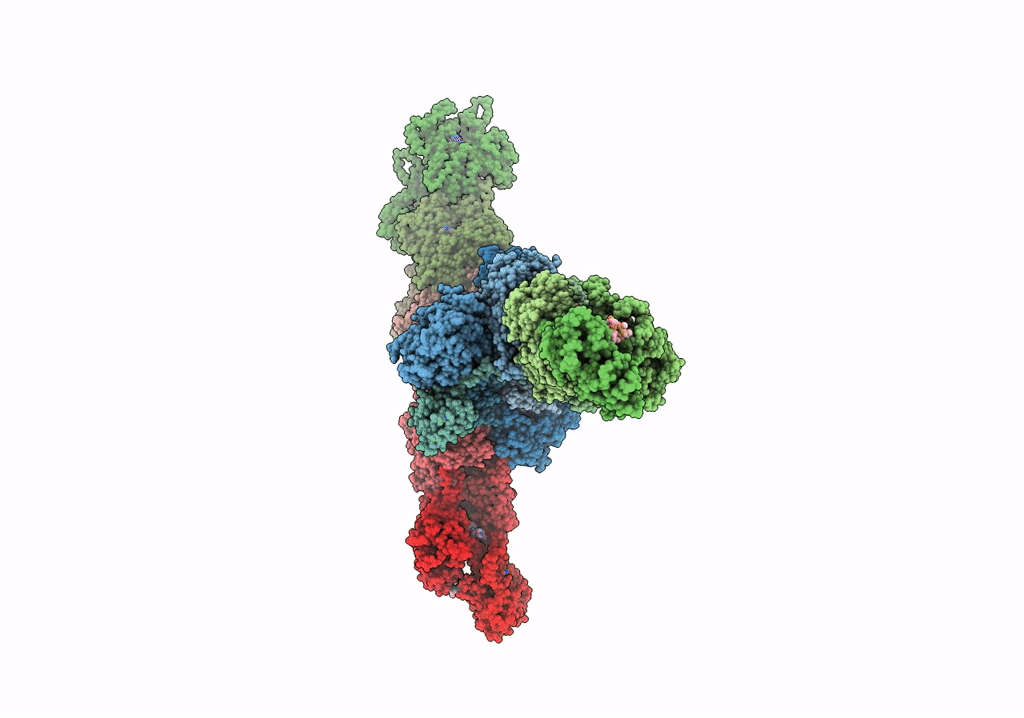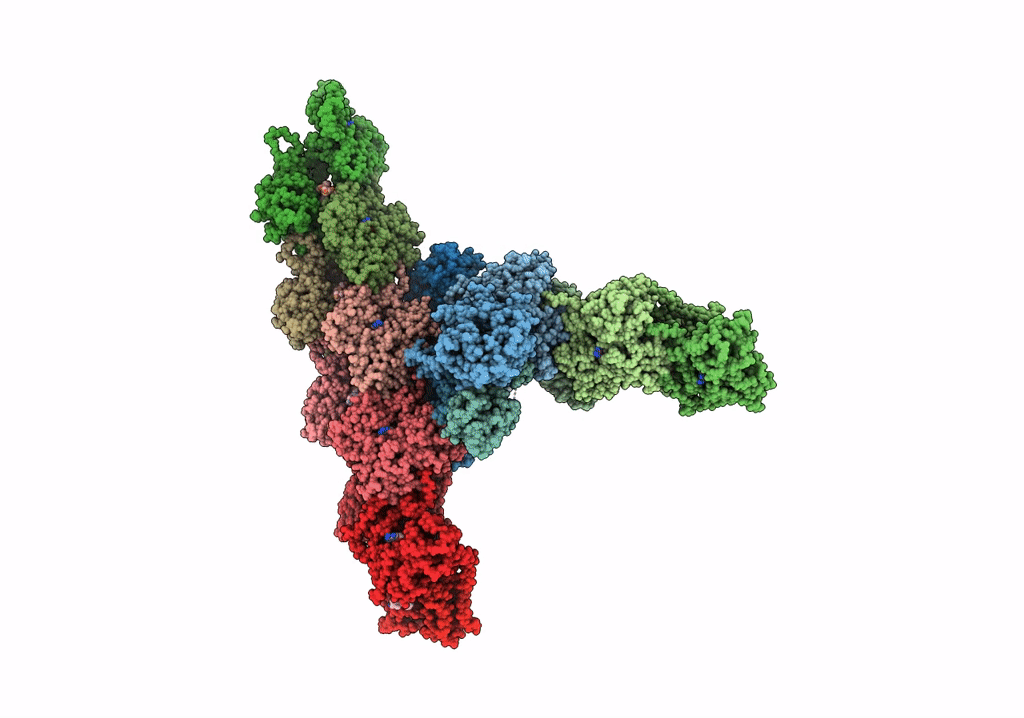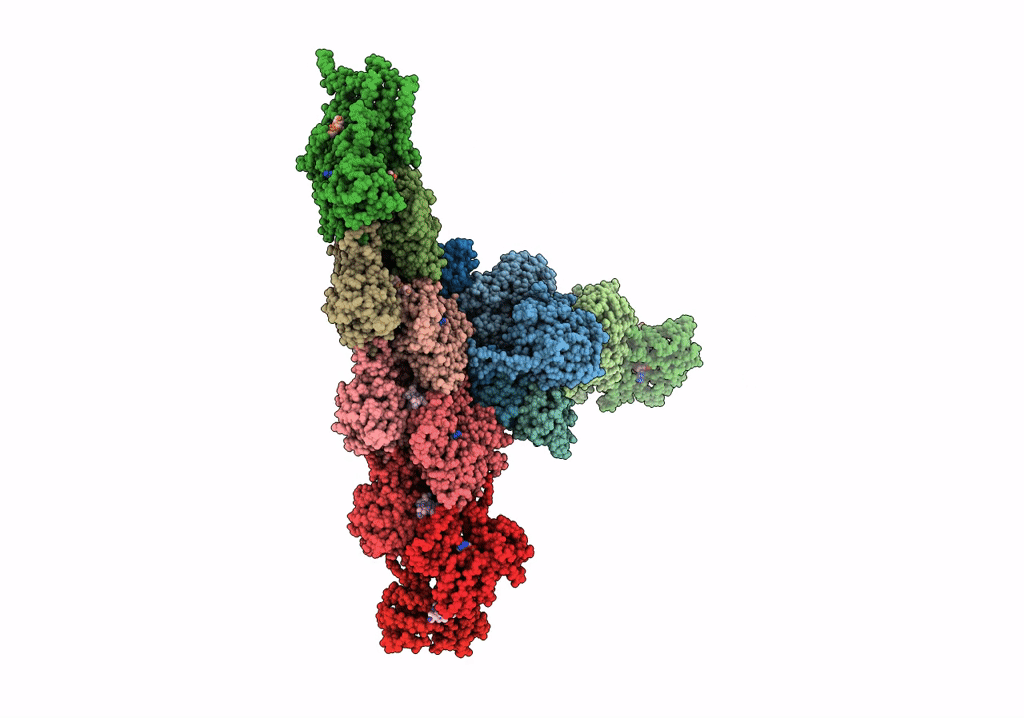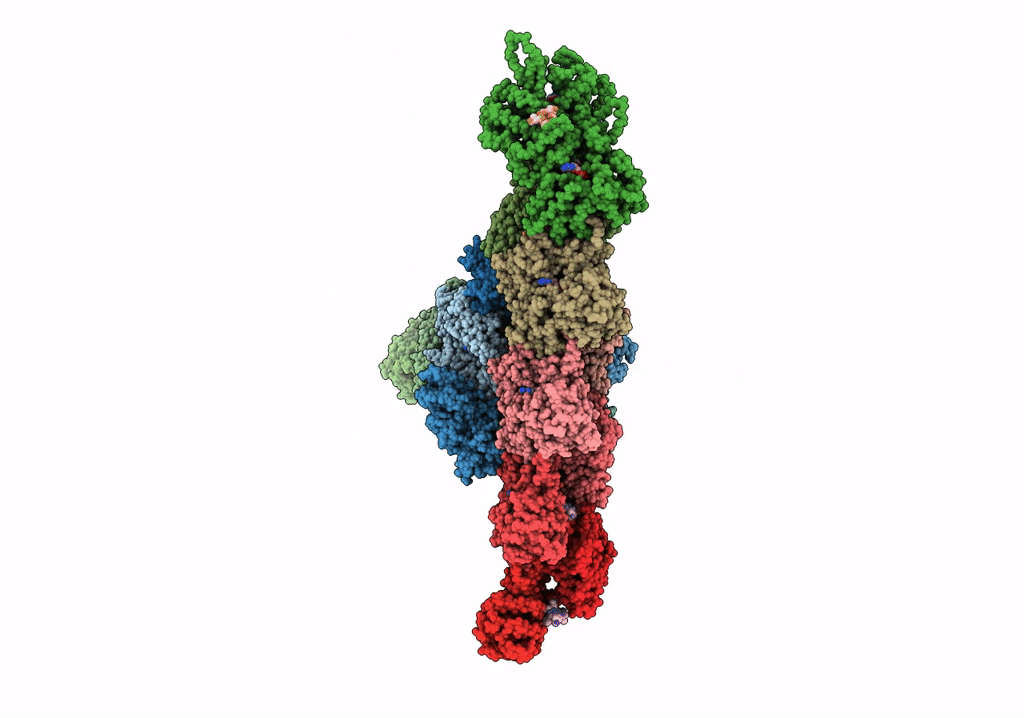
Single-particle Cryo-EM structure of Arp2/3 complex at branched-actin junction.
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Bos taurus (Taxon ID: 9913)
Oryctolagus cuniculus (Taxon ID: 9986)
Amanita phalloides (Taxon ID: 67723)
Oryctolagus cuniculus (Taxon ID: 9986)
Amanita phalloides (Taxon ID: 67723)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
3.90 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE


