Deposition Date
2021-11-25
Release Date
2022-07-27
Last Version Date
2024-11-13
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
7SYO
Keywords:
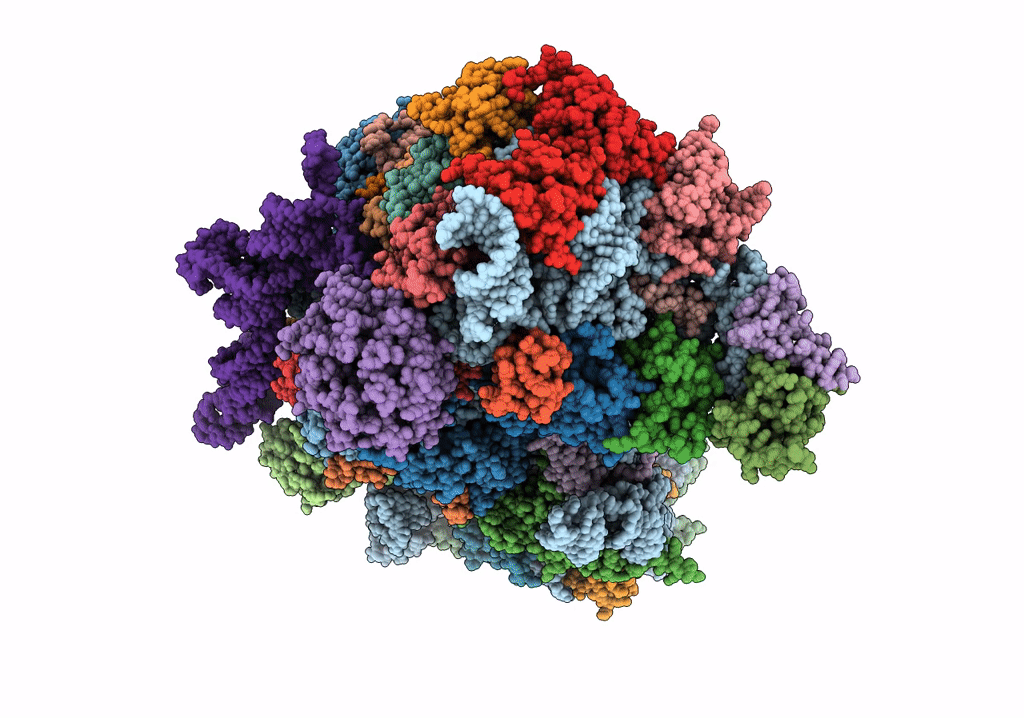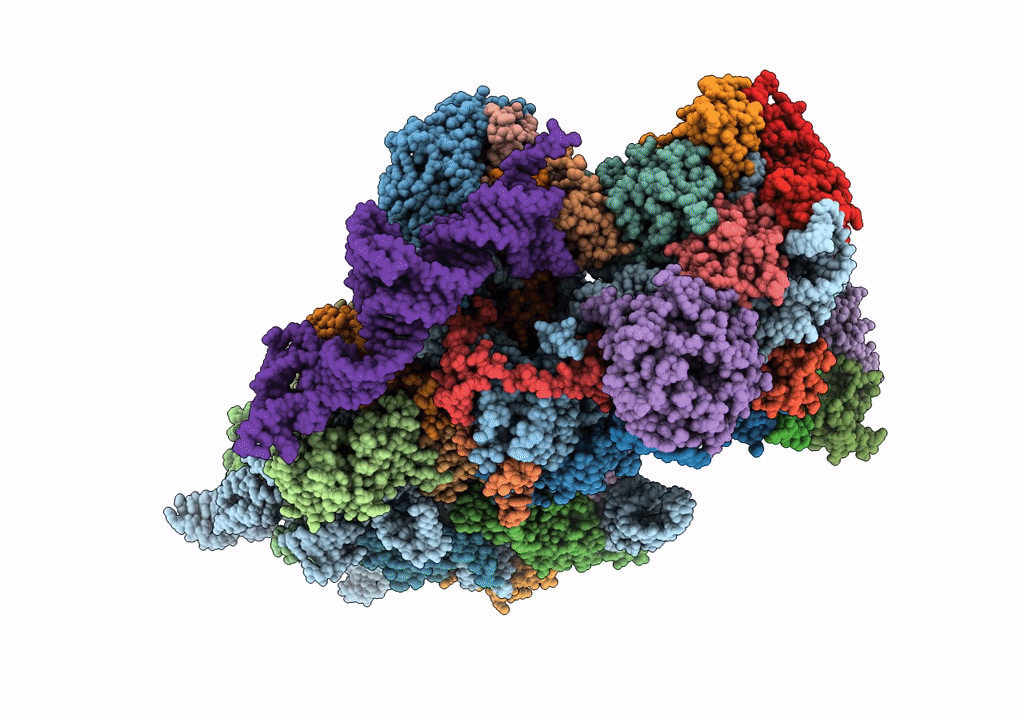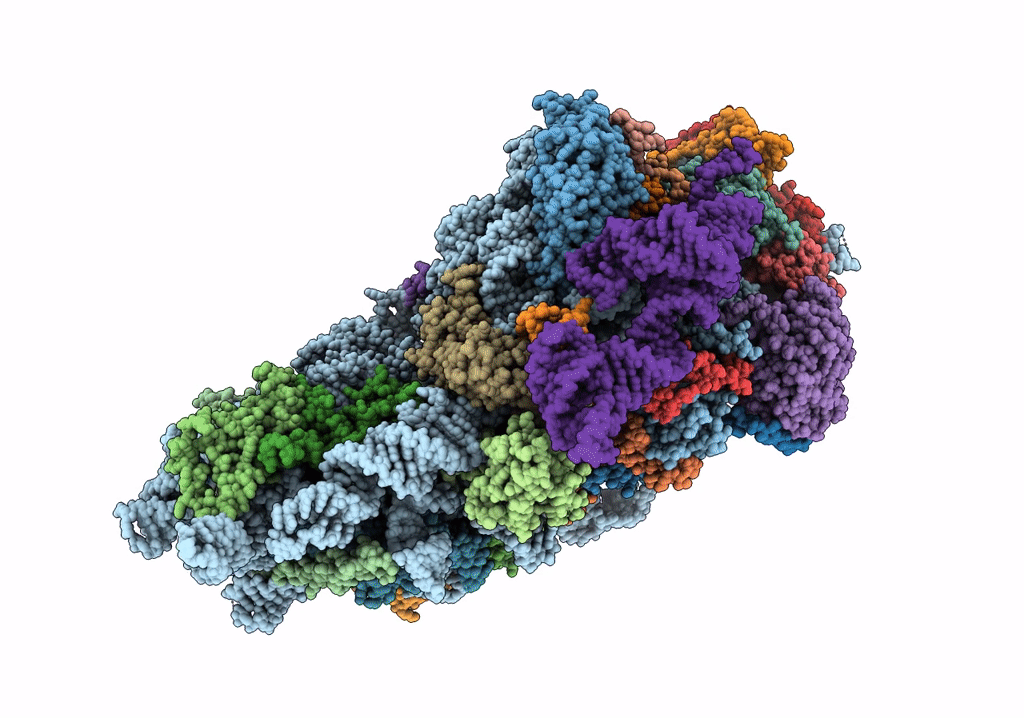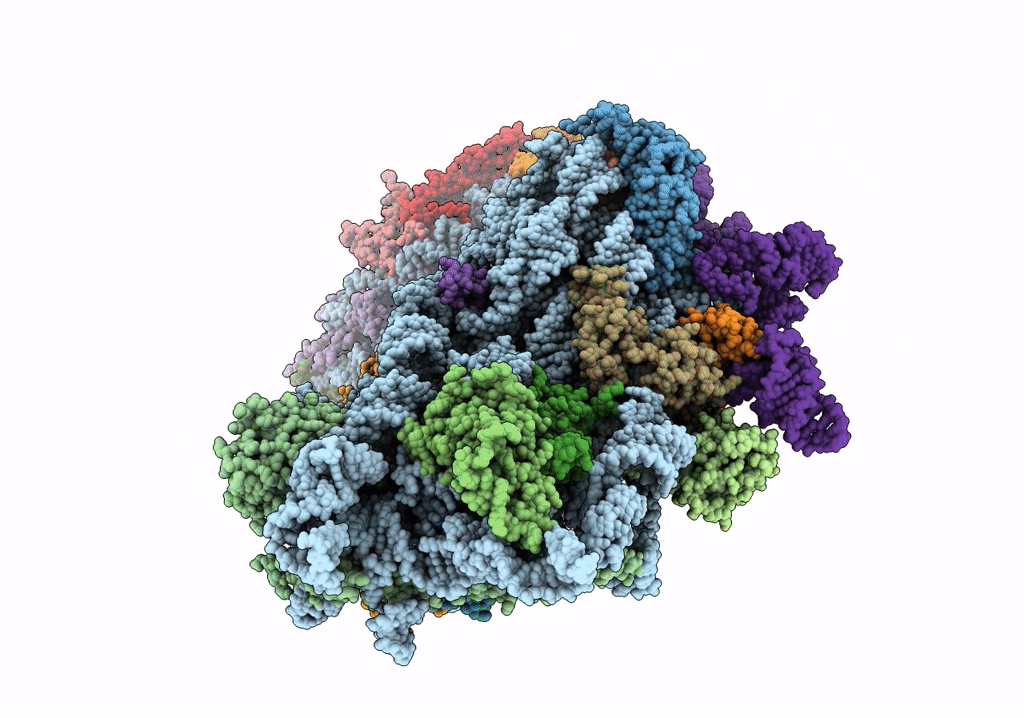
Title:
Structure of the HCV IRES bound to the 40S ribosomal subunit, head open. Structure 9(delta dII)
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Hepatitis C virus (isolate 1) (Taxon ID: 11104)
Oryctolagus cuniculus (Taxon ID: 9986)
Oryctolagus cuniculus (Taxon ID: 9986)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
4.60 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE


