Deposition Date
2021-11-07
Release Date
2022-11-23
Last Version Date
2024-10-23
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
7SR4
Keywords:
Title:
Single chain trimer HLA-A*02:01 (H98L, Y108C) with HPV.16 E7 peptide YMLDLQPETTDLYC
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Human papillomavirus type 16 (Taxon ID: 333760)
Pongo pygmaeus (Taxon ID: 9600)
Homo sapiens (Taxon ID: 9606)
Lama glama (Taxon ID: 9844)
Pongo pygmaeus (Taxon ID: 9600)
Homo sapiens (Taxon ID: 9606)
Lama glama (Taxon ID: 9844)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
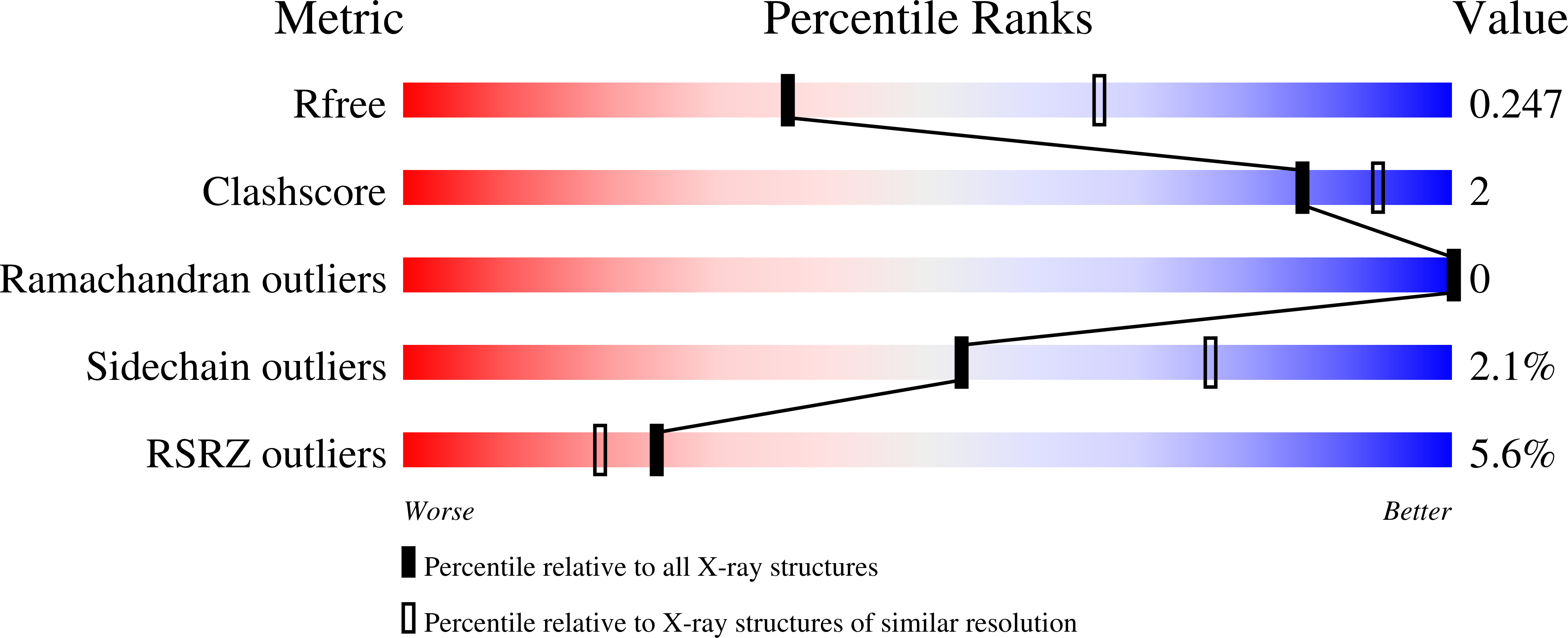
Resolution:
2.59 Å
R-Value Free:
0.24
R-Value Work:
0.21
R-Value Observed:
0.21
Space Group:
P 41 21 2