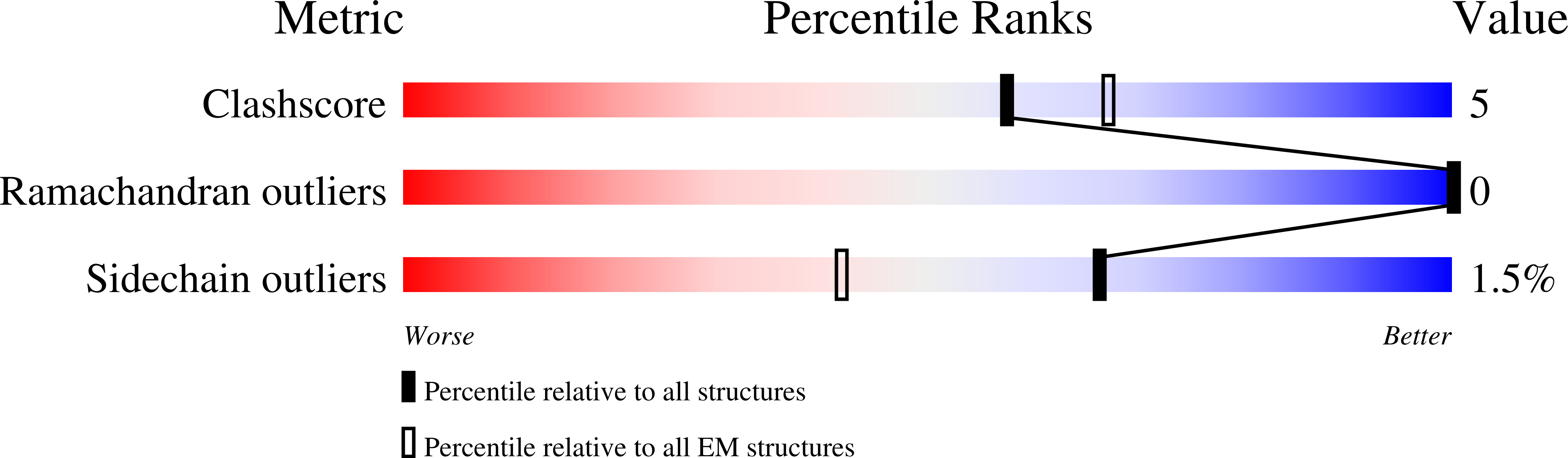
Deposition Date
2021-10-14
Release Date
2022-02-02
Last Version Date
2024-06-05
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
7SII
Keywords:
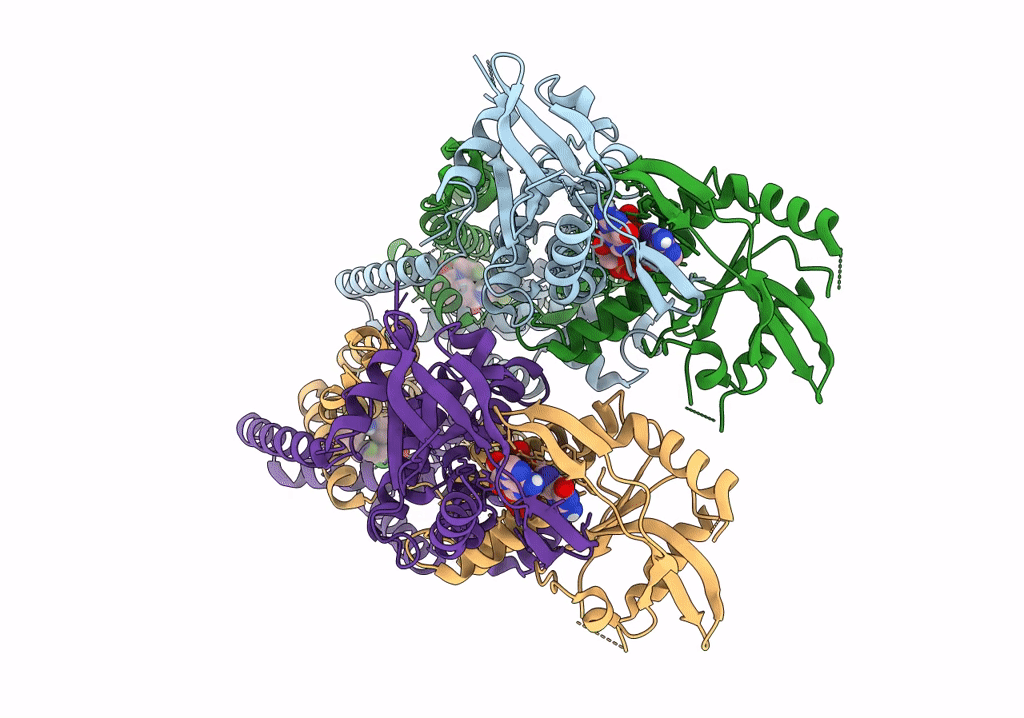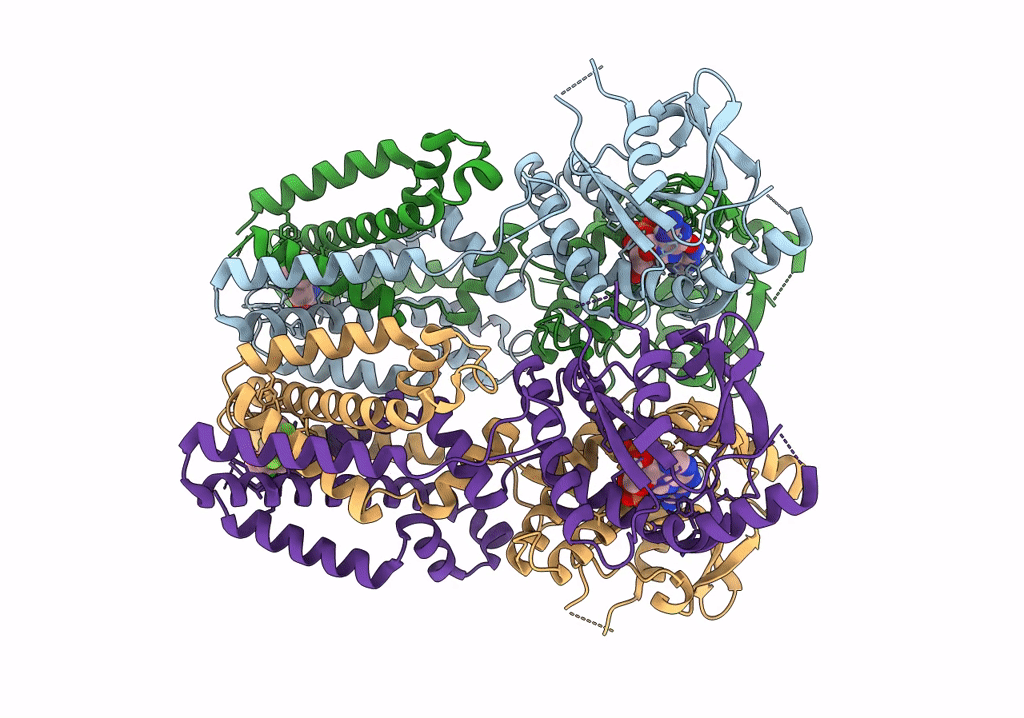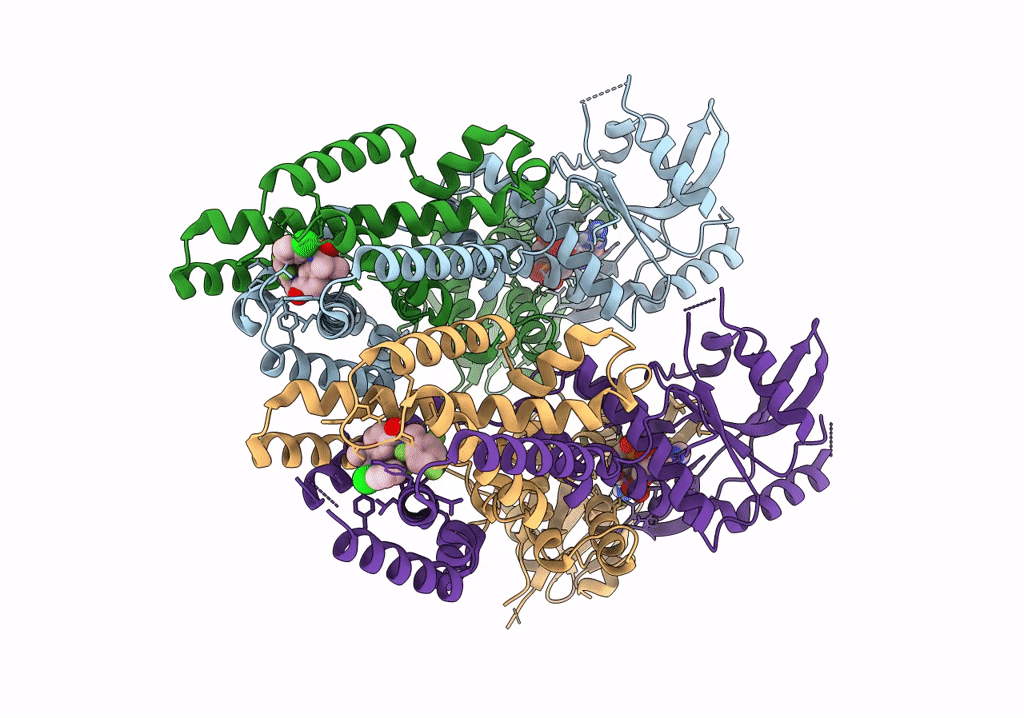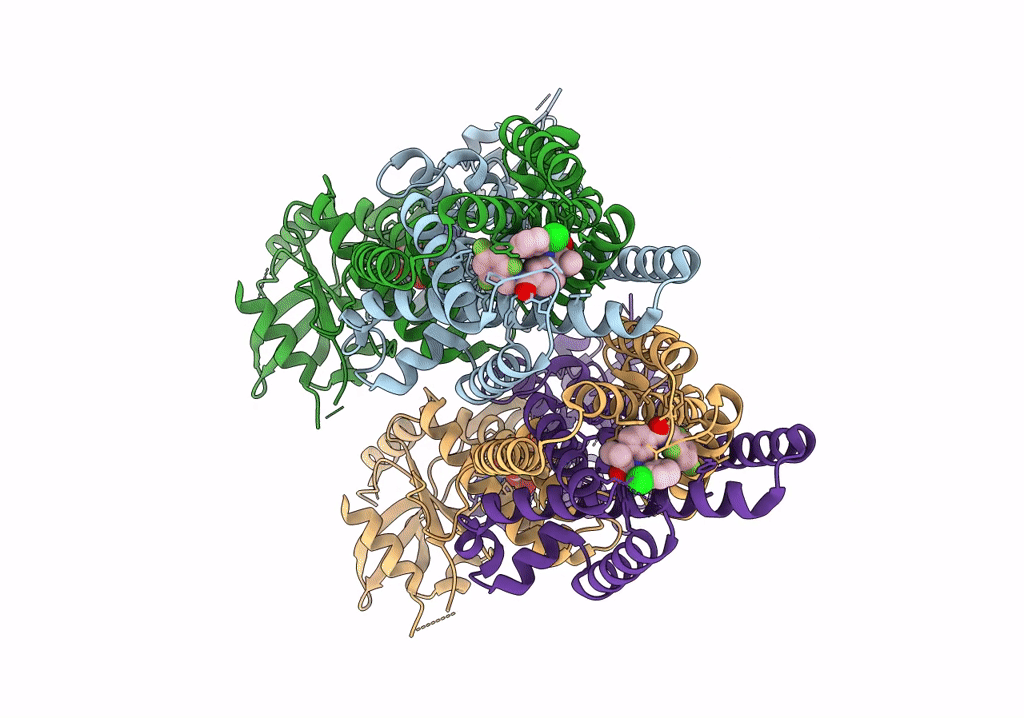
Title:
Human STING bound to both cGAMP and 1-[(2-chloro-6-fluorophenyl)methyl]-3,3-dimethyl-2-oxo-N-[(2,4,6-trifluorophenyl)methyl]-2,3-dihydro-1H-indole-6-carboxamide (Compound 53)
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Homo sapiens (Taxon ID: 9606)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
3.45 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE