Deposition Date
2021-08-27
Release Date
2021-10-27
Last Version Date
2024-11-13
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
7RZ4
Keywords:
Title:
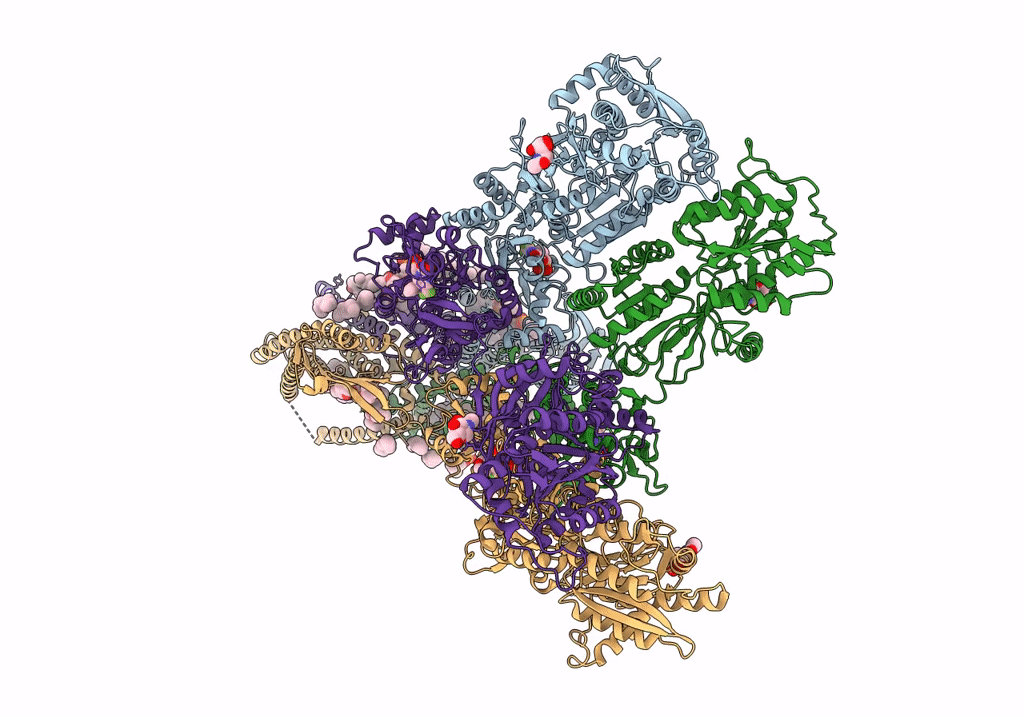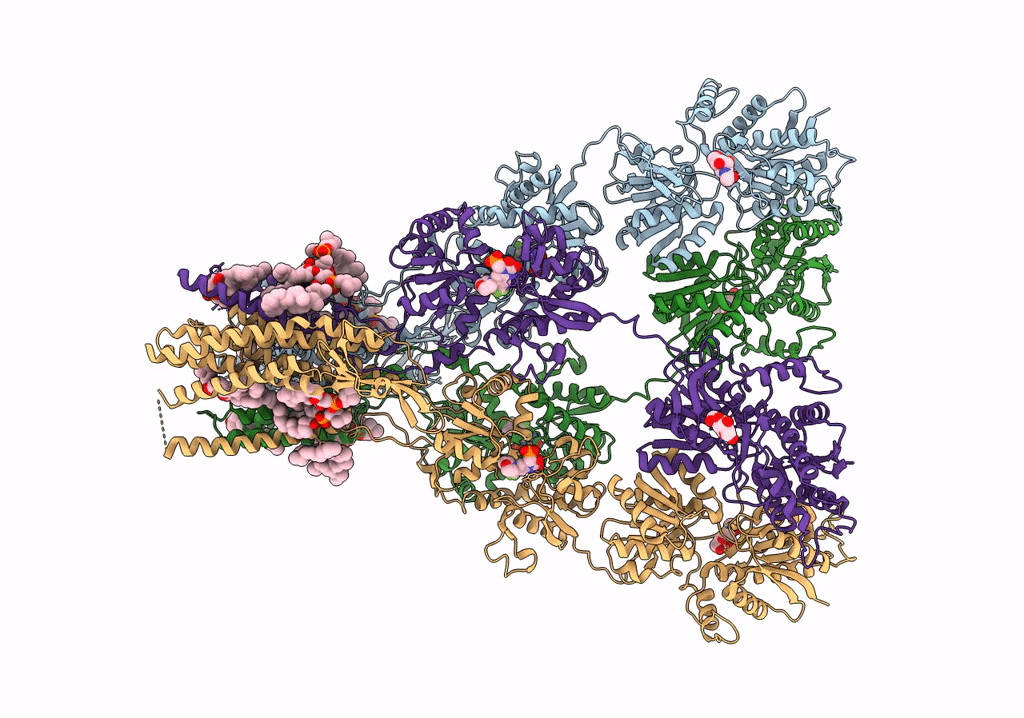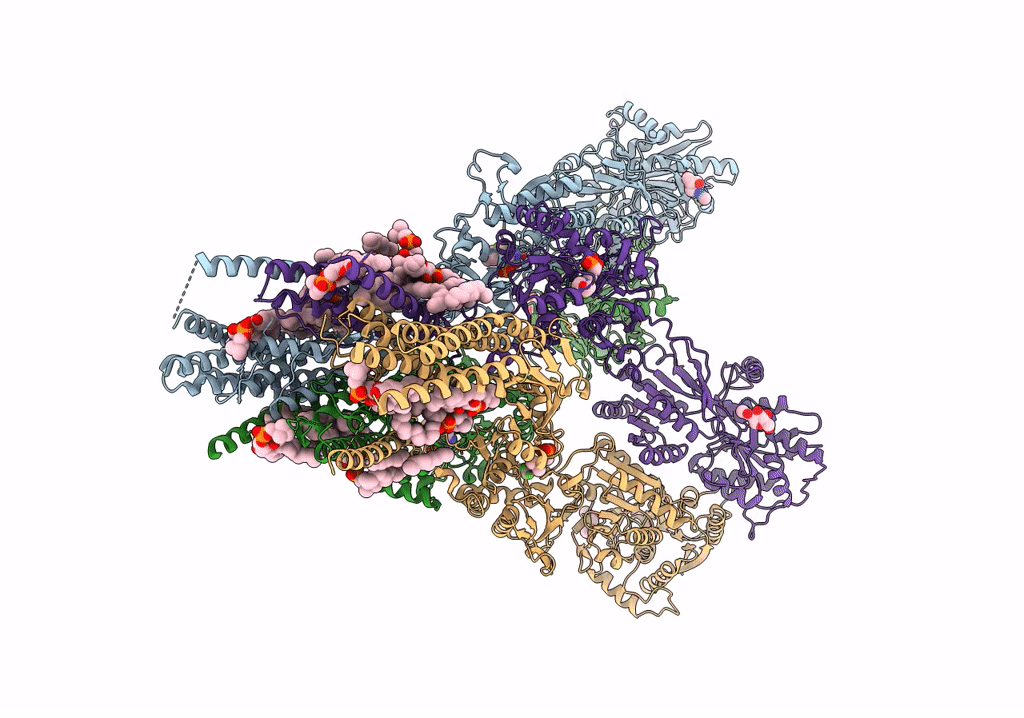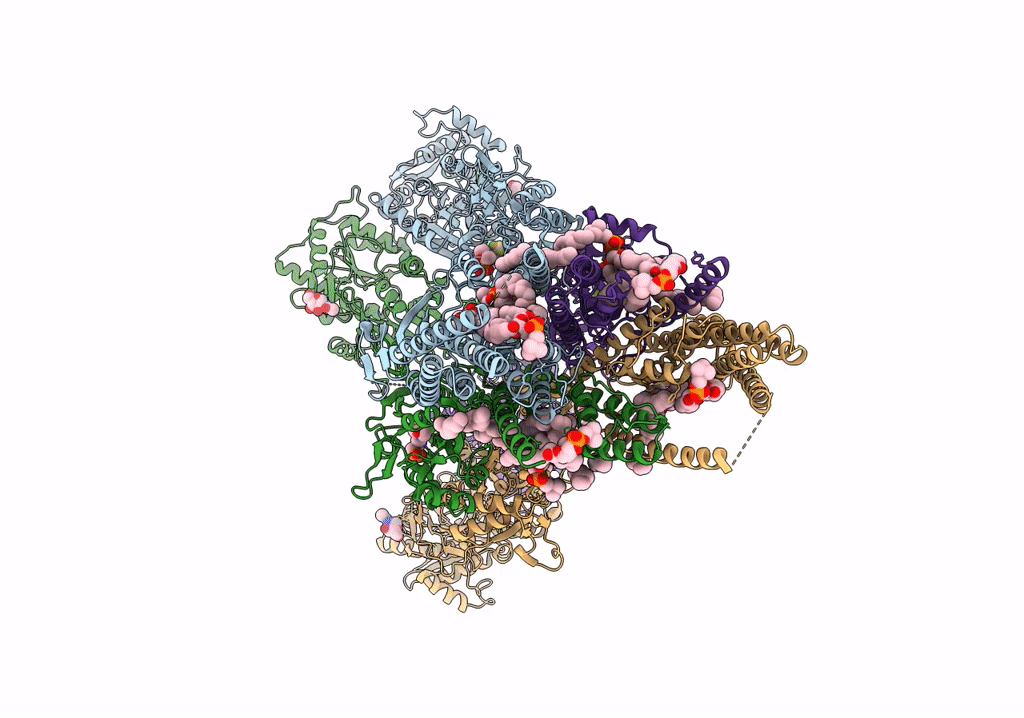
Structure of the complex of AMPA receptor GluA2 with auxiliary subunit TARP gamma-5 bound to competitive antagonist ZK 200775
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Rattus norvegicus (Taxon ID: 10116)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
3.60 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE


