Deposition Date
2021-08-27
Release Date
2022-08-31
Last Version Date
2024-10-16
Entry Detail
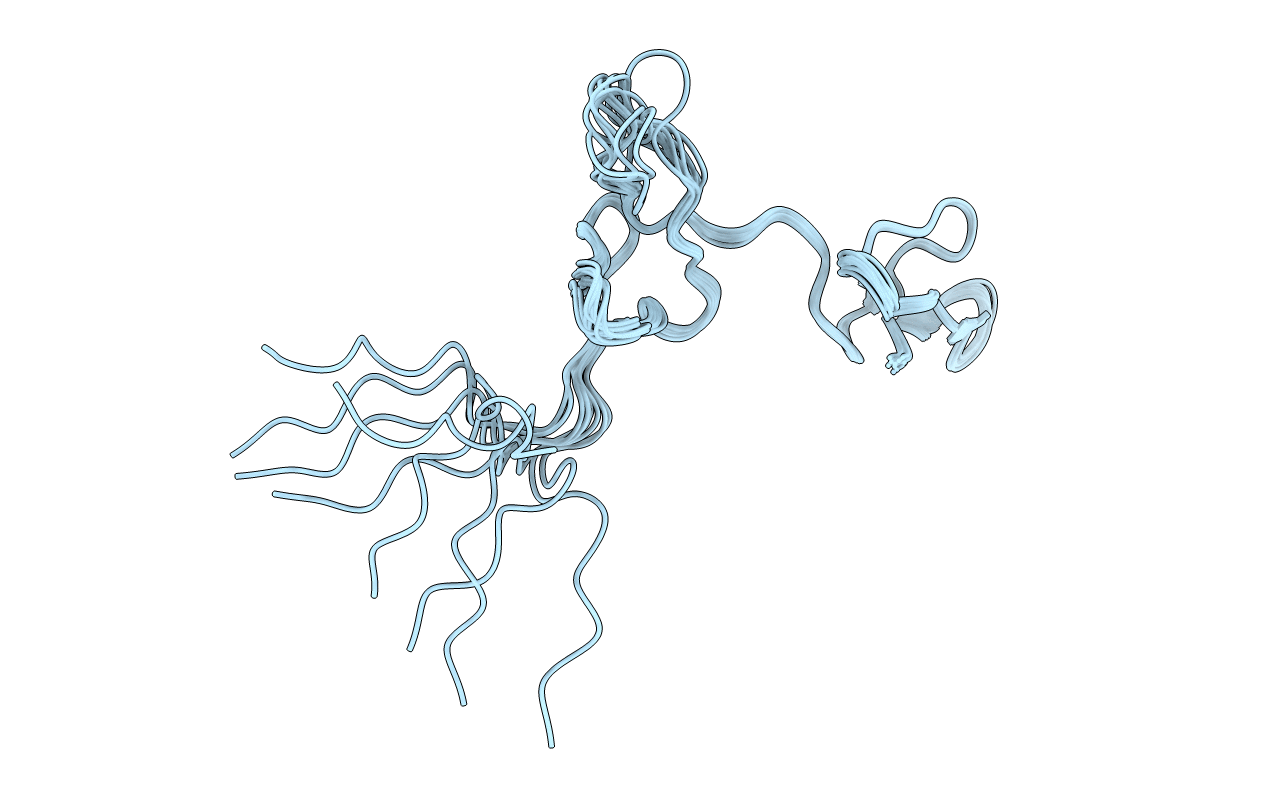
PDB ID:
7RZ3
Keywords:
Title:
The solution structure of remipede double-ICK toxin phi-Xibalbin3-Xt3a
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Xibalbanus tulumensis (Taxon ID: 1519145)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Conformers Calculated:
30
Conformers Submitted:
10
Selection Criteria:
target function


