Deposition Date
2021-07-30
Release Date
2022-02-16
Last Version Date
2022-03-02
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
7ROL
Keywords:
Title:
Amyloid-related segment of alphaB-crystallin residues 90-100 with G95W mutation, bromo derivative
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Homo sapiens (Taxon ID: 9606)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
2.00 Å
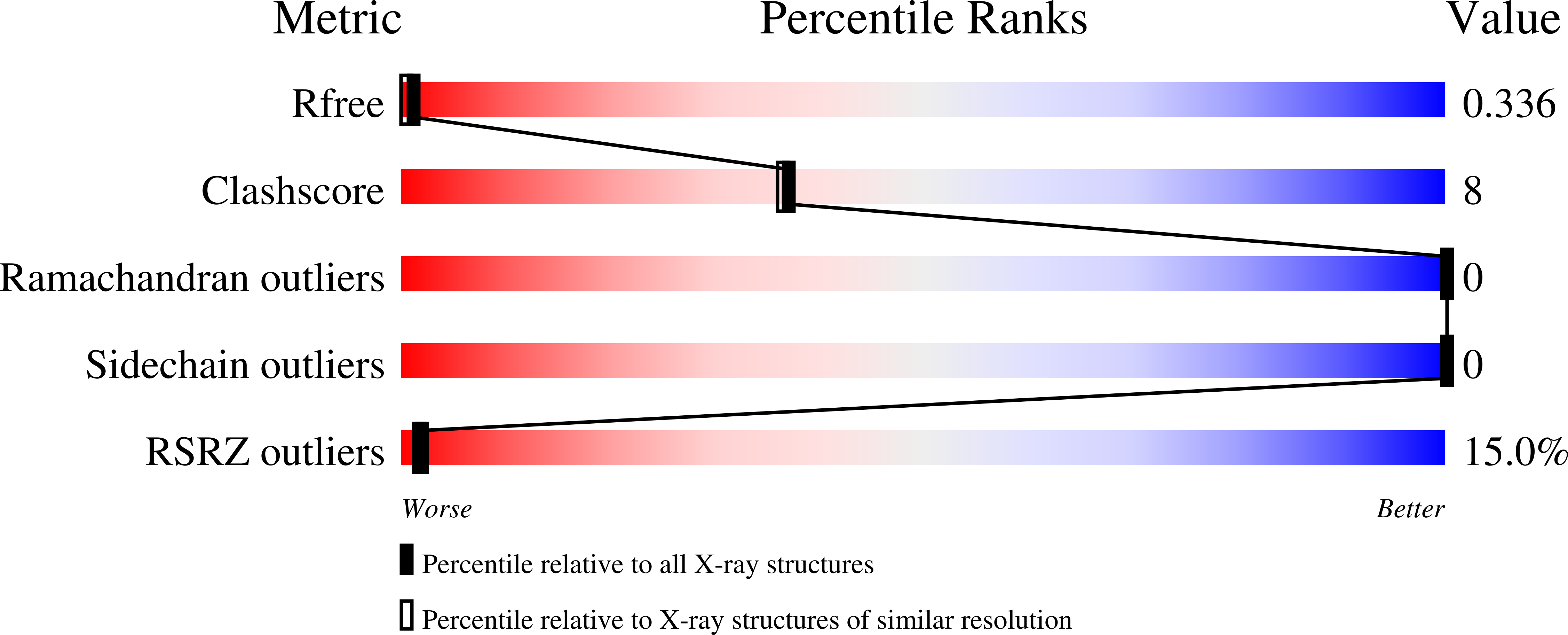
R-Value Free:
0.33
R-Value Work:
0.29
Space Group:
P 64