Deposition Date
2021-08-23
Release Date
2022-09-07
Last Version Date
2024-02-07
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
7PJ6
Keywords:
Title:
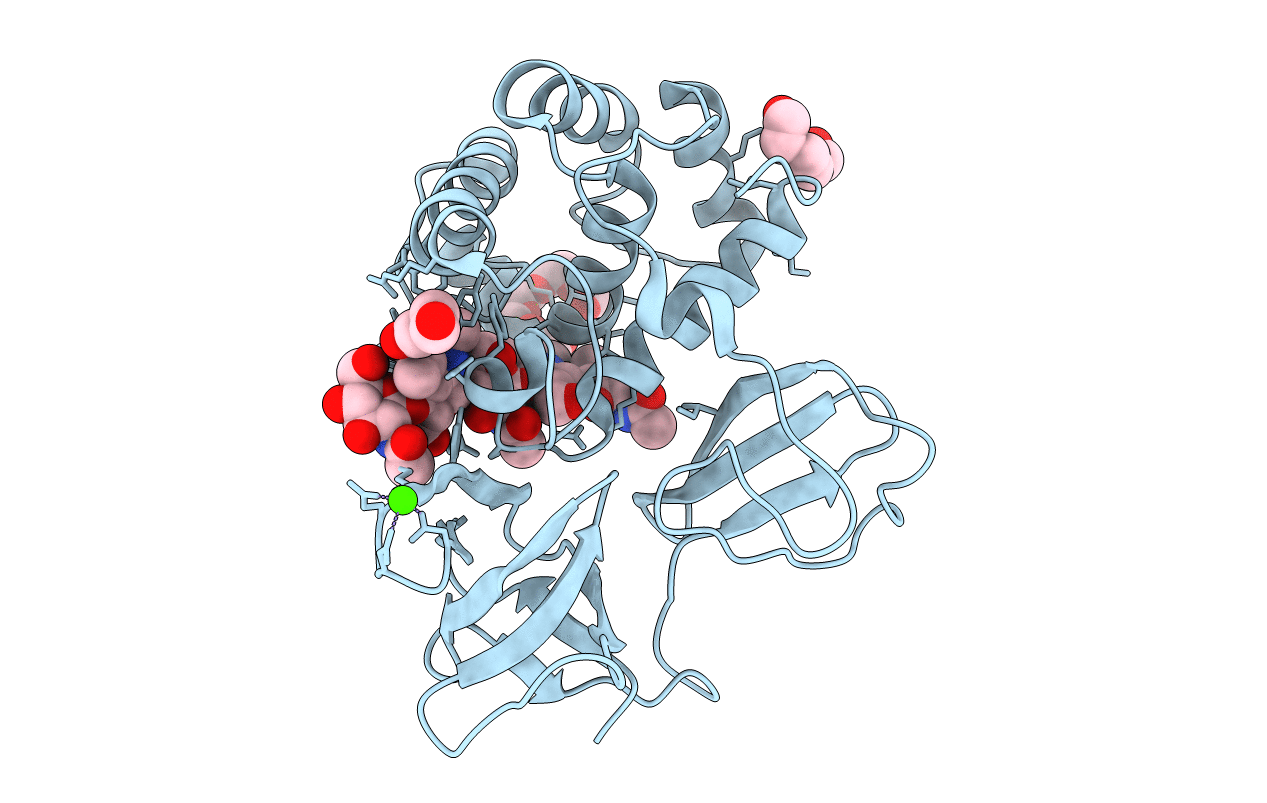
Crystal structure of catalytic domain of LytB (E585Q) from Streptococcus pneumoniae in complex with NAG-NAM-NAG-NAM-NAG peptidolycan analogue
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
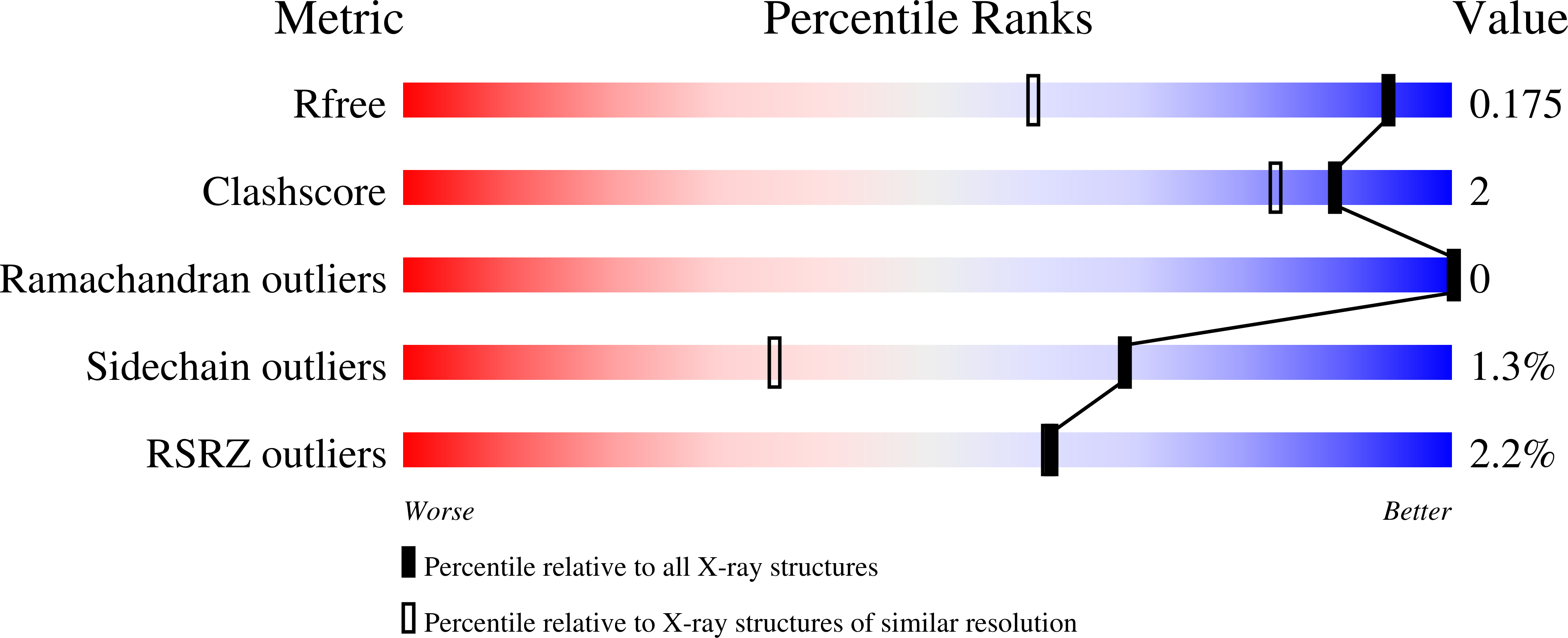
Resolution:
1.30 Å
R-Value Free:
0.17
R-Value Work:
0.14
Space Group:
C 2 2 21