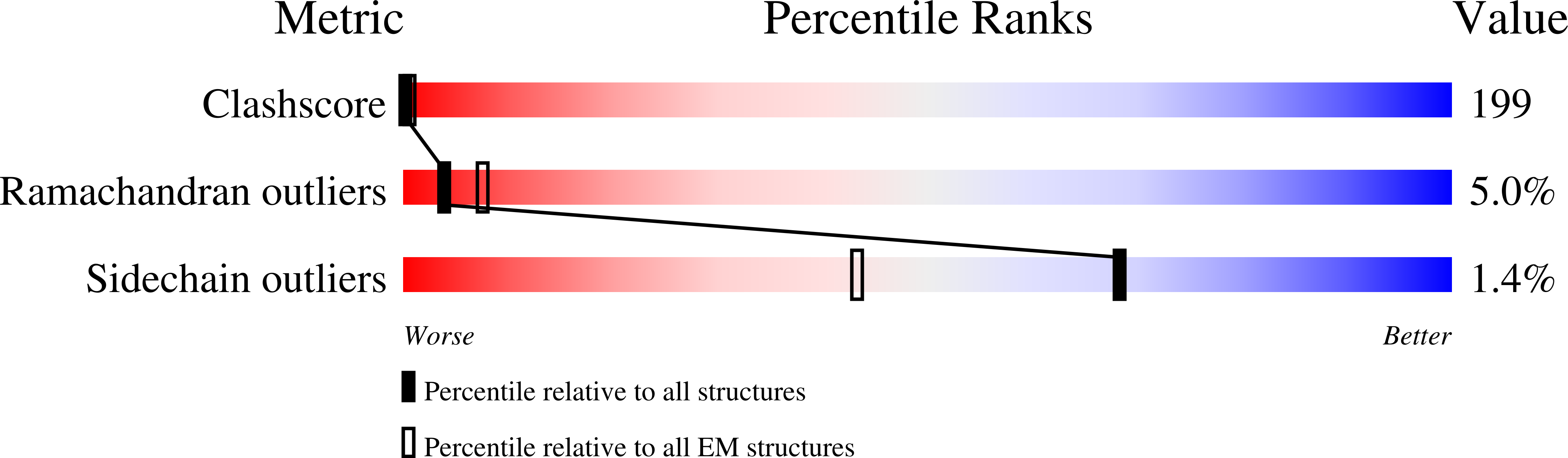
Deposition Date
2021-07-09
Release Date
2021-09-29
Last Version Date
2024-07-17
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
7P3X
Keywords:
Title:
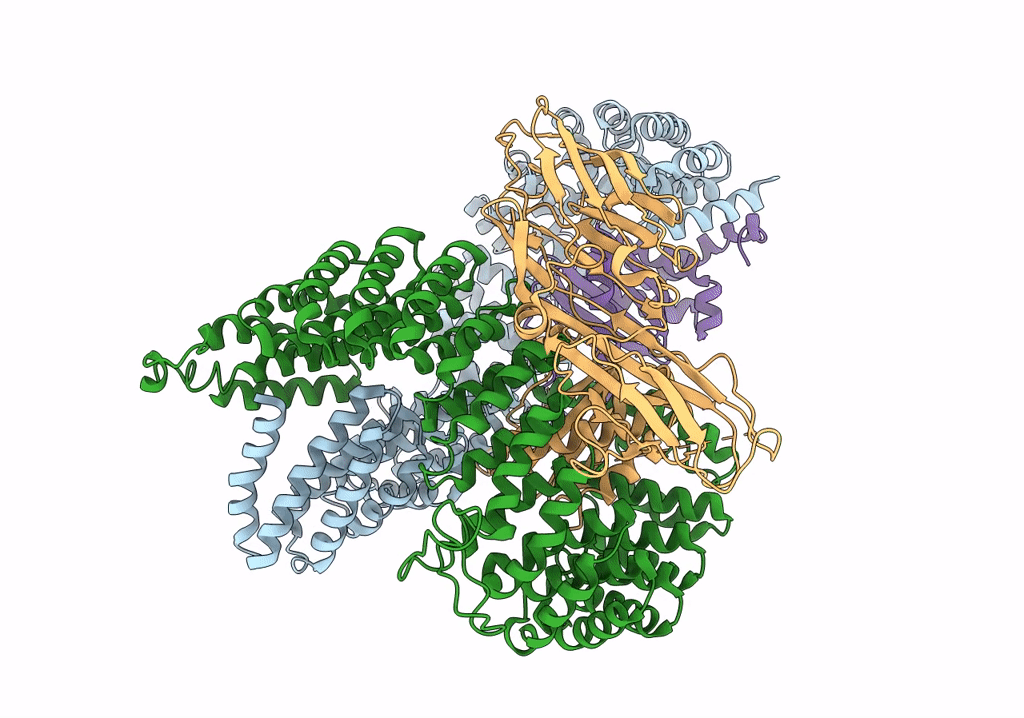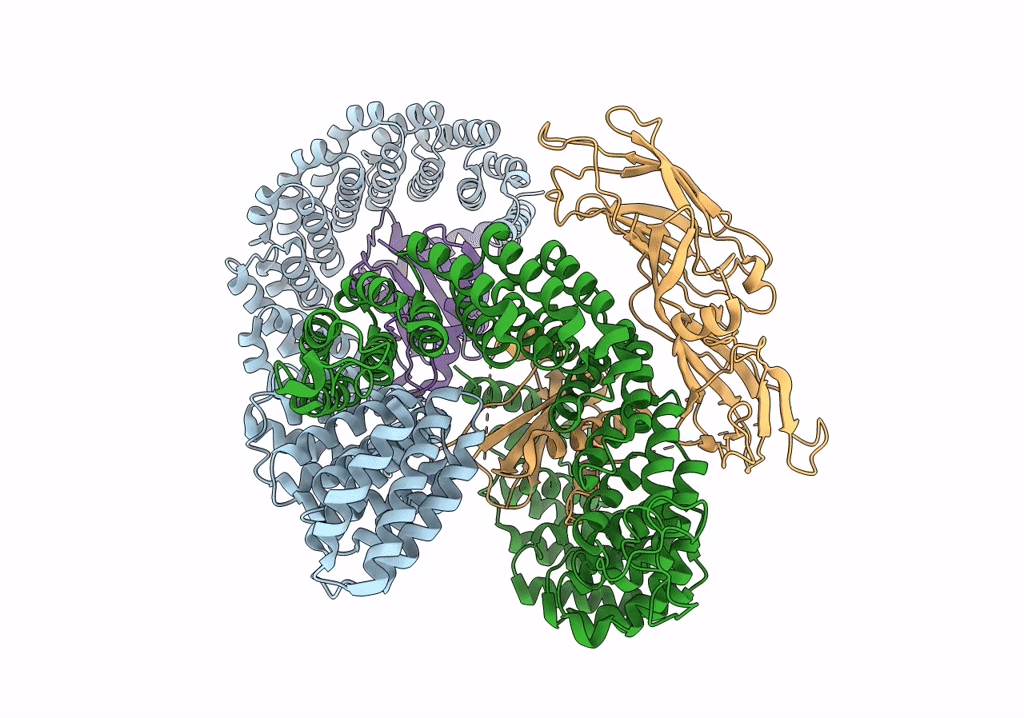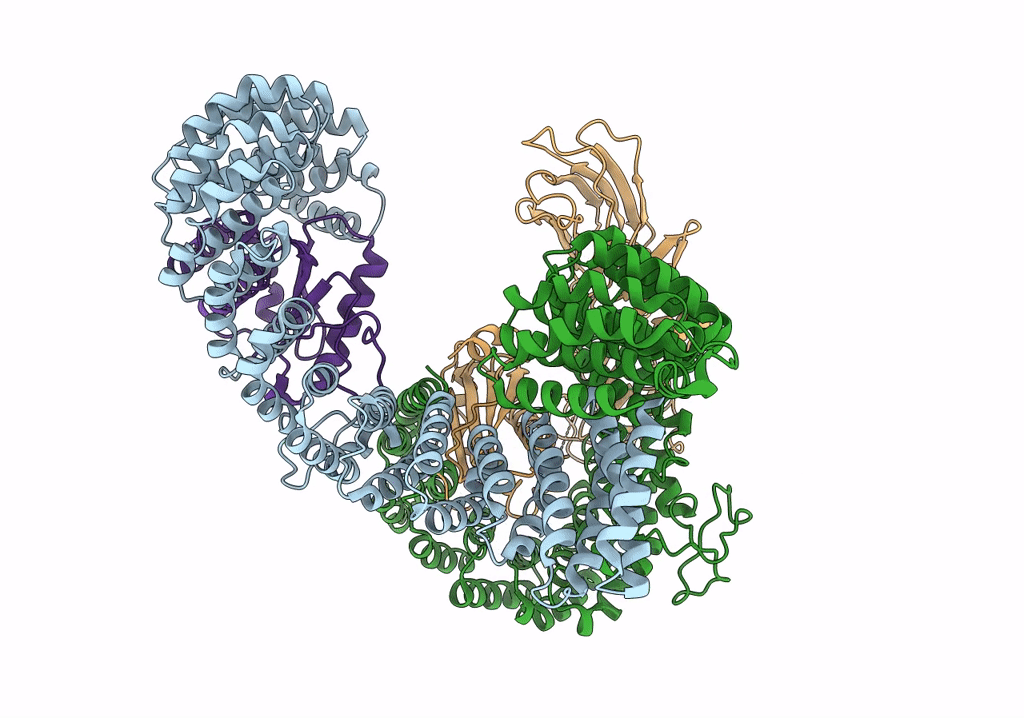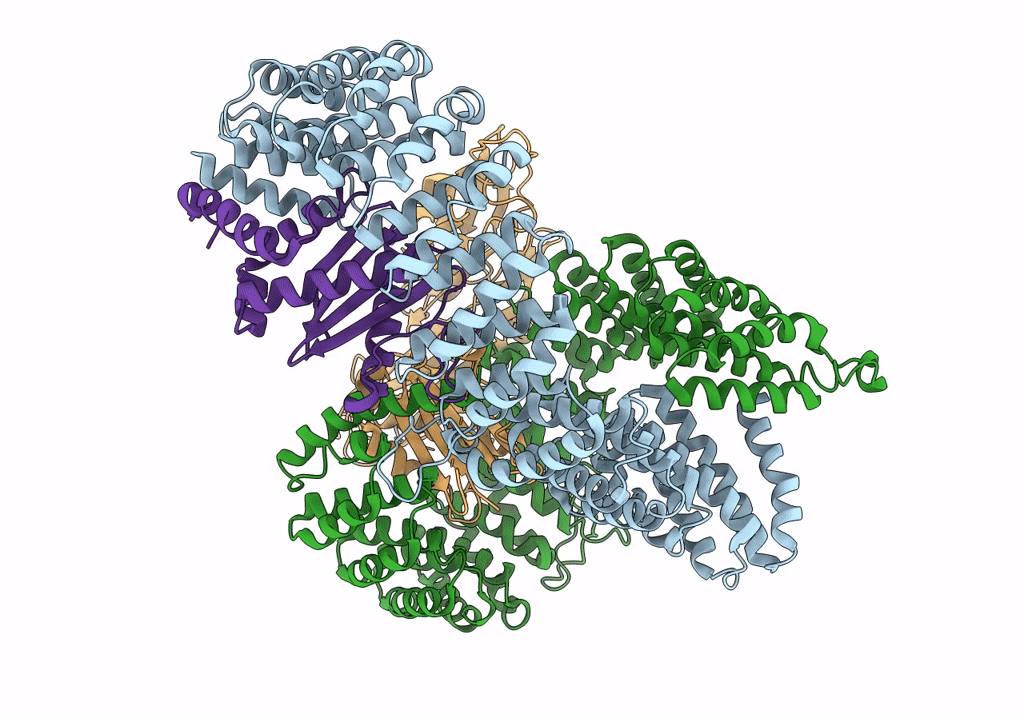
Homology model of the full-length AP-3 complex in a compact open conformation
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Taxon ID: 4932)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
9.10 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE