Deposition Date
2021-07-08
Release Date
2022-02-02
Last Version Date
2024-07-17
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
7P3N
Keywords:
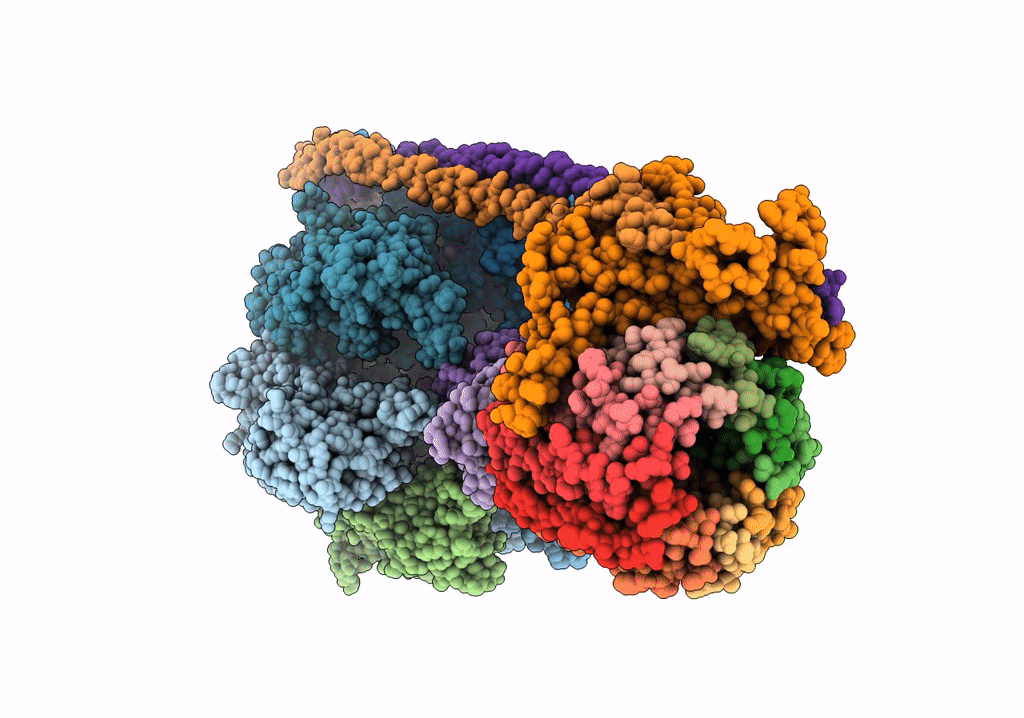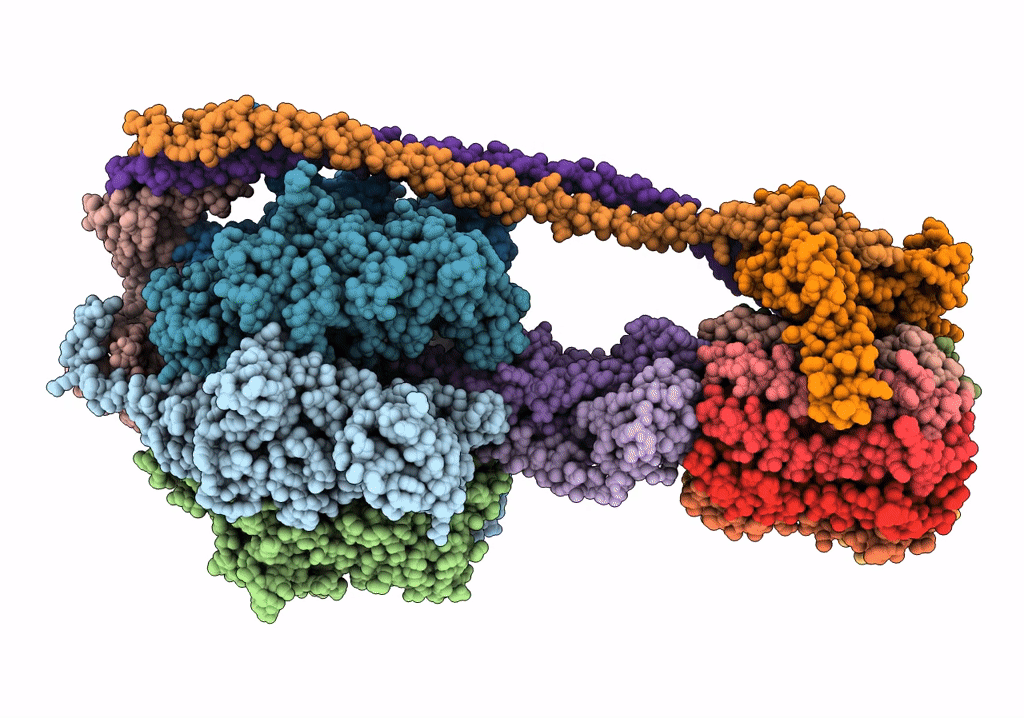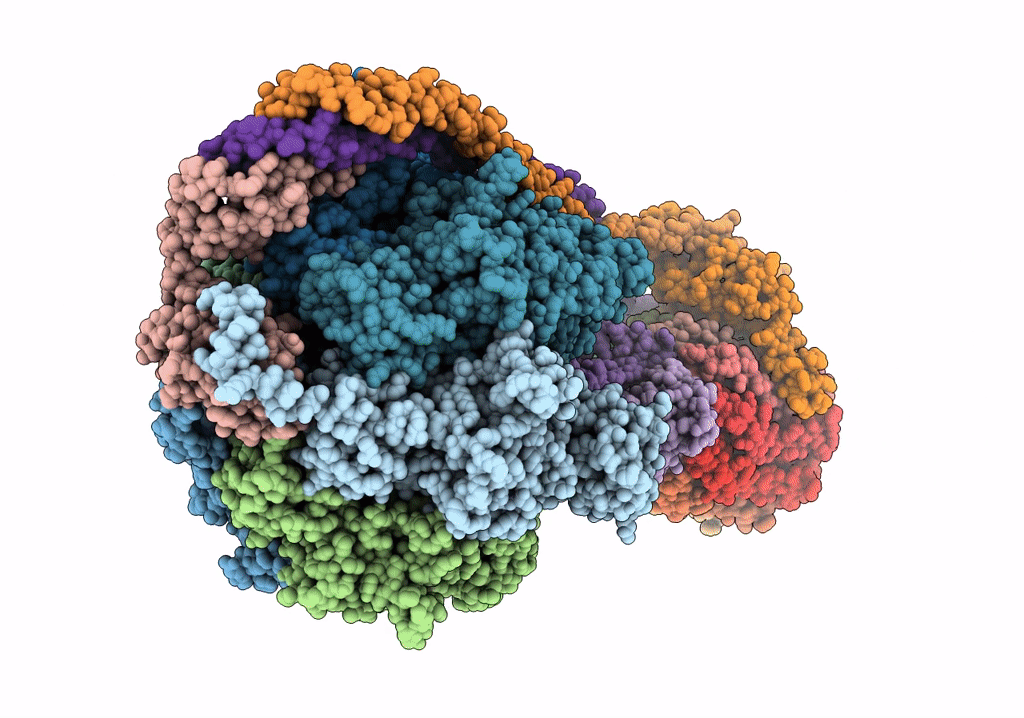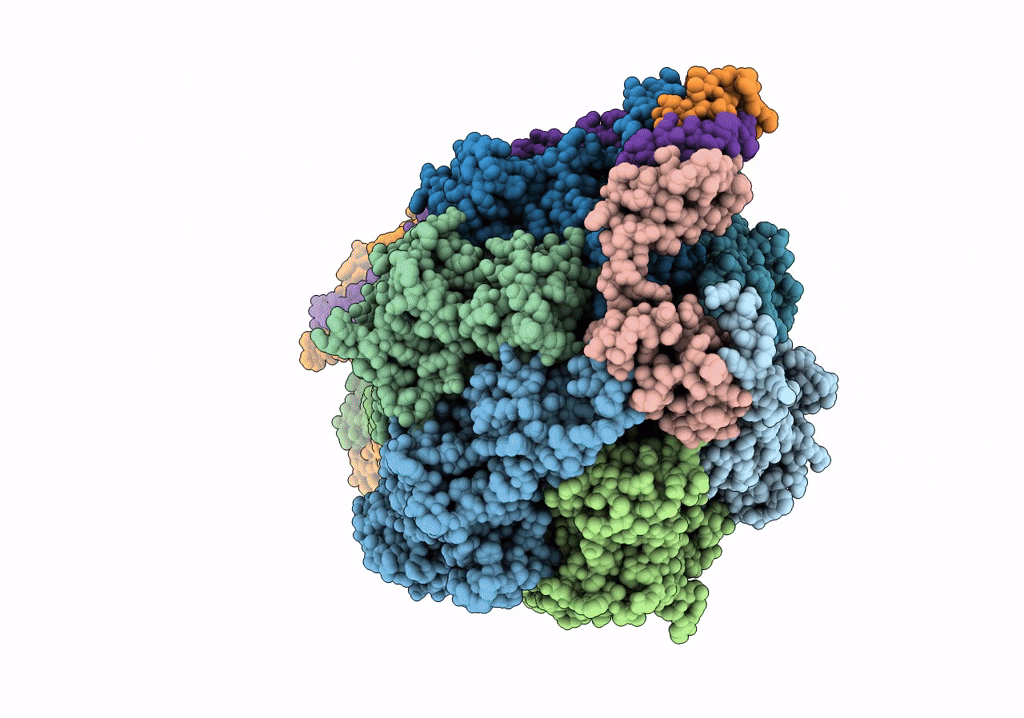
Title:
F1Fo-ATP synthase from Acinetobacter baumannii (state 2)
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC 17978 (Taxon ID: 400667)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
4.60 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE


