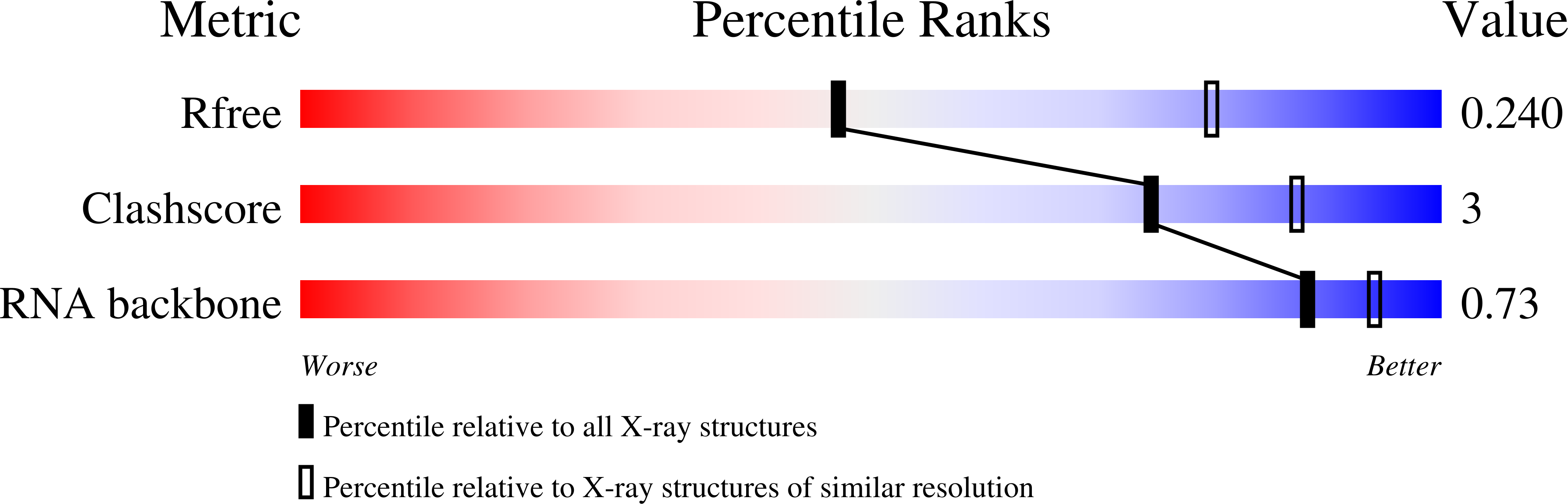
Deposition Date
2021-06-29
Release Date
2022-08-03
Last Version Date
2024-02-07
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
7OZZ
Keywords:
Title:
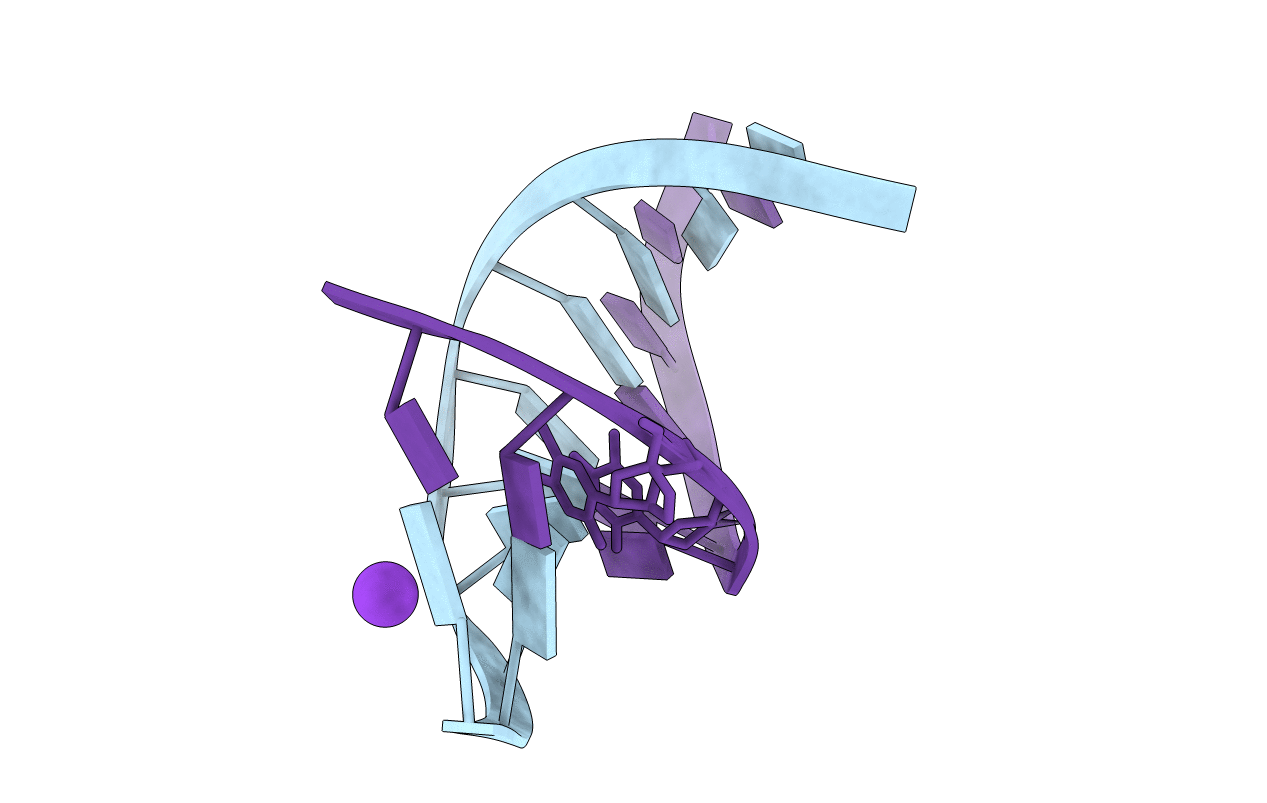
The crystal structure of a DNA:RNA hybrid duplex sequence CTTTTCTTTG with LNA-amide modification
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
synthetic construct (Taxon ID: 32630)
Host Organism:
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
2.70 Å
R-Value Free:
0.23
R-Value Work:
0.20
R-Value Observed:
0.20
Space Group:
P 61