Deposition Date
2021-04-09
Release Date
2021-10-13
Last Version Date
2024-01-31
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
7O65
Keywords:
Title:
Crystal structure of human mitochondrial ferritin (hMTF) Fe(II)-loaded for 90 minutes showing either a dioxygen or a superoxide anion coordinated to iron ions in the ferroxidase site
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Homo sapiens (Taxon ID: 9606)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
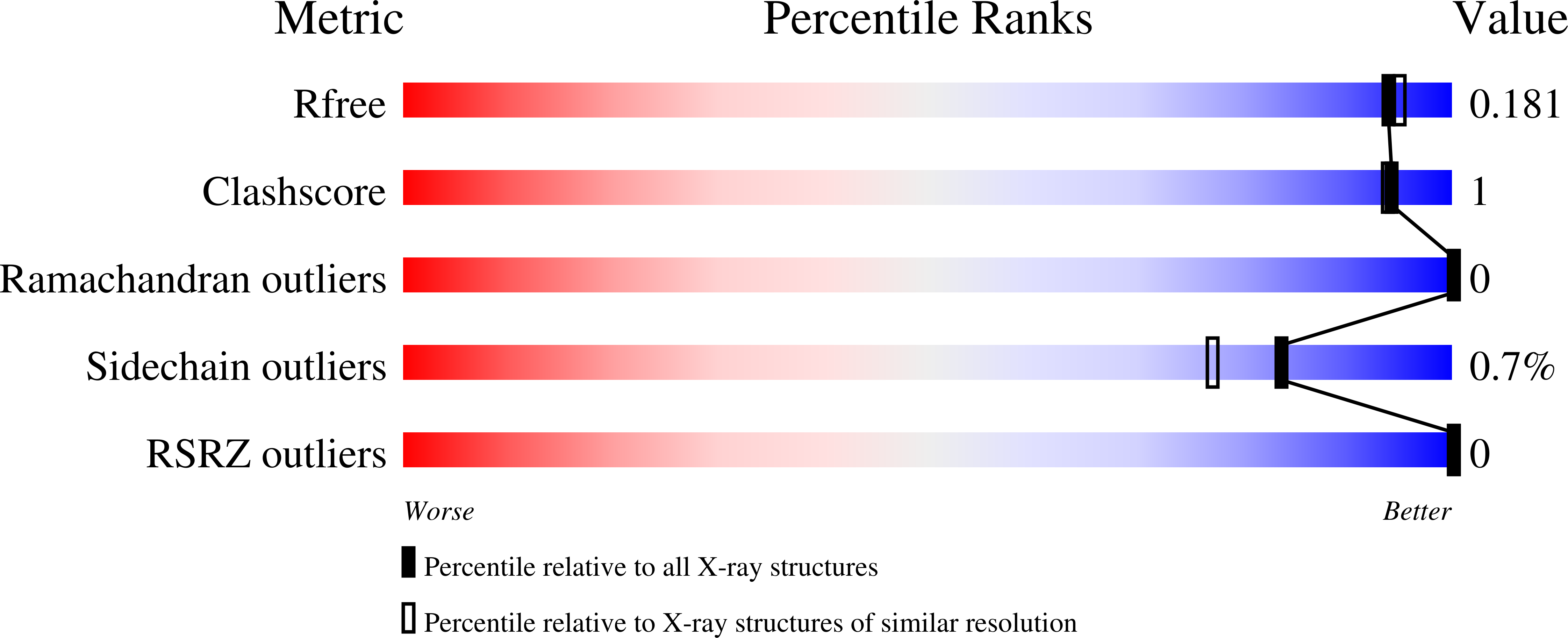
Resolution:
1.70 Å
R-Value Free:
0.18
R-Value Work:
0.15
R-Value Observed:
0.15
Space Group:
F 4 3 2