Deposition Date
2021-05-24
Release Date
2021-09-29
Last Version Date
2024-11-20
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
7MZT
Keywords:
Title:
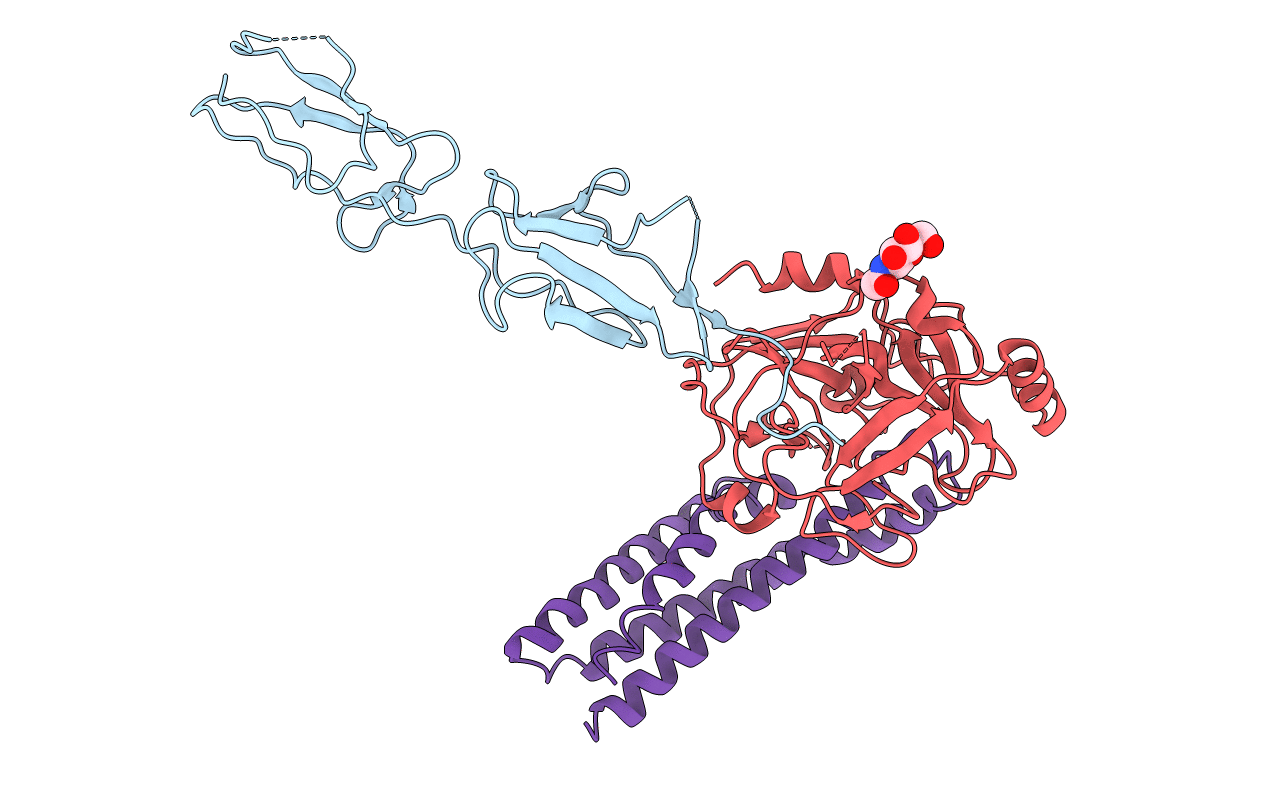
Borrelia burgdorferi BBK32-C in complex with an autolytic fragment of human C1r at 4.1A
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Borrelia burgdorferi (strain ATCC 35210 / B31 / CIP 102532 / DSM 4680) (Taxon ID: 224326)
Homo sapiens (Taxon ID: 9606)
Homo sapiens (Taxon ID: 9606)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
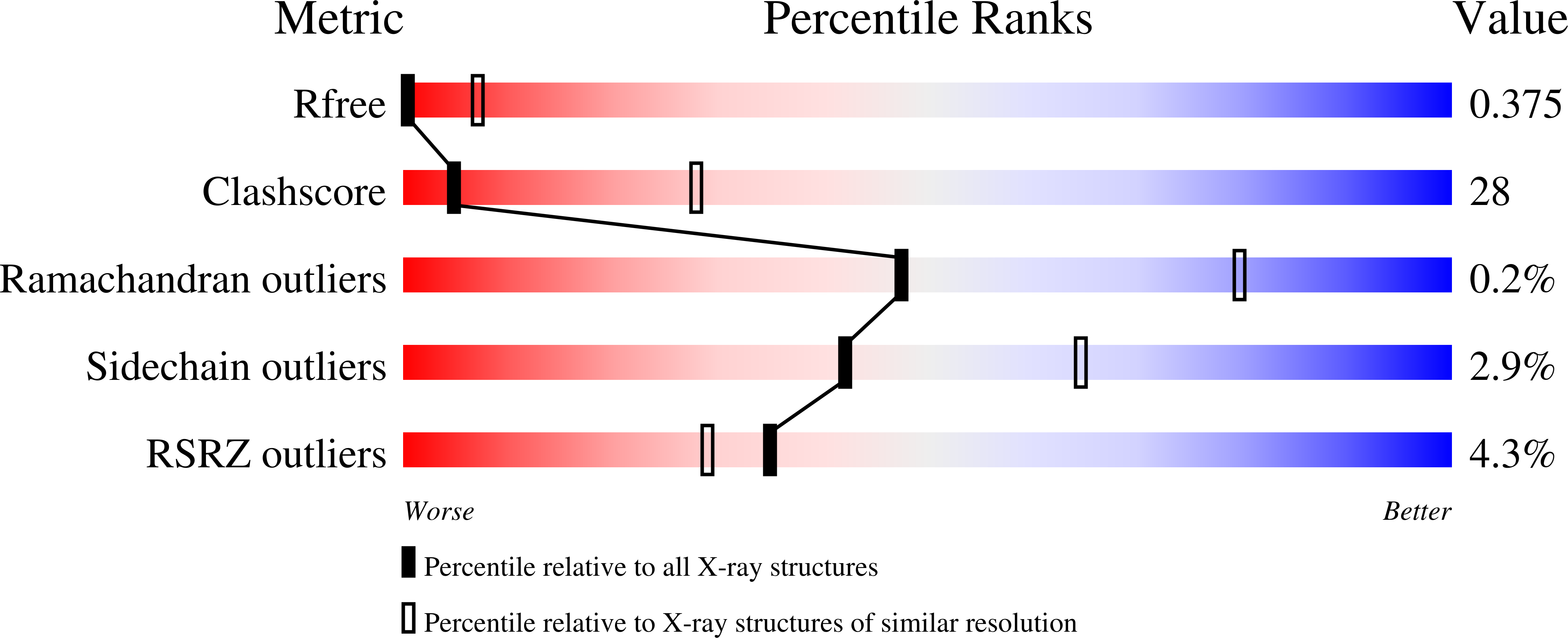
Resolution:
4.07 Å
R-Value Free:
0.37
R-Value Work:
0.36
R-Value Observed:
0.36
Space Group:
P 21 21 2